Summary
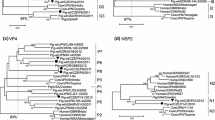
We have sequenced gene 5 encoding NSP1 for three human, two porcine, two bovine, one feline, and five equine rotavirus strains, and compared the nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences with the published sequences for other various strains. Subgroup I human strains L26, 69M, and DS-1 were found to have a similar NSP1 sequence despite their different G serotypes, VP4 genotypes, and RNA patterns. The NSP1 sequence of the human strain K8 showed a high degree of homology to those of porcine strains OSU and YM. A high degree of homology was found among three equine strains (H2, FI-14, and FI23), but they differed from the other equine strains L338 and H1. The strain H1 was similar to the porcine strains. The feline strain Cat2 showed a high homology to bovine strains UK, RF, and A44. Thus, species-specific and interspecies relatedness of NSP1 sequences among human, porcine, bovine, feline and equine rotaviruses was found. Overall genomic relatedness of strains L26 and YM to various human and animal strains was also examined by RNA-RNA hybridization assay. The present and previous hybridization results showed that there is a good correlation in most strains between overall genomic property (or genogroup) and NSP1 sequence homology.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Both GW, Bellamy AR, Mitchell DB (1994) Rotavirus protein structure and function. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 185: 67–105
Bremont M, Charpilienne A, Chabanne D, Cohen J (1987) Nucleotide sequence and expression inEscherichia coli of the gene encoding the nonstructural protein NCVP2 of bovine rotavirus. Virology 161: 138–144
Brottier P, Nandi P, Bremont M, Cohen J (1992) Bovine rotavirus segment 5 protein expressed in the baculovirus system interacts with zinc and RNA. J Gen Virol 73: 1931–1938
Dunn SJ, Cross TL, Greenberg HB (1994) Comparison of the rotavirus nonstructural protein NSP1 (NS53) from different species by sequence analysis and Northern blot hybridization. Virology 203: 178–183
Estes MK, Cohen J (1989) Rotavirus gene structure and function. Microbiol Rev 53: 410–449
Flores J, Perez I, White L, Perez M, Kalica AR, Marquina R, Wyatt RG, Kapikian AZ, Chanock RM (1982) Genetic relatedness among human rotaviruses as determined by RNA hybridization. Infect Immun 37: 648–655
Gombold JL, Ramig RF (1986) Analysis of reassortment of genome segments in mice mixedly infected with rotaviruses SA11 and RRV. J Virol 57: 110–116
Gorziglia M, Hoshino Y, Buckler-White A, Blumentals I, Glass R, Flores J, Kapikian AZ, Chanock RM (1986) Conservation of amino acid sequence of VP8 and cleavage region of 84-kDa outer capsid protein among rotaviruses recovered from asymptomatic neonatal infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83: 7039–7043
Graham A, Kudesia G, Allen AM, Desselberger U (1987) Reassortment of human rotavirus possessing genome rearrangements with bovine rotavirus: evidence for host cell selection. J Gen Virol 68: 115–122
Hein J (1990) Unified approach to alignment and phylogenies. Methods Enzymol 183: 626–645
Higgins DG, Bleasby AJ, Fuchs R (1992) CLUSTAL V: improved software for multiple sequence alignment. Comput Appl Biosci 8: 189–191
Hua J, Chen X, Patton JT (1994) Deletion mapping of the rotavirus metalloprotein NS53 (NSP1): the conserved cysteine-rich region is essential for virus-specific RNA binding. J Virol 68: 3990–4000
Hua J, Mansell EA, Patton JT (1993) Comparative analysis of the rotavirus NS53 gene: conservation of basic and cysteine-rich regions in the protein and possible stem-loop structures in the RNA. Virology 196: 372–378
Hua J, Patton JT (1994) The carboxyl-half of the rotavirus nonstructural protein NS53 (NSP1) is not required for virus replication. Virology 198: 567–576
Kapikian AZ, Chanock RM (1990) Rotaviruses. In: Fields BN, Knipe DM, Chanock RM, Hirsch MS, Melnick JL, Monath TP, Roizman B (eds) Virology, 2nd ed. Raven Press, New York, pp 1353–1404
Kobayashi N, Kojima K, Taniguchi K, Urasawa T, Urasawa S (1994) Genotypic diversity of reassortants between simian rotavirus SA11 and human rotaviruses having different antigenic specificities and RNA patterns. Res Virol 145: 303–311
Kobayashi N, Taniguchi K, Urasawa T, Urasawa S (1994) Effect of the selection pressure with anti-VP7 and anti-VP4 neutralizing monoclonal antibodies on reassortant formation between two human rotaviruses. Arch Virol 135: 383–396
Mitchell DB, Both GW (1990) Conservation of a potential metal binding motif despite extensive sequence diversity in the rotavirus nonstructural protein NS53. Virology 174: 618–621
Myers EW, Miller W (1988) Optimal alignments in linear space. Comput Appl Biosci 4: 11–17
Nakagomi O, Kaga E, Nakagomi T (1992) Human rotavirus strain with unique VP4 neutralization epitopes as a result of natural reassortment between members of the AU-1 and Wa genogroups. Arch Virol 127: 365–371
Nakagomi O, Nakagomi T (1991) Genetic diversity and similarity among mammalian rotaviruses in relation to interspecies transmission of rotavirus. Arch Virol 120: 43–55
Nakagomi O, Ohshima A, Aboudy Y, Shif I, Mochizuki M, Nakagomi T, Gotlieb-Stematsky T (1990) Molecular identification by RNA-RNA hybridization of a human rotavirus that is closely related to rotaviruses of feline and canine origin. J Clin Microbiol 28: 1198–1203
Nishikawa K, Hoshino Y, Taniguchi K, Green KY, Greenberg HB, Kapikian AZ, Chanock RM, Gorziglia M (1989) Rotavirus VP7 neutralization epitopes of serotype 3 strains. Virology 171: 503–515
Ohshima A, Takagi T, Nakagomi T, Matsuno S, Nakagomi O (1990) Molecular characterization by RNA-RNA hybridization of a serotype 8 human rotavirus with ‘super-short’ RNA electropherotype. J Med Virol 30: 107–112
Palombo EA, Bishop RF (1994) Genetic analysis of NSP1 genes of human rotaviruses isolated from neonates with asymptomatic infection. J Gen Virol 75: 3635–3639
Patton JT, Salter-Cid L, Kalbach A, Mansell EA, Kattoura M (1993) Nucleotide and amino acid sequence analysis of the rotavirus nonstructural RNA-binding protein NS35. Virology 192: 438–446
Ramig RF, Ward RL (1991) Genomic segment reassortment in rotaviruses and other reoviridae. Adv Virus Res 39: 163–207
Sereno MM, Gorziglia MI (1994) The outer capsid protein VP4 of murine rotavirus strain Eb represents a tentative new P type. Virology 199: 500–504
Taniguchi K, Nishikawa K, Urasawa T, Urasawa S, Midthun K, Kapikian AZ, Gorziglia M (1989) Complete nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding VP4 of a human rotavirus (strain K8) which has unique VP4 neutralization epitopes. J Virol 63: 4101–4106
Taniguchi K, Urasawa T, Kobayashi N, Gorziglia M, Urasawa S (1990) Nucleotide sequence of VP4 and VP7 genes of human rotaviruses with subgroup I specificity and long RNA pattern: implication for new G serotype specificity. J Virol 64: 5640–5644
Taniguchi K, Urasawa T, Pongsuwanna Y, Choonthanom M, Jayavasu C, Urasawa S (1991) Molecular and antigenic analyses of serotypes 8 and 10 of bovine rotaviruses in Thailand. J Gen Virol 72: 2929–2937
Taniguchi K, Urasawa T, Urasawa S (1994) Species specificity and interspecies relatedness in VP4 genotypes demonstrated by VP4 sequence analysis of equine, feline, and canine rotavirus strains. Virology 200: 390–400
Taniguchi K, Wakasugi F, Pongusuwanna Y, Urasawa T, Ukae S, Chiba S, Urasawa S (1992) Identification of human and bovine rotavirus serotypes by polymerase chain reaction. Epidemiol Infect 109: 303–312
Tian Y, Tarlow O, Ballard A, Desselberger U, McCrae MA (1994) Genomic concatemerization/deletion in rotaviruses: a new mechanism for generating rapid genetic change of potential epidemiological importance. J Virol 67: 6625–6632
Urasawa S, Hasegawa A, Urasawa T, Taniguchi K, Wakasugi F, Suzuki H, Inouye S, Pongprot B, Supawadee J, Suprasert S, Rangsiyanond P, Tonusin S, Yamazi Y (1992) Antigenic and genetic analyses of human rotaviruses in Chiang Mai, Thailand: evidence for a close relationship between human and animal rotaviruses. J Infect Dis 166: 227–234
Urasawa S, Urasawa T, Wakasugi F, Kobayashi N, Taniguchi K, Lintag IC, Saniel MC, Goto H (1990) Presumptive seventh serotype of human rotavirus. Arch Virol 113: 279–282
Ward RL, Nakagomi O, Knowlton DR, McNeal MM, Nakagomi T, Clemens JD, Sack DA, Schiff GM (1990) Evidence for natural reassortants of human rotaviruses belonging to different genogroups. J Virol 64: 3219–3225
Wu H, Taniguchi K, Urasawa T, Urasawa S (1993) Genomic relatedness of five equine rotavirus strains with different G serotype and P type specificities. Res Virol 144: 455–464
Xu L, Tian Y, Tarlow O, Harbour D, McCrae MA (1994) Molecular biology of rotaviruses. IX. Conservation and divergence in genome segment 5. J Gen Virol 75: 3413–3421
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Sequence data from this article have been deposited with the GSDB, DDBJ, EMBL and NCBI Data Libraries under Accession Nos. D38150 (strain L26), D38151 (strain 69M), D38152 (strain K8), D38153 (strain OSU), D38154 (strain YM), D38155 (strain FI-14), D38156 (strain FI23), D38157 (strain H2), D38158 (strain L338), U23726 (strain A44), D38148 (strain A5-13), U23727 (strain Cat2), and U23728 (strain H1).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kojima, K., Taniguchi, K. & Kobayashi, N. Species-specific and interspecies relatedness of NSP1 sequences in human, porcine, bovine, feline, and equine rotavirus strains. Archives of Virology 141, 1–12 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01718584
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01718584