Abstract
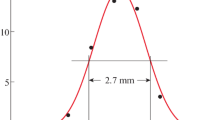
By means of a time resolution it was found that the electric breakdown of air at atmospheric pressure between a charged plate and a spike, on which a torch discharge is burning, gaves rise to comparatively stable ellipsoidal plasma formations — plasmoids. Their dimensions stay within 2÷10 mm, velocity 0÷4 ms, acceleration −210÷1500 ms−2. Their life time is 10−2 s in magnitude. They decay either at the spike electrode, or when the actual breakdown takes place, or they desintegrate in the inter-electrode space.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Holstein T.: Phys. Rev.69 (1946), 50.
Varnerin L., Brown S. C.: Phys. Rev.79 (1950), 946.
Truneček V.: IXth Internat. Conf. Phenomena Ioniz. Gases, Bucharest 1969, 354.
Farský V.: Čs. čas. fys.A 16 (1966), 95.
Kapica P. L.: DAN 101. (1955), 245.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kapoun, K. Breakdown of a gas in superimposed d.c. and h.f. electric fields. Czech J Phys 21, 1246–1249 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01699487
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01699487