Summary
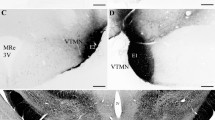
Complete hypothalamic deafferentations were made in male rats with a modified Haläsz knife to isolate tuberoinfundibular dopaminergic neurons from the rest of the brain. A radioenzymatic procedure was employed to quantify dopamine and norepinephrine concentrations in various regions of the hypothalamus. Dopamine concentrations were unaltered while norepinephrine concentrations were reduced 50% in the median eminence and hypothalamic island 16–33 days after surgery. Basal serum prolactin concentrations were unaltered in these rats but were elevated 16 hours after the injection of haloperidol and 1 hour afterα-methyltyrosine. The isolation of tuberoinfundibular neurons from the rest of the brain did not alter the ability of haloperidol to increase the rate ofα-methyltyrosine-induced decline of dopamine in the median eminence. These results indicate that the haloperidol-induced, prolactin-mediated increase of dopamine turnover in the median eminence results from a direct action of this hormone on neurons within the medial basal hypothalamus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andén, N.-E., Roos, B.-E., Werdinius, B. Effects of chlorpromazine, haloperidol and reserpine on the levels of phenolic acids in rabbit corpus striatum. Life Sci.3, 149–158 (1969).
Annunziato, L., Di Renzo, G., Lombardi, G., Scopacasa, F., Schettini, G., Preziosi, P., Scapagnini, U. Role of central noradrenergic neurons in control of thyrotropin secretion in rats. Endocrinology100, 738–744 (1977).
Ben-Jonathan, N., Porter, J. C. A sensitive radioenzymatic assay for dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine in plasma and tissue. Endocrinology98, 1497–1507 (1976).
Bertler, A., Falck, B., Owman, C., Rosengren, E. The localization of monoaminergic blood-brain barrier mechanisms. Pharmacol. Rev.18, 369–385 (1966).
Björklund, A., Moore, R. Y., Nobin, A., Stenevi, U. The organization of tubero-hypophyseal and reticulo-infundibular catecholamine neuron system in the rat brain. Brain Res.51, 171–191 (1973).
Brownstein, M. J., Palkovits, M., Tappaz, M. L., Saavedra, J. M., Kizer, J. S. Effect of surgical isolation of the hypothalamus on its neurotransmitter content. Brain Res.117, 287–295 (1976).
Carlsson, A., Lindqvist, M. Effect of chlorpromazine or haloperidol on formation of 3-methoxytyramine and normetanephrine in mouse brain. Acta Pharmacol. (Kbh.)20, 140–143 (1963).
Clemens, J. A., Gallo, R. V., Whitmoyer, D. I., Sawyer, C. H. Prolactin responsive neurons in the rabbit hypothalamus. Brain Res.25, 371–379 (1971).
Cuello, A. C., Weiner, R. L. Ganong, W. F. Effect of lateral deafferentation on the morphology and catecholamine content of the mediobasal hypothalamus. Brain Res.59, 191–200 (1973).
Dang, B. T., Voogt, J. L. Termination of pseudopregnancy following hypothalamic implantation of prolactin. Endocrinology100, 873–880 (1977).
Duke, J. E., Smith, G. C. The blood-brain barrier in the hypothalamohypophyseal complex. J. Anat. (Lond.)118, 395–396 (1974).
Eikenburg, D. C., Ravitz, A. J., Gudelsky, G. A., Moore, K. E. Effects of estrogen on prolactin and tuberoinfundibular dopaminergic neurons. J. Neural Transmission45, 235–244 (1977).
Fuxe, K. Cellular localization of monoamines in the median eminence and infundibular stem of some mammals. Acta Physiol. Scand.58, 383–384 (1963).
Fuxe, K., Agnati, L., Tsuchiya, K., Hökfelt, T., Johansson, O., Jonsson, G., Lindbrink, P., Löfström, A., Ungerstedt, U. Effect of antipsychotic drugs on central catecholamine neurons of rat brain. In: Antipsychotic drugs, Pharmacodynamics and Pharmacokinetics (Sedvall, G., ed.), pp. 117–132. New York: Pergamon Press. 1975.
Fuxe, K., Hökfelt, T., Nilsson, O. Castration, sex hormones, and tuberoinfundibular dopamine neurons. Neuroendocrinology5, 107–120 (1969).
Gudelsky, G. A., Moore, K. E. A comparison of the effects of haloperidol on dopamine turnover in the striatum, olfactory tubercle and median eminence. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.202, 149–156 (1977).
Gudelsky, G. A., Simpkins, J., Mueller, G. P., Meites, J., Moore, K. E. Selective actions of prolactin on catecholamine turnover in the hypothalamus and on serum LH and FSH. Neuroendocrinology22, 206–215 (1976).
Hökfelt, T., Fuxe, K. Effects of prolactin and ergot alkaloids on the tuberoinfundibular dopamine (DA) neurons. Neuroendocrinology9, 100–122 (1972).
Krulich, L., Hefco, E., Aschenbrenner, J. E. Mechanism of the effects of hypothalamic deafferentation on prolactin secretion in the rat. Endocrinology96, 107–118 (1975).
Löfström, A., Jonsson, G., Fuxe, K. Microfluorometric quantitation of catecholamine fluorescence in rat median eminence. I. Aspects on the distribution of dopamine and noradrenaline nerve terminals. J. Histochem. Cytochem.24, 415–429 (1976).
Lowry, O. H., Rosenbrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., Randall, R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem.193, 265–275 (1951).
Mac Leod, R. M. Regulation of prolactin secretion. In: Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology (Martini, L., Ganong, W. F., eds.), pp. 169–194. New York: Raven Press. 1976.
Poulain, P., Carette, B. Actions of applied prolactin on septal and preoptic neurons in the guinea pig. Brain Res.116, 172–176 (1976).
Sokal, R. R., Rohlf, F. J. Biometry. San Francisco: W. H. Freeman and Co. 1969.
Tindal, J. S., Knoggs, G. S. Pathways in the forebrain of the rat concerned with the release of prolactin. Brain Res.119, 211–221 (1977).
Turpen, C., Dunn, J. D. The effect of isolation or ablation of the medial basal hypothalamus on serum prolactin levels in male rats. Neuroendocrinology20, 224–234 (1976).
Voogt, J. L., Meites, J. Suppression of proestrous and suckling-induced increase in serum prolactin by hypothalamic implant of prolactin. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med.142, 1056–1058 (1973).
Weiner, R. I. Role of brain catecholamines in the control of LH and prolactin secretion. In: Hypothalamic Hormones (Motta, M., Crosignani, P. G., Martini, L., eds.), pp. 249–253. London: Academic Press. 1975.
Weiner, R. I., Shryne, J. E., Gorski, R. A., Sawyer, C. H. Changes in the catecholamine content of the rat hypothalamus following deafferentation. Endocrinology90, 867–873 (1972).
Wilk, S., Watson, E., Stanley, M. E. Differential sensitivity of two dopaminergic structures in rat brain to haloperidol and to clozapine. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.195, 265–270 (1975).
Yamada, Y. Effects of iontophoretically-applied prolactin on unit activity of the rat brain. Neuroendocrinology18, 263–271 (1975).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gudelsky, G.A., Annunziato, L. & Moore, K.E. Localization of the site of the haloperidol-induced, prolactin-mediated increase of dopamine turnover in the median eminence: Studies in rats with complete hypothalamic deafferentations. J. Neural Transmission 42, 181–192 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01675309
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01675309