Summary
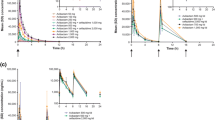
The concentration of antibiotic in a focus of infection depends both on the peak serum concentration and on the area under the serum concentration time curve (AUC). A knowledge of the relationship between increased doses and the corresponding response in serum concentration would be relevant as a basis for determining an adequate clinical dosage. Dose-related changes in the two pharmacokinetic variables, peak serum concentration and AUC, after single doses of bacampicillin are compared with data on different aminopenicillins from other studies. With ampicillin there is a nonlinear relationship between both dose-peak and dose-AUC. The results indicate that the poor absorption of oral ampicillin can only be partially compensated for by increasing the oral dose. But with amoxycillin and the ampicillin esters the absorbed amount (AUC) is a linear function of the dose in the dosage range investigated. The increase in peak serum level with high doses of oral ampicillin is far less than proportional, while this tendency was less pronounced for amoxycillin and still less for pivampicillin, talampicillin and bacampicillin.
Zusammenfassung
Die Konzentration eines Antibiotikums in einem Infektionsherd hängt sowohl von der Serumspitzenkonzentration als auch von der Fläche unter der Serum Konzentrations-Zeitkurve (AUC) ab. Die Kenntnis der Beziehung zwischen Dosiserhöhung und dem folgenden Verhalten der Serumkonzentration wäre entscheidend als Basis für die Festlegung einer angemessenen klinischen Dosierung. Dosis-abhängige Veränderungen in den beiden pharmakokinetischen Variablen, der Serum Spitzenkonzentration und der AUC nach Einzeldosen Bacampicillin werden mit Daten von verschiedenen Aminopenicillinen aus anderen Studien verglichen. Bei Ampicillin besteht eine nicht-lineare Beziehung zwischen Dosis und Spitzenspiegel und Dosis und AUC. Die Ergebnisse zeigen, daß die schlechte Absorption von oralem Ampicillin nur teilweise durch Erhöhung der oralen Dosis kompensiert werden kann. Bei Amoxycillin und den Ampicillin Estern hingegen ist die absorbierte Menge (AUC) eine lineare Funktion der Dosis im untersuchten Dosierungsbereich. Die Erhöhung des Serumspitzenspiegels mit hohen Dosen oralem Ampicillin ist wesentlich geringer als proportional, bei Amoxycillin ist diese Tendenz weniger und bei Pivampicillin, Talampicillin und Bacampicillin entschieden weniger ausgeprägt.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature
Continuous versus intermittent intravenous antibiotics. The Medical Letter 10 (1968) 57–58.
Barza, M., Brusch, J., Bergeron, M. G., Weinstein, L. Penetration of antibiotics into fibrin loci in vivo. III. Intermittent vs. continuous infusion and the effect of probenecid. J. Infect. Dis. 129 (1974) 73–78.
Kunst, M. W., Mattie, H. Cefazolin and cephradine: Relationship between serum concentrations and tissue contents in mice. Infection 6 (1978) 166–170.
Bergan, T. Kinetics of tissue penetration. Are high plasma peak concentrations or sustained levels preferable for effective antibiotic therapy? Scand. J. Infect. Dis. Suppl. 14 (1978) 36–46.
Hallander, H. O., Flodström, A., Sjövall, J. Pharmacological and clinical study of bacampicillin in acute peritonsillitis-a comparision with ampicillin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 11 (1977) 185–190.
Wagner, J. G. Fundamentals of clinical pharmacokinetics, Drug Intelligence Publications Inc., Hamilton/Illinois, 1975, p. 247.
Sjövall, J., Magni, L.: To be published.
Magni, L., Sjöberg, B., Sjövall, J., Wessman, J. Clinical pharmacological studies with bacampicillin. In:Williams, J. D., Geddes, A. M. (ed.): Chemotherapy vol. 5: Penicillins and cephalosporins Plenum Press, New York, 1976, p. 109–114.
Jones, K. H., Langley, P. F., Lees, L. J. Bioavailability and metabolism of talampicillin. Chemotherapy 24 (1978) 217–226.
Duval, J., Soussy, C. J. Activité antibactérienne et pharmacocinétique de l'amoxicilline. Comparaison avec l'ampicilline. Méd. Malad. Infect. 3 (1973) 525–531.
Spyker, D. A., Rugloski, R. J., Vann, R. L., O'Brien, W. M. Pharmacokinetics of amoxicillin: Dose dependence after intravenous, oral and intramuscular administration. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 11 (1977) 132–141.
Loo, J. C. K., Foltz, E. L., Wallick, H., Kwan, K. C. Pharmacokinetics of pivampicillin and ampicillin in man. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 16 (1974) 35–43.
Knudsen, E. T., Rolinson, G. N., Stevens, Shirley Absorption and excretion of “Penbritin”. Br. Med. J. 2 (1961) 198–200.
Magni, L., Sjövall, J., Syvälahti, E. Comparative clinical pharmacology of bacampicillin and high oral doses of ampicillin. Infection 6 (1978) 283–289.
Welling, P. G., Huang, H., Koch, P. A., Craig, W. A., Madsen, P. O. Bioavailability of ampicillin and amoxicillin in fasted and nonfasted subjects. J. Pharm. Sci. 66 (1977) 549–552.
Daehne, W. v., Frederiksen, E., Gundersen, E., Lund, F., Mørch, P., Petersen, H. J., Roholt, K., Tybring, L., Godtfredsen, W. O. Acyloxymethyl esters of ampicillin. J. Med. Chem. 13 (1970) 607–612.
Clayton, J. P., Cole, M., Elson, S. W., Ferres, H. BRL 8988 (Talampicillin), a well-absorbed oral form of ampicillin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 5 (1974) 670–671.
Bodin, N-O., Ekström, B., Forsgren, U., Jalar, L.-P., Magni, L., Ramsay, C.-H., Sjöberg, B. Bacampicillin: a new orally well-absorbed derivative of ampicillin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 8 (1975) 518–525.
Swahn, Å. On the absorption and metabolism of some penicillins in man. Dissertation, Stockholm, 1974.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sjövall, J. Dose dependence in human absorption of aminopenicillins. Infection 7 (Suppl 5), S458–S462 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01659771
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01659771