Summary
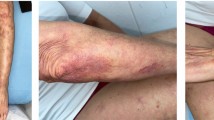
Bacterial infections of the skin or soft tissue responded to ciprofloxacin 500 mg tablets b.i.d. The treatment was well tolerated and effective, so that this drug can be recommended in cutaneous infections caused by sensitive bacteria.
Zusammenfassung
Bakterielle Infektionen der Haut und der Weichteile haben auf eine Behandlung mit 2 × 500 mg Ciprofloxacin Tabletten angesprochen. Die Therapie wurde gut vertragen und war wirksam, so daß dieses Medikament für Hautinfektionen, die durch Ciprofloxacin-empfindliche Erreger verursacht sind, empfohlen werden kann.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature
Blumer, J. L., O'Brien, C. A., Lemon, E., Capretta, T. M. Skin and soft tissue infections, pharmacologic approaches. Ped. Infect. Dis. 4 (1985) 336–341.
Gentry, L. O. Treatment of skin, skin structure, bone and joint infection with ceftazidime. Am J. Med. 79 (1985) 67–74.
Karakusis, P. H., Trenholme, G. M., Levin, S. A review of the use of cefotaxime in the treatment of skin and skin structure infections with special reference to gram-positive pathogens. Infection 13, Suppl. 1 (1985) S46-S49.
Pankey, G. A., Katner, H. P., Valainis, G. T., Clarkson, M. J., Cortez, L. M., Dalovisio, J. R. Overview on bacterial infections of the skin and soft tissue and clinical experience with ticarcillin plus clavulanate potassium in their treatment. Am. J. Med. 79 (1985) 106–115.
Parish, L. C., Witkowski, J. A., Snow, R., Eron, L., Mogabgab, W. J. Cephalosporins in cutaneous infections. A prospective comparison of two dosage regimens of ceftazidime for therapy of skin and skin structure infections. Int. J. Dermatol. 25 (1986) 258–265.
Rao, B., See, R. C., Chuah. S. K., Bansal, M. B., Lou, M. A., Thadepalli, H. Ticarcillin plus clavulanic acid versus moxalactam in the treatment of skin and soft tissue infections. Am. J. Med. 79 (1985) 126–129.
Bauernfeind, A.: Antimicrobial activity of ciprofloxacin: an overview 1st International Ciprofloxacin Workshop Leverkusen 1985, Proceedings (1986) 7–11.
Bergan, T., Thorsteinsson, S. B.: Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of ciprofloxacin 1st International Ciprofloxacin Workshop, Leverkusen 1985, Proceedings (1986) 111–121.
Bergogne-Berezin, E.: Penetration of ciprofloxacin into tissue: a review 1st International Ciprofloxacin Workshop, Leverkusen 1985, Proceedings (1986) 183–188.
Parish, L. C., Asper, R. Systemic treatment of cutaneous infections — a comparative study of ciprofloxacin and cefotaxime. Am. J. Med. 82 (1987) 227–229.
Perez-Ruvalcaba, J. A., Quintero-Perez, N. P., Morales-Reyes, J. J., Huitron-Ramirez, J. A., Rodriguez-Chagollan, J. J., Rodriguez-Noriega, E. Double-blind comparison of ciprofloxacin with cefotaxime in the treatment of skin and skin structure infections. Am. J. Med. 82 (1987) 242–246.
Ramirez-Ronda, C. H., Saavedra, S., Rivera-Vasquez, C. R. Comparative double blind study of oral ciprofloxacin and intravenous cefotaxime in skin and skin structure infections. Am. J. Med. 82 (1987) 220–223.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gorkiewicz-Petkow, A., Jablonska, S., Petkow, L. et al. Bacterial infections of the skin treated with ciprofloxacin. Infection 16 (Suppl 1), S55–S56 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01650509
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01650509