Summary
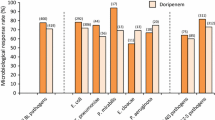
Cefadroxil, a new semisynthetic cephalosporin, was administered to 109 patients with a wide range of infectious diseases covering abscesses, wound infections, furunculosis, ear-nose-throat infections, lower respiratory tract infections, gastro-enterological infections and miscellaneous infections. Excellent clinical response was obtained in 102 cases (93.6%) whereas eradication of the causative pathogens reached 80.7% (88 cases). Side-effects were noted in 11 cases (10%), included rash, abdominal pain, nausea and diarrhoea, and can be partly explained by the fact that approximately half of the patients in this study were treated for gastro-enterological diseases.
Zusammenfassung
Cefadroxil, ein neues, halbsynthetisches Cephalosporin, wurde 109 Patienten mit einer breitgefächerten Reihe von Infektionskrankheiten einschließlich Abszessen, Wundinfektionen, Furunkeln, Hals-Nasen-Ohren-Infektionen, Infektionen der unteren Atemwege, gastroenterologischen Infektionen und anderen weiteren Infektionen verabreicht. Ein ausgezeichnetes klinisches Ansprechen wurde bei 102 Fällen (93,6%) erzielt, die Elimination des pathogenen Erregers gelang bei 80,7% (88 Fällen). Nebenwirkungen wurden bei 11 Fällen (10%) beobachtet, eingeschlossen Exanthem, Bauchschmerzen, Übelkeit und Erbrechen; sie können teilweise dadurch erklärt werden, daß annähernd die Hälfte der Patienten wegen gastroenterologischer Erkrankungen behandelt wurde.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature
Pfeffer, M. et al. Comparative human oral clinical pharmacology of cefadroxil, cephalexin and cephradine. Antimicrob. Ag. Chemother. 11 (1977) 331–338.
Hartstein, A. I. et al. Comparison of pharmacological and antimicrobial properties of cefadroxil and cephalexin. Antimicrob. Ag. Chemother. 12 (1977) 93–97.
Santella, P. J., Fernández, C. A., Rondel, R. K.: The clinical evaluation of cefadroxil: a new oral cephalosporin. Proc. 10th Intern. Congress of Chemotherapy, Zurich (1977).
Hendrickx, J. et al. Clinical evaluation of cefadroxil: a multicenter trial. I. Acute lower respiratory tract infections. Drugs Exptl. and Clin. Res. 4 (1978) 89–93.
Reynaert, J. et al. Clinical evaluation of cefadroxil: a multicenter trial. II. Urinary tract infections. Drugs Exptl. and Clin. Res. 4 (1978) 95–103.
Bravo-Sandoval, J. et al. Antimicrobial therapy of septic abortion with an aminoglycoside or a cephalosporin. Invest. Med. Int. 3 (1976) 438.
Cedrato, A. Cefadroxil, a new cephalosporin in the treatment of respiratory infections in children. Invest. Med. Int. 3 (1977) 87.
Gómez-Del-Campo C. et al.: Comparative levels of Cefadroxil versus cephalexin in blood, bile, gall bladder, and liver, after 500 mg and multiple oral doses. In: 16th Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, Chicago, III., Abstract 363 (1976).
Leitner, F. et al.: Bactericidal activity of cefadroxil, cephalexin and cephradine in an in vitro pharmacokinetic model. Proc. 10th Intern. Congress of Chemotherapy, Zurich (1976).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Erstveröffentlichung: Drugs Exptl. clin. Res. 4 (1978) 105.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pijck, J., Vuye, A., Hallynck, T. et al. Clinical evaluation of cefadroxil: A multicenter trial III. Miscellaneous infections. Infection 8 (Suppl 5), S623–S625 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01639683
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01639683