Summary
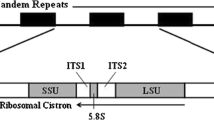
The structure of the ribosomal DNA has been analyzed in three species of theCynareae tribe using Southern blot hybridization.Silybum marianum possesses two types of ribosomal genes 12.3 and 13.4 kb long;Cirsium vulgare has at least four types of rDNA repeats 10.6, 10.5, 11.7 and 11.9 kb long;Carlina acaulis only one type of ribosomal genes 9.7 kb long. The rRNA genes of the three species studied showed an identical restriction mapping in the 18 S and 25 S regions. However species differentiation in length and/or nucleotide sequences are present in the external spacer and very probably in the internal transcribed spacer.
By cytophotometric studies and byin vitro rRNA/DNA filter hybridization, the DNA amount/4 C nucleus and the rDNA percentage were calculated in nine species of theCynareae tribe:Cynara cardunculus subsp.scolymus (artichoke),Cynara cardunculus subsp.cardunculus (wild artichoke),Onopordon acanthium, O. illyricum, Galactites tomentosa, Carduus nutans, Silybum marianum, Cirsium vulgare andCarlina acaulis. The DNA amount/4 C nucleus in eight species are similar, ranging from 4.24 pg inGalactites tomentosa to 5.96 pg inCirsium vulgare, whileCarlina acaulis has a DNA amount/ 4C nucleus of 11.8 pg. The rDNA percentages range from 0.192% inOnopordon acanthium to 1.022% inSilybum marianum, whileCarlina acaulis has 0.038% of rDNA. This latter species is clearly distinct within theCynareae tribe.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bellomaria B, Hruska K (1984) Numeri cromosomici per la flora italiana. Inf Bot Ital 15: 53–57
Bennett MD, Smith JB (1976) Nuclear DNA amounts in Angiosperm. Phil Trans R Soc B 274: 227–274
Colombo P, Marceno C, Princiotta R (1983) Numeros cromosomaticos de plantas occidentales. An Jard Bot Madrid 40: 263–270
Fernandes A, Queiros M (1971) Contribution a la connaissance cytotaxinomique des spermatophyta du Portugal II.Compositae. Bol Soc Brot (Ser 2) 45: 5–121
Gillespie D, Spiegelman S (1965) A quantitative assay for DNA/RNA hybrids with DNA immobilized on a membrane. J Mol Biol 12: 829–842
Goldberg RB, Demis WP, Siegel A (1972) Nucleic acid hybridization studies within the genusCurcurbita. Genetics 72: 253–266
Larsen K (1955) Cytotaxonomical studies on the Mediterranean flora. Bot Notiser 108: 163–275
Love A, Love D (1982) IOPB Chromosome number reports LXXVI. Taxon 31: 583–587
Maggini F, Barsanti P, Marazia T (1978) Individual variation of the nucleolus organizer regions inAllium cepa andA. sativum. Chromosoma (Berl) 66: 173–183
Moore RJ, Frankton C (1962) Cytotaxonomic studies in the tribeCynareae (Compositae). Can J Bot 40: 281–299
Southern EM (1975) Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol 98: 503–517
Tucci GF, Maggini F (1986) Ribosomal RNA genes in species of theCynareae tribe (Compositae) I. Protoplasma 132: 76–84
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maggini, F., Tucci, G.F. & Gelati, M.T. Ribosomal RNA genes in species of theCynareae tribe (Compositae). II. Protoplasma 144, 125–131 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01637245
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01637245