Summary
[3H]Agmatine (amino-4-guanidobutane) has been shown to be potentially useful for identifying and assessing the ACh sensitivity of specific neurons. Small cationic amines are able to permeate ACh-activated ion channels in sympathetic neurons and vertebrate endplates. Sensory neurons of the photic pathway in the nudibranch molluscHermissenda crassicornis are cholinergic and the synaptic interactions between the photic and vestibular systems have been well characterized electrophysiologically. We have therefore tested the feasibility of using autoradiography with [3H]agmatine, (a) to identify known ACh-responsive postsynaptic cells and (b) to examine its ability to serve as an indicator of physiologic activity within the photic and vestibular pathways under conditions of darkness and light stimulation.
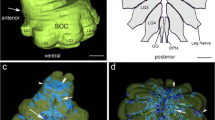
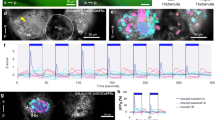
Scintillation counting revealed that ∼ 70% of the radioactivity was associated with the CNS while ∼ 30% was found in the processing fluids, indicating that routine glutaraldehyde-osmium fixation and subsequent processing for epoxy embedding allows retention of substantial amounts of the radiolabel. The autoradiographic results consistently demonstrated that the uptake patterns for [3H]agmatine did reflect some of the known neuronal interactions under the experimental conditions of light and dark. The accuracy extended to the second order cells of the optic ganglion and to putative interneurons along the photic tract in the cerebropleural ganglion. Since all the neurons in these pathways are unipolar with their synaptic interactions occurring only at the terminal endings, the radiolabel accumulated in the somata resulted from retrograde axonal transport. In the photic-vestibular pathways, the highest silver grain densities were found over structures (cell bodies or axon tracts) with increased synaptic activity coupled with higher levels of cellular activity (i.e. increased excitatory postsynaptic potentials or increased spontaneous impulse activity). Slightly less label was found in cells which received increased numbers of inhibitory postsynaptic potentials that produced hyperpolarization and a transient cessation of impulse activity under conditions of illumination. Therefore, the uptake levels of [3H]agmatine as revealed by autoradiography appear to reflect not only changes in sensitivity or density of ACh-activated channels but also changes in cellular activity as indicated by increased amounts of retrograde transport. These results represent the first example of the effective use of this radiolabel as an indicator of synaptic activity in invertebrates and in sensory systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akaike, T. &Alkon, D. L. (1980) Sensory convergence on central visual neurons inHermissenda.Journal of Neurophysiology 44, 501–13.
Alkon, D. L. (1973a) Neuronal organization of a molluscan visual system.Journal of General Physiology 61, 444–61.
Alkon, D. L. (1973b) Intersensory interactions inHermissenda.Journal of General Physiology 62, 185–202.
Alkon, D. L. (1974) Sensory interactions in the nudibranch molluskHermissenda crassicornis.Federation Proceedings 33, 1083–90.
Alkon, D. L. (1976) The economy of photoreceptor function in a primitive nervous system. InNeural Principles in Vision (edited byZettler, F. &Weiler, R.), pp. 410–26. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
Alkon, D. L. (1980) Cellular analysis of a gastropod (Hermissenda crassicornis) model of associative learning.Biological Bulletin 159, 505–60.
Alkon, D. L. (1984) Calcium-mediated reduction of ionic currents: a biophysical memory trace.Science 226, 1037–45.
Alkon, D. L. &Fuortes, M. G. F. (1972) Responses of photoreceptors inHermissenda.Journal of General Physiology 60, 631–49.
Alkon, D. L. &Sakakibara, M. (1985) Calcium activates and inactivates a photoreceptor soma potassium current.Biophysical Journal 48, 983–95.
Ascher, P., Marty, A. &Neild, T. O. (1978) Life time and elementary conductance of the channels mediating the excitory effects of acetylcholine inAplysia neurones.Journal of Physiology (London) 278, 177–206.
Basinger, S. F., Gordon, W. C. &Lam, D. M. K. (1979) Differential labelling of retinal neurons by3H-2-deoxyglucose.Nature 280, 682–4.
Blackett, N. M. &Parry, D. M. (1977) A simplified method of ‘hypothetical grain’ analysis of electron microscope autoradiographs.Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry 25, 206–14.
Brady, S. T., Lasek, R. J. &Allen, R. D. (1982) Fast axonal transport in extruded axoplasm from squid giant axon.Science 218, 1129–31.
Brunder, D. G. &Lieberman, E. M. (1985) The ionic basis of the membrane potential of glial cells surrounding the medial giant axon of the crayfish.Biophysical Journal 47, 146A.
Buchner, E. &Buchner, S. (1980) Mapping stimulus-induced nervous activity in small brains by [3H]2-deoxy-D-glucose.Cell and Tissue Research 211, 51–64.
Bullock, T. H. &Horridge, G. A. (1965)Structure and Function in the Nervous Systems of Invertebrates, Vol. II. San Francisco: W. H. Freeman and Company.
Carlson, K. E., Price, C. H. &Aizenman, E. (1984) Selective retrograde axonal transport of free glycine in identified neurons ofAplysia.Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology 4, 231–47.
Colonnier, M., Tremblay, J. P. &McLennan, H. (1979) Synaptic contacts on glial cells in the abdominal ganglion ofAplysia californica.Journal of Comparative Neurology 188, 391–400.
Crow, T., Heldman, E., Hacopian, V., Enos, R. &Alkon, D. L. (1979) Ultrastructure of photoreceptors in the eye ofHermissenda labelled with intracellular injections of horseradish peroxidase.Journal of Neurocytology 8, 181–95.
Cuénod, M., Bagnoli, P., Beaudet, A., Rustioni, A., Wiklund, L. &Streit, P. (1982) Transmitter-specific retrograde labeling of neurons. InCytochemical Methods in Neuroanatomy (edited byChan-Palay, V. &Palay, S. L.), pp. 17–44. New York: Alan R. Liss.
Dwyer, T. M., Adams, D. J. &Hille, B. (1980) The permeability of the endplate channel to organic cations in frog muscle.Journal of General Physiology 75, 469–92.
Geiselman, C. W. &Burke, C. N. (1973) Exact anhydride: epoxy percentages for Araldite and Araldite-Epon embedding.Journal of Ultrastructure Research 43, 220–7.
Goh, Y. &Alkon, D. L. (1984) Sensory, interneuronal, and motor interactions withinHermissenda visual pathway.Journal of Neurophysiology 52, 156–69.
Grafstein, B. &Forman, D. S. (1980) Intracellular transport in neurons.Physiological Reviews 60, 1167–283.
Grossman, Y., Alkon, D. L. &Heldman, E. (1979) A common origin of voltage noise and hair cell generator potentials.Journal of General Physiology 73, 23–48.
Harris, W. V. &Salpeter, M. M. (1983) Soluble compound electron microscope (EM) autoradiography.Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry 31, 495–500.
Heldman, E. &Alkon, D. L. (1978) Neurotransmitter synthesis in the nervous system of the molluscHermissenda.Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology 59, 117–25.
Heldman, E., Grossman, Y., Jerussi, T. P. &Alkon, D. L. (1979) Cholinergic features of photoreceptor synapses inHermissenda.Journal of Neurophysiology 42, 153–65.
Hubel, D. H., Wiesel, T. N. &Stryker, M. P. (1978) Anatomical demonstration of orientation columns in Macaque monkey.Journal of Comparative Neurology 177, 361–80.
Kai Kai, M. A. &Pentreath, V. W. (1981) High resolution analysis of [3H]2-deoxyglucose incorporation into neurons and glial cells in invertebrate ganglia: histological processing of nervous tissue for selective marking of glycogen.Journal of Neurocytology 10, 693–708.
Kehoe, J. S. (1972) Ionic mechanisms of a two component cholinergic inhibition inAplysia neurones.Journal of Physiology (London) 225, 85–114.
Kennedy, C., Desrosiers, M. H., Sakurada, O., Shinohara, M., Reivich, M., Jehle, J. W. &Sokoloff, L. (1976). Metabolic mapping of the primary visual system of the monkey by means of the autoradiographic [14C]deoxyglucose technique.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 73, 4230–4.
Kiss, J., Mezey, É. &Palkovits, M. (1981) Axonterminal uptake and retrograde axonal transport of labelled amino acids and their incorporation into proteins of neuronal perikarya.Neuroscience 6, 2035–46.
Koval, L. M., Kononenko, N. I. &Skibo, G. G. (1984) The axosomatic contacts on the bursting neuron of the snailHelix pomatia. I. Ultrastructural features of the axosomatic contacts.Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology 4, 31–41.
Kuzirian, A. M. (1983) Neuroanatomy ofHermissenda: a model system for the study of associative learning.Journal of Molluscan Studies 12A, 73–81.
Kuzirian, A. M., Alkon, D. L. &Harris, L. G. (1981) An infraciliary network in statocyst hair cells.Journal of Neurocytology 10, 497–514.
Kuzirian, A. M., Hill, L., Neary, J. T. &Alkon, D. L. (1984) Autoradiography using tritiated agmatine as an indicator of physiologic activity inHermissenda visual neurons.Abstracts of the Society for Neuroscience 10, 26.
Lancet, D., Greer, C. A., Kauer, J. S. &Shepherd, G. M. (1982) Mapping of odor-related neuronal activity in the olfactory bulb by high-resolution 2-deoxyglucose autoradiography.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 79, 670–4.
Lieberman, E. M., Villegas, J. &Villegas, G. M. (1981). The nature of the membrane potential of glial cells associated with medial giant axon of the crayfishProcambarus clarkii.Neuroscience 6, 261–72.
Matsumoto, M., Sasaki, K. &Sato, M. (1984) Desensitization of acetylcholine receptors observed inAplysia ganglion cells.Journal of the Iwate Medical Association 36, 157–60.
Mayorova, V. F. &Troitskaya, L. P. (1972) Axosomatic synapses in pedal ganglia of the Gastropoda molluscLymnaea stagnalis.Doklady Akademii Nauk SSSR 204, 1471–2.
Mesulam, M-M. (1982) (ed.) Principles of horseradish peroxidase neurohistochemistry and their applications for tracing neural pathways — Axonal transport, enzyme histochemistry and light microscopic analysis. InTracing Neural Connections with Horseradish Peroxidase, pp. 1–152. Chichester: John Wiley and Sons.
Ornberg, R. L., Neale, E. A., Smith, C. B., Yarowsky, P. &Bowers, L. M. (1979) Radioautographic localization of glucose utilization by neurons in culture.Journal of Cell Biology 83, 142a.
Pentreath, V. W. (1982) Potassium signalling of metabolic interactions between neurons and glial cells.Trends in Neuroscience 5, 339–45.
Pentreath, V. W. &Kai Kai, M. A. (1982) Significance of the potassium signal from neurones to glial cells.Nature 295, 59–61.
Price, C. H., McAdoo, D. J., Farr, W. &Okuda, R. (1979) Bidirectional axonal transport of free glycine in identified neurons R3-R14 ofAplysia.Journal of Neurobiology 10, 551–71.
Redshaw, J. D. &Bisby, M. A. (1985). Comparison of the effects of sciatic nerve crush or resection on the proteins of fast axonal transport in rat dorsal root ganglion cell axons.Experimental Neurology 88, 437–46.
Reingold, S. C., Sejnowski, T. J., Gelperin, A. &Kelley, D. B. (1981) [3H]-2-deoxyglucose autoradiography in a molluscan nervous system.Brain Research 208, 416–20.
Saji, M. &Obata, K. (1981) Stimulus-dependent labelling of cultured ganglionic cell with [14C]2-deoxyglucose.Brain Research 212, 435–46.
Sejnowski, T. J., Reingold, S. C., Kelley, D. B. &Gelperin, A. (1980) Localization of [3H]-2-deoxyglucose in single molluscan neurones.Nature 287, 449–51.
Senft, S. L., Allen, R. D., Crow, T. &Alkon, D. L. (1982) Optical sectioning of HRP-stained molluscan neurons.Journal of Neuroscience Methods 5, 153–9.
Sokoloff, L. (1979) Mapping of local cerebral activity by measurement of local cerebral glucose utilization with [14C] deoxyglucose.Brain 102, 653–68.
Sokoloff, L., Reivich, M., Kennedy, C., Desrosiers, M. H., Patlak, C. S., Pettigrew, K. D., Sakurada, O. &Shinohara, M. (1977) The [14C] deoxyglucose method for the measurement of local cerebral glucose utilization; theory, procedure, and normal values in the conscious and anesthetized albino rat.Journal of Neurochemistry 28, 897–916.
Stensaas, L. J., Stensaas, S. S. &Trujillo-Cenóz, O. (1969) Some morphological aspects of the visual system ofHermissenda crassicornis (Mollusca: Nudibranchia).Journal of Ultrastructure Research 27, 510–32.
Stommel, E. W., Stephens, R. E. &Alkon, D. L. (1980) Motile statocyst cilia transmit rather than transduce mechanical stimuli.Journal of Cell Biology 87, 652–62.
Tabata, M. &Alkon, D. L. (1982) Positive synaptic feedback in visual system of nudibranch molluskHermissenda crassicornis.Journal of Neurophysiology 48, 174–91.
Telford, J. N. &Matsumura, F. (1969) The expandable loop: an improved wire-loop device for producing thin photographic films suited to autoradiographic electron microscopy.Stain Technology 44, 259–60.
Yoshikami, D. (1980) Permeability of acetylcholine-activated postsynaptic channels in sympathetic neurons.Abstracts of the Society for Neuroscience 6, 778.
Yoshikami, D. (1981) Transmitter sensitivity of neurons assayed by autoradiography.Science 212, 929–30.
Zaitseva, O. V. (1978) Characteristics of the neuronal composition of the central nervous system of nudibranch molluscs.Journal of Evolutionary Biochemistry and Physiology 14, 416–23.
Zs-Nagy, I. &Sakharov, D. A. (1969) Axo-somatic synapses in procerebrum of Gastropoda.Experientia 25, 258–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuzirian, A.M., Meyhöfer, E., Hill, L. et al. Autoradiographic measurement of tritiated agmatine as an indicator of physiologic activity inHermissenda visual and vestibular neurons. J Neurocytol 15, 629–643 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01611862
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01611862