Summary
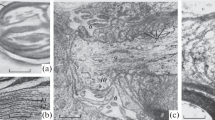
The acute effects of batrachotoxin, a steroidal neurotoxin which opens the membrane sodium channel, were observed morphologically at various time points up to 3 h after injection into rat peroneal nerve. Three changes were found. First, there was massive swelling of the axon at the node of Ranvier accompanied by retraction of paranodal myelin. Second, a similar swelling of unmyelinated axons was seen. Third, extracellular fluid accumulated along the internode in the adaxonal space, the intraperiod line of myelin and, rarely, the external mesaxon, with concomitant shrinkage of the axon. The first two changes might be explained on the basis of massive shift of sodium through the batrachotoxin-modified sodium channel into the axon and subsequent osmotic shift of fluid. The reason for the third change is not clear but probably also has a ionic basis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albuquerque, E. X. (1972) The mode of action of batrachotoxin.Federation Proceedings 31, 1133–8.
Albuquerque, E. X., Daly, J. W. &Witkop, B. (1971) Batrachotoxin: chemistry and pharmacology.Science 172, 995–1002.
Allen, C. N., Akaike, A. &Albuquerque, E. X. (1984) The frog interosseal muscle fiber as a new model for patch clamp studies of chemosensitive- and voltage-sensitive ion channels: actions of acetylcholine and batrachotoxin.Journal de Physiologie (Paris)79, 338–43.
Baker, M., Bostock, H., Brook, G. A. &Love, S. (1985)Phoneutria andLeiurus venoms induce spontaneous compound action potentials in rat spinal roots.Journal of Physiology 369, 63P.
Barrett, E. F. &Barrett, J. N. (1982) Intracellular recording from vertebrate myelinated axons: mechanism of the depolarizing afterpotential.Journal of Physiology 323, 117–44.
Blank, W. F., Bunge, M. B. &Bunge, R. P. (1974) The sensitivity of the myelin sheath, particularly the Schwann cell-axolemmal junction, to lowered calcium levels in cultured sensory ganglia.Brain Research 67, 503–18.
Boegman, R. J. &Albuquerque, E. X. (1978) Batrachotoxin blocks fast axon transportin vivo.Federation Proceedings 37, 525.
Boegman, R. J., Deshpande, S. S. &Albuquerque, E. X. (1980) Consequences of axonal transport blockade induced by batrachotoxin on mammalian neuromuscular junction. I. Early pre- and post-synaptic changes.Brain Research 187, 183–96.
Boegman, R. J. &Riopelle, R. J. (1980) Batrachotoxin blocks slow and retrograde axonal transportin vivo.Neuroscience Letters 18, 143–7.
Carafoli, E. &Crompton, M. (1978) The regulation of intracellular calcium. InCurrent Topics in Membranes and Transport. Membrane Properties: Mechanical Aspects, Receptors, Energetics and Calcium-Dependence of Transport, Vol. 10 (edited byBronner, F. &Kleinzeller, A.) pp. 151–216. New York: Academic Press.
Carafoli, E., Tiozzo, R., Lugli, G., Crovetti, F. &Kratzing, C. (1974) The release of calcium from heart mitochondria by sodium.Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology 6, 361–71.
Chiu, S. Y., Schräger, P. &Ritchie, J. M. (1984) Neuronal-type Na+ and K+ channels in rabbit cultured Schwann cells.Nature 311, 156–7.
Deshpande, S. S., Boegman, R. J. &Albuquerque, E. X. (1981) Consequences of axonal transport blockade by batrachotoxin on mammalian neuromuscular junction. II. Late pre- and post-synaptic changes.Brain Research 225, 115–29.
Friede, R. L. &Bischhausen, R. (1978) How do axons control myelin formation? The model of 6-aminonicotinamide neuropathy.Journal of the Neurological Sciences 35, 341–53.
Hall, S. M. &Williams, P. L. (1971) The distribution of electron-dense tracers in peripheral nerve fibres.Journal of Cell Science 8, 541–55.
Hirano, A. (1983) Reaction of the periaxonal space to some pathologic processes. InProgress in Neuropathology Vol. 5, (edited byZimmerman, H. M.), pp. 99–112. New York: Raven Press.
Hirano, A. &Dembitzer, H. M. (1981) The periaxonal space in an experimental model of neuropathy: the mutant Syrian hamster with hindleg paralysis.Journal of Neurocytology 10, 261–9.
Huang, L-J. M., Moran, N. &Ehrenstein, G. (1982) Batrachotoxin modifies the gating kinetics of sodium channels in internally perfused neuroblastoma cells.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 79, 2082–5.
Huang, L-J. M., Moran, N. &Ehrenstein, G. (1984) Gating kinetics of batrachotoxin-modified sodium channels in neuroblastoma cells determined from single-channel measurements.Biophysical Journal 45, 313–22.
Hudson, C. S., Deshpande, S. S. &Albuquerque, E. X. (1984) Consequences of axonal transport blockade by batrachotoxin on mammalian neuromuscular junction. III. An ultrastructural study.Brain Research 296, 319–32.
Jacobs, J. M., Miller, R. H., Whittle, A. &Cavanagh, J. B. (1979) Studies on the early changes in acute isoniazid neuropathy in the rat.Acta neuropathologica (Berlin)47, 85–92.
Karnovsky, M. J. (1965) A formaldehyde-glutaraldehyde fixative of high osmolality for use in electron microscopy.Journal of Cell Biology 27, 137A-138A.
Khodorov, B. I. &Revenko, S. V. (1979) Further analysis of the mechanisms of action of batrachotoxin on the membrane of myelinated nerve.Neuroscience 4, 1315–30.
Krueger, B. K., French, R. J., Blaustein, M. B. &Worley, J. F. III (1982) Incorporation of Ca++ activated K+ channels, from rat brain, into planar iipid bilayers.Biophysical Journal 37, 170a.
Latorre, R. &Miller, C. (1983) Conduction and selectivity in potassium channels.Journal of Membrane Biology 71, 11–30.
Love, S., Cruz-Höfling, M. A. &Duchen, L. W. (1986) Morphological abnormalities in myelinated nerve fibres caused byLeiurus, Centruroides andPhoneutria venoms and their prevention by tetrodotoxin.Quarterly Journal of Experimental Physiology 71, 115–22.
Meves, H., Rubly, N. &Watt, D. D. (1982) Effect of toxins isolated from the venom of the scorpionCentruroides sculptumtus on the Na currents of the node of Ranvier.Pflügers Archiv 393, 56–62.
Moore, G. R. W., Boegman, R. J., Robertson, D. M. &Riopelle, R. J. (1981) Batrachotoxin induced axonal necrosis in peripheral nerves.Brain Research 207, 481–5.
Moore, G. R. W., Robertson, D. M. &Boegman, R. J. (1983) Batrachotoxin induced axonal necrosis followed by regeneration.Brain Research 279, 246–9.
Moore, J. W. (1978) On sodium conductance gates in nerve membranes. InPhysiology and Pathobiology of Axons (edited byWaxman, S. G.), pp. 145–53. New York: Raven Press.
Ochs, S. &Worth, R. (1975) Batrachotoxin block of fast axoplasmic transport in mammalian nerve fibers.Science 187, 1087–9.
Quandt, F. M. &Narahashi, T. (1982) Modification of single Na+ channels by batrachotoxin.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 79, 6732–6.
Raine, C. S. (1982) Differences between the nodes of Ranvier of large and small diameter fibres in the P.N.S.Journal of Neurocytology 11, 935–47.
Robertson, J. D. (1958) Structural alterations in nerve fibers produced by hypotonic and hypertonic solutions.Journal of Biophysical and Biochemical Cytology 4, 349–64.
Shrager, P., Chiu, S. Y. &Ritchie, J. M. (1985) Voltage-dependent sodium and potassium channels in mammalian cultured Schwann cells.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 82, 948–52.
Spencer, P. S., Peterson, E. R., Madrid, A. R. &Raine, C. S. (1973) Effects of thallium salts on neuronal mitochondria in organotypic cord-ganglia-muscle combination cultures.Journal of Cell Biology 58, 79–95.
Waxman, S. G. &Ritchie, J. M. (1985) Organization of ion channels in the myelinated nerve fiber.Science 228, 1502–7.
Worth, R. M. &Ochs, S. (1982) Dependence of batrachotoxin block of axoplasmic transport on sodium.Journal of Neurobiology 13, 537–49.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moore, G.R.W., Boegman, R.J., Robertson, D.M. et al. Acute stages of batrachotoxin-induced neuropathy: a morphologic study of a sodium-channel toxin. J Neurocytol 15, 573–583 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01611858
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01611858