Summary
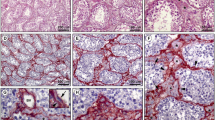
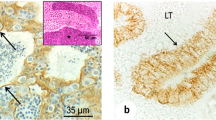
In 11 testes of different developmental stages (from 10-week-old embryos to adult) the cytokeratin and vimentin expression patterns of rete testis and epididymis were investigated immunohistochemically in formaldehyde-fixed paraffin-embedded material. In addition, immunofluorescence microscopy including double immunofluorescence was performed on frozen sections of 3 of these 11 cases. Rete testis and epididymis cells displayed a heterogeneous co-expression of cytokeratin and vimentin. In double immunohistochemistry, differences in distribution of keratin and vimentin intermediate filaments with predominance of cytokeratins in the apical cytoplasmic regions and of vimentin filaments in the basal portions of the cells were found. Cytokeratin expression preceded the appearance of vimentin: cytokeratin was already detectable in 10-week-old embryos, while weak vimentin immunoreactivity was first seen in 12-week-old embryos and became conspicuous in testes around the perinatal period. In testes of children up to 2 years of age the cytoplasmic distribution of cytokeratin and vimentin was more homogeneous. Predominance of the basal cell portions for vimentin and the apical regions for cytokeratin staining were less pronounced than in adult testes. In the proximal and distal parts of the epididymis a different intermediate filament expression pattern was found with a clear predominance of cytokeratin near the rete.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achtstätter T, Moll R, Moore B, Franke WW (1985) Cytokeratin polypeptide patterns of different epithelia of the human male urogenital tract: immunofluorescence and gel electrophoretic studies. J Histochem Cytochem 33:415–426
Benjamin E, Law S, Bobrow LG (1987) Intermediate filaments cytokeratin and vimentin in ovarian sex cord-stromal tumours with correlative studies in adult and fetal ovaries. J Pathol 152:253–263
Byskov AG (1978) The anatomy and ultrastructure of the rete system in the fetal mouse ovary. Biol Reprod 19:720–735
Caselitz J, Osborn M, Seifert G, Weber K (1981) Intermediate-sized filament proteins (prekeratin, vimentin, desmin) in the normal parotid gland and parotid gland tumors: immunofluorescence study. Virchows Arch [A] 393:273–286
Cremer T, Treiss I, Cremer T, Hager D, Franke WW (1981) Characterization of cells of amniotic fluids by immunological identification of intermediate-sized filaments: presence of cells of different tissue origin. Hum Genet 59:373–379
Czernobilsky B, Moll R, Levy R, Franke WW (1985) Co-expression of cytokeratin and vimentin filaments in mesothelial, granulosa and rete ovarii cells of the human ovary. Eur J Cell Biol 37:175–190
Denk H, Franke WW, Dragosics B, Zeiler J (1981) Pathology of cytoskeleton of Mallory bodies (alcoholic hyalin) in murine and human hepatocytes by immunofluorescence microscopy using antibodies to cytokeratin polypeptides from hepatocytes. Hepatology 1:9–20
Domagala W, Halczy-Kowalik L, Weber K, Osborn MC (1988) Coexpression of glial fibrillary acid protein, keratin and vimentin: a unique feature useful in the diagnosis of pleomorphic adenoma of the salivary gland in fine needle aspiration biopsy smears. Acta Cytol 32:403–408
Feitz WFJ, Debruyne FMJ, Ramaekers FCS (1987) Intermediate filament proteins as tissue specific markers in normal and neoplastic testicular tissue. Int J Androl 10:51–56
Franke WW, Schmid E, Osborn M, Weber K (1978) Different intermediate-sized filaments distinguished by immunofluorescence microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci 76:5034–5038
Franke WW, Grund C, Schmid E (1979a) Intermediate-sized filaments present in Sertoli cells are of the vimentin type. Eur J Cell Biol 19:269–275
Franke WW, Schmid E, Breitkreutz D, Lüder M, Boukamp P, Fusenig NE, Osborn M, Weber K (1979b) Simultaneous expression of two different types of intermediate-sized filaments in mouse keratinocytes proliferating in vitro. Differentiation 14:35–50
Franke WW, Schmid E, Winter S, Osborn M, Weber K (1979c) Widespread occurrence of intermediate-sized filaments of the vimentin-type in cultured cells from diverse vertebrates. Exp Cell Res 123:25–46
Franke WW, Grund C, Jackson BW, Illmensee K (1983) Formation of cytoskeletal elements during mouse embryogenesis. IV. Ultrastructure of primary mesenchymal cells and their cell-cell interactions. Differentiation 25:121–141
Gatter KC, Dunnill MS, Heryet A, Mason DY (1987) Human lung tumours: does intermediate filament coexpression correlate with other morphological or immunocytochemical features? Histopathology 11:705–714
Herpers MJHM, Ramaekers FCS, Aldeweireldt J, Moesker O, Sloof J (1986) Co-expression of glial fibrillary acid proteinand vimentin-type intermediate filaments in human astrocytomas. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 70:333–339
Holthöfer H, Miettinen A, Lehto VP, Lehtonen E, Virtanen I (1984) Expression of vimentin and cytokeratin types of intermediate filament proteins in developing and adult human kidney. Lab Invest 50:552–559
Hsu SM, Raine L, Fanger H (1981) Use of avidin-biotin peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem 29:577–580
Kasper M, Goertchen R, Stosiek P, Perry G, Karsten U (1986) Coexistence of cytokeratin, vimentin and neurofilament protein in human choroid plexus. Virchows Arch [A] 410:173–177
Kasper M, Moll R, Stosiek P (1988) Distribution of intermediate filaments in human umbilical cord: triple expression of cytokeratin, vimentin and desmin. Zool Jahrb Anat 117:227–233
Kimura N, Sasano N, Namiki T, Nakazato Y (1989) Coexpression of cytokeratin, neurofilament and vimentin in carcinoid tumors. Virchows Arch [A] 415:69–77
Krepler R, Denk H, Artlieb U, Moll R (1982) Immunocytochemistry of intermediate filament proteins present in pleomorphic adenomas of the human parotid gland: characterization of different cell types in the same tumor. Differentiation 21:191–199
Lane EB, Hogan BLM, Kurkinen M, Garrels JI (1983) Coexpression of vimentin and cytokeratins in parietal endoderm cells of early mouse embryo. Nature 303:701–704
Lehtonen E, Lehto VP, Paasiuvo R, Virtanen I (1983) Parietal and visceral endoderm differ in their expression of intermediate filaments. EMBO J 2:1023–1028
Miettinen M, Lehto VP, Virtanen I (1983) Expression of intermediate filaments in normal ovaries and ovarian epithelial, sex cordstromal, and germinal tumors. Int J Gynecol Pathol 2:64–71
Miettinen M, Virtanen I, Talerman A (1985) Intermediate filament proteins in human testis and testicular germ-cell tumors. Am J Pathol 120:402–410
Moll R, Franke WW, Schiller DL, Geiger B, Krepler R (1982) The catalog of human cytokeratins: patterns of expression in normal epithelia, tumors and cultured cells. Cell 31:11–24
Pitz S, Moll R, Störkel S, Thoenes W (1987) Expression of intermediate filament proteins in subtypes of renal cell carcinomas and in renal oncocytomas: distinction of two classes of renal cell tumors. Lab Invest 56:642–653
Ramaekers FCS, Feitz W, Moesker O, Schaart G, Herman C, Debruyne F, Vooijs GP (1985) Antibodies to cytokeratin and vimentin in testicular tumour diagnosis. Virchows Arch [A] 408:127–142
Regauer S, Franke WW, Virtanen I (1985) Intermediate filament cytoskeleton of amnion epithelium cells and cultured amnion epithelial cells: expression of epidermal cytokeratins in cells of a simple epithelium. J Cell Biol 100:997–1009
Steinert PM, Roop DR (1988) Molecular and cellular biology of intermediate filaments. Annu Rev Biochem 57:593–625
Von Vorstenbosch CJAHV, Colenbrander B, Wensing CJG, Ramaekers FCS, Vooijs GP (1984) Cytoplasmic filaments in fetal and neonatal pig testis. Eur J Cell Biol 34:292–299
Zatloukal K, Denk H, Spurey G, Lackinger E, Preisegger KH, Franke WW (1990) High molecular weight component of Mallory bodies detected by a monoclonal antibody. Lab Invest 62:427–434
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dinges, H.P., Zatloukal, K., Schmid, C. et al. Co-expression of cytokeratin and vimentin filaments in rete testis and epididymis. Vichows Archiv A Pathol Anat 418, 119–127 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01600287
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01600287