Abstract
Heat transfer due to an axisymmetric laminar gas jet impinging onto a flat solid surface of uniform temperature is studied numerically, taking into account the temperature dependence of all fluid physical properties. Numerical solutions are obtained for the jet Reynolds numbers 200–2000, jet mouth-to-surface distances 1–4 times the jet nozzle diameter, and for helium-4, air, and carbon dioxide. Effects of the temperature dependence of the fluid properties are investigated using various kinds of reference temperatures and a viscosity correction method. A method of estimating the values of the local Nusselt number for temperature-dependent fluid from the constant-property solutions is proposed.
Zusammenfassung
Die Wärmeübertragung durch einen auf eine flache Oberfläche gleichförmiger Temperatur achsensymmetrisch auftreffenden Gasstrahl wird numerisch unter Berücksichtigung der Temperaturabhängigkeit der physikalischen Eigenschaften von Fluiden untersucht. Die numerischen Lösungen werden für die Reynoldschen Strahlzahlen von 200 bis 2000, für die Abstände vom Düsenmund zur Oberfläche vom 1- bis 4-fachen des Düsenstrahldurchmessers und für Helium-4, Luft und Kohlendioxyd erhalten. Die Wirkungen der Temperaturabhängigkeiten von Fluideigenschaften werden unter Verwendung verschiedener Bezugstemperaturen und einer Viskositätskorrekturmethode untersucht. Ausgehend von der Lösung für konstante Stoffwerte wird eine Methode zur Schätzung der Werte der lokalen Nusseltzahl für temperaturabhängige Fluide vorgeschlagen.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- c f :
-
local skin friction coefficient, Eq. (7)
- c p :
-
specific heat of fluid at constant pressure
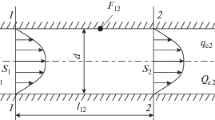
- d :
-
diameter of nozzle
- D :
-
diffusivity of fluid
- h D :
-
local mass transfer coefficient
- h x :
-
local heat transfer coefficient, Eq. (8)
- l :
-
distance between jet mouth and solid surface
- L :
-
dimensionless distance between jet mouth and solid surface, Table 1
- Nu :
-
local Nusselt number for constant property fluid, Eq. (9)
- (Nu) r :
-
local Nusselt number for a fluid of temperature-dependent properties, Eq. (10)
- p :
-
pressure
- P :
-
dimensionless pressure, Table 1
- Pr :
-
Prandt1 number, μc p/λ
- Re :
-
jet Reynolds number, ϱūd/μ
- S :
-
source term in Eq. (5), Table 2
- Sc :
-
Schmidt number of fluid, μ/(ϱD)
- Sh :
-
local Sherwood number for constant property fluid,h D d/D
- St :
-
local Stanton number,Nu/(Re Pr)
- T :
-
temperature
- T :
-
reference temperature
- u, v :
-
velocity components inx- and radial-directions
- U, V :
-
dimensionless velocity components inx- and radial-directions, Table 1
- ū :
-
average velocity at jet mouth
- u 0 :
-
jet velocity at the center of nozzle exit
- x, r :
-
axial and radial coordinates
- X, R :
-
dimensionless axial and radial coordinates, Table 1
- Γ :
-
coefficient of diffusion term, Table 2
- ϑ :
-
dimensionless temperature, Table 1
- λ :
-
thermal conductivity of fluid
- μ :
-
absolute viscosity of fluid
- ϱ :
-
density of fluid
- τ w :
-
wall shear stress, Eq. (7)
- φ :
-
dimensionless variable, Eq. (5)
- f :
-
value at film temperature
- j :
-
value at jet mouth
- w :
-
value at solid surface
- 0:
-
value at stagnation-point
- *:
-
normalized by fluid properties at jet temperature
References
Martin, H.: Heat and mass transfer between impinging gas jets and solid surfaces. In: Adv. in Heat Transfer 13 (ed. Hartnett, J. P.; Irvine, T. F.). New York: Academic Press 1977
Kataoka, K.; Harada, T.; Sahara, R.: Mechanism for enhancement of heat transfer in turbulent impinging jets. In: Current Research in Heat and Mass Transfer (ed. Murthy, M. V. K. et al.) New York: Hemisphere 1988
Goldstein, R. J.; Behbahani, A. I.; Heppelmann, K. K.: Steamwise distribution of recovery factor and the local heat transfer coefficient to an impinging circular air jet. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 29 (1986) 1227–1235
Law, H.-S.; Masliyah, J. H.: Mass transfer due to a confined laminar impinging axisymmetric jet. Ind. Eng. Chem., Fundam. 23 (1984) 446–454
Popiel, Cz. O.; van der Meer, Th. H.; Hoogendoorn, C. J.: Convective heat transfer on a plate in an impinging round hot gas jet of low Reynolds number. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 23 (1980) 1055–1068
Kapur, D. N.; Macleod, N.: The determination of local mass-transfer coefficients by holographic interferometry-I. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 17 (1974) 1151–1162
Sparrow, E. M.; Wong, T. C.: Impingement transfer coefficients due to initially laminar slot jets. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 18 (1975) 597–605
van Heiningen, A. R. P.; Mujumdar, A. S.; Douglas, W. J. M.: Numerical prediction of the flow field and impingement heat transfer caused by a laminar slot jet. ASME J. of Heat Transfer 98 (1976) 654–658
Sholtz, M. T.; Trass, O.: Mass transfer in a non uniform impinging jet, Part 1 & 2. AIChE J. 16 (1970) 82–96
Deshpande, M. D.; Vaishnav, R. N.: Submerged laminar jet impingement on a plane. J. Fluid Mech. 114 (1982) 213–236
Saad, N. R.; Douglas, W. J. M; Mujumdar, A. S.: Prediction of heat transfer under an axisymmetric laminar impinging jet. Ind. Eng. Chem., Fundam. 16 (1977) 148–154
Kakaç, S.: The effect of temperature-dependent fluid properties on convective heat transfer. In: Handbook of single-phase convective heat transfer. New York: John Wiley 1987
Aihara, T.; Maruyama, S.; Choi, J. S.: Laminar free convection with variable fluid properties in vertical ducts of different cross-sectional shapes. Proc. 8th Int. Heat Transfer Conf. (1986) 1581–1586
Aihara, T.; Maruyama, S.: Laminar free convective heat transfer in vertical uniform-heat-flux ducts (numerical solutions with constant/temperature-dependent fluid properties). Heat Transfer Japanese Research 15 (1986) 69–86
Patankar, S. V.: A calculation procedure for two-dimensional elliptic situations. Num. Heat Transfer 4 (1981) 409–425
Welch, J. E.; Harlow, F. H.; Shannon, J. P.; Daly, B. J.: The MAC method: A computing technique for solving viscous, incompressible, transient fluid-flow problems involving free surfaces. Report LA-3425: Los Alamos Scientific Lab., Univ. of Calif. 1966
Patankar, S. V.: Numerical heat transfer and fluid flow. New York: McGraw-Hill 1980
Pun, W. M.; Spalding, D. B.: A general computer program for two-dimensional elliptic flows. Report No. HTS/76/2: Mech. Engrg. Dept., Imperial College 1977
Scholtz, M. T.; Trass, O.: Mass transfer in laminar radial wall jet. AIChE J. 9 (1963) 548–554
Publication committe of Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers: JSME Data Book: The thermophysical properties of fluids. Tokyo: JSME 1982
PROPATH Group: PROPATH: A program package for thermophysical property, ver. 3.1. Fukuoka: Computer Center of Kyushu Univ. 1986
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aihara, T., Kim, J.K. & Maruyama, S. Effects of temperature-dependent fluid properties on heat transfer due to an axisymmetric impinging gas jet normal to a flat surface. Wärme- und Stoffübertragung 25, 145–153 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01590145
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01590145