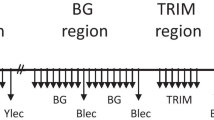
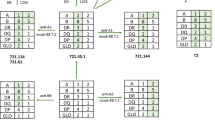
Abstract
At least four genes regulate the primary immune response to ovalbumin in mice. The ability to be sensitized to transfer delayed type hypersensitivity to ovalbumin is controlled by two genes. One gene,OVA-β, is linked to theH-2 complex and maps to the left ofI-E. The linkage of the other gene,OVA-Bg1, has not been determined, but it segregates independently of theLy M locus, of the heavy chain allotype genes and of certain genes controlling coat color. At least two genes regulate the ability to respond with a primary antiovalbumin antibody response. One gene,OVA-α, is linked to theH-2 complex and maps to the right ofI-E. Discordance of the minimum dose of antigen needed to elicit delayed type hypersensitivity response and antibody suggests that non-H-2 gene(s) regulating the primary antibody response are different fromOVA-Bg1.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BSA:
-
bovine serum albumin
- DTH:
-
delayed type hypersensitivity
- H-2 :
-
major histocompatibility complex of mouse
- Ir :
-
gene — immune response gene
- OVA:
-
ovalbumin
- SRBC:
-
sheep red blood cells
References
Amerding, D., Katz, D. H., and Benacerraf, B.: Immune response genes in inbred rats. II. Segregration studies of GT and GA genes and their linkage to the major histocompatibility locus.Immunogenetics 1:340–351, 1974
Ando, I. and Fachet, J.: Genetic control of the primary and secondary IgG response to SRBC erythrocytes in mice.Scand. J. Immunol. 6:601–606, 1977
Benacerraf, B. and Dorf, M. E.: Genetic control of specific immune responses and immune suppressions by I-region genes.Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol. 41:465–475, 1976
Benacerraf, B. and Katz, D. H.: The histocompatibility-linked immune response genes.Adv. Cancer Res. 21:2–173, 1975
Benedict, A. A., Pollard, L. W., and Mauer, P. H.: Genetic control of immune responses in chickens. II. Responses to methylated bovine serum albuminpoly (GLU60 ALA30 Tyr10) aggregates.Immunogenetics 4:199–204, 1977
Biozzi, G., Stiffel, C., Mouton, D., Bouthillier, Y., and Decreusefond, C.: Cytodynamics of the immune response of mice genetically selected for “high” and “low” antibody synthesis.J. Exp. Med. 135:1071–1094, 1972
Chiorazzi, N., Fox, D. A., and Katz, D. H.: Hapten-specific IgE antibody response in mice. VII. Conversion of IgE “non-responders” strains to IgE “responder” strains by elimination of T cell activity.J. Immunol. 118:48–54, 1977
Dickler, H. B., Ahmed, A., and Sachs, D.: B lymphocyte Fc-receptor-associated non H-2 antigens are determined by a single polymorphic locus which is linked to Mls locus.J. Exp. Med. 146:1678–1691, 1977
Dorf, M. E., Balmer, H., de Grott, L., and Benacerraf, B.: Histocompatibility-linked immune response genes in Rhesus monkey.Transplant. Proc. 6:119–123, 1974a
Dorf, M. E., Dunham, E. K., Johnson, J. P., and Benacerraf, B.: Genetic control of the immune response: The effect of non-H-2 linked genes on antibody production.J. Immunol. 112:1329–1336, 1974b
Duncan, W. B. and Streilein, J. W.: Analysis of the major histocompatibility complex in Syrian hamsters. I. Skin graft rejection, graft-versus host reactions and immune response genes in inbred strains.Transplantation 25:12–16, 1978
Dunham, E. K., Dorf, M. E., Shreffler, D. C., and Benacerraf, B.: Mapping the H-2 linked genes governing, respectively, the immune response to a glutamic acid-alanine-tyrosine copolymer and to limiting doses of ovalbumin.J. Immunol. 111:1621–1625, 1973
Eichmann, K.: Genetic control of antibody specificity in the mouse.Immunogenetics 2:491–506, 1975
Fachet, J. and Ando, I.: Genetic control of contact sensitivity to oxazolone in inbred, H-2 congenic and intra-H-2 recombinant strains.Eur. J. Immunol. 7:223–226, 1977
Geczy, A. F. and De Weck, A. L.: Molecular basis of T cell dependent genetic control of the immune response in the guinea pig.Prog. Allergy 22:147–213, 1977
Grumet, F. C.: Genetic control of the immune response. A selective defect in immunologic (IgG) memory in non-responder mice.J. Exp. Med. 110:110–125, 1972
Hart, D. A., Wang, A., Pawlak, L. L., and Nisonoff, A.: Suppression of idiotypic specificities in adult mice by administration of antiidiotypic antibody.J. Exp. Med. 135:1293–1300, 1972
Herzenberg, L. A., Okumura, K., Cantor, H., Sato, V. L., Shen, F. W., Boyse, E. A., and Herzenberg, L. A.: T-cell regulation of antibody response: Demonstration of allotype-specific helper T cells and their specific removal by suppressor T cells.J. Exp. Med. 144:330–344, 1976
Klein, J.:Biology of the Mouse Histocompatibility-2 Complex. Springer Verlag, New York, 1975
Kolsch, E. and Falkenberg, F. W.: Genetic control of the immune response to phage Fd IV complementation between H-2 linked Ir genes.J. Immunol. 119:2214–2219, 1977
Lubet, M. T.: Regulation of the immune response to ovalbumin in mice. Doctoral dissertation, University of Texas Health Science Center at Dallas, 1978
Lubet, M. T. and Kettman, J. R.: Primary antibody and delayed hypersensitivity response of mice to ovalbumin.Immunogenetics 6:69–79, 1978
Lubet, M. T. and Kettman, J. R.: Regulation of the primary immune response to ovalbumin in mice: Activation of T cells mediating delayed-type hypersensitivity, non-specific help, and specific help and their sensitivity to radiation.J. Immunol. 123:426–433, 1979
Marsh, D. G., Bias, W. B., and Hsu, S. H.: Association of HL-A7 and cross-reacting group with a specific reagenic antibody response in allergic man.Science 179:691–693, 1973
Miller, J. F. A. P., Vadas, M. A., Whitelaw, A., Gamble, J., and Bernard, C.: Histocompatibility linked immune responses and restrictions imposed on sensitized lymphocytes.J. Exp. Med. 145:1623–1628, 1977
Mozes, E.: Expression of immune response (Ir) genes in T and B cells.Immunogenetics 2:397–410, 1975
Paul, W. E. and Benacerraf, B.: Functional specificity of thymus dependent lymphocytes.Science 195:1293–1300, 1977
Sachs, D. H., Berzofsky, J. A., Fathman, C. G., Pisetsky, D. S., Schechter, A. N., and Schwartz, R. N.: The immune response to staphylococcal nuclease: A probe of cellular and humoral antigen specific receptors.Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol. 41:295–306, 1976
Schirrmacher, V., Rubin, B., Pross, H., and Wigzell, H.: Cytotoxic immune cells with specificity for defined soluble antigens. IV. Antibody as mediator of specific cytotoxicity.J. Exp. Med. 139:93–106, 1974
Schmitt-Verhulst, A.-M., Mozes, E., and Sela, M.: Genetic control of the immune response to a thymus independent synthetic polypeptide.Immunogenetics 1:357–369, 1974
Schultz, L. E. and Bailey, D. W.: Genetic control of contact sensitivity in mice: Effect of H-2 and non-H-2 loci.Immunogenetics 1:570–583, 1975
Seman, M., Chevalien, F., and Stanislawski, M.: Evidence for independent genetic regulation of the expression of different antibody classes of anti-sheep red blood cell responses.Eur. J. Immunol. 8:262–268, 1978
Smith, S. M., Ness, D. B., Talcott, J. A., and Grumet, F. C.: Genetic control of IgM responses to (T, G)-A--L H-2 and Ig-1 linkage.Immunogenetics 4:221–232, 1977
Strosberg, D.: Inherited control mechanisms in mammalian gene expression.In E. Sercarz, L. Herzenberg and C. F. Fox (eds.):Immune System: Genetics and Regulation, pp. 115–123. Academic Press Inc., New York, 1977
Tonkonogy, S. L. and Winn, H. J.: A new alloantigenic system associated with the Mls locus in the mouse.J. Immunol. 116:835–841, 1976
Vaz, N. M., Phillips-Quagliata, J. M., Levine, B. B., and Vaz, E. M.: H-2 linked genetic control of immune responsiveness to ovalbumin and ovomucoid.J. Exp. Med. 134:1335–1348, 1971
Vaz, N. M., de Souz, C. M., and Maia, L. C. S.: Genetic control of immune responsiveness in mice. Responsiveness to ovalbumin in (C57BL × DBA/2)F1 mice.Int. Arch. Allergy Appl. Immunol. 46:275–279, 1974
Zinkernagel, R. M.: H-2 restriction of virus-specific T-cell mediated effector functions in vivo. II. Adoptive transfer of delayed type hypersensitivity to murine lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus is restricted by the K and D region.J. Exp. Med. 144:776–787, 1976
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lubet, M.T., Kettman, J.R. Multigenic regulation of the primary immune response to ovalbumin in mice. Immunogenetics 9, 45–55 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01570392
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01570392