Abstract
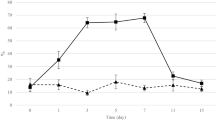
The effect of ampicillin, clindamycin and metronidazole upon the 7α-dehydroxylation of cholic acid by the microflora in the intestine was tested in healthy subjects. Clindamycin gave a significant decrease in the 7α-dehydroxylation. With the other two antibiotics, no significant changes were seen.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Aries V, Hill MJ. (1970) Degradation of steroids by intestinal bacteria. II. Enzymes catalysing the oxidoreduction of the 3-, 7- and 12-hydroxyl groups in cholic acid, and the dehydroxylation of the 7-hydroxyl group. Biochim Biophys Acta 202:535–543
Bokkenheuser V, Hoshita T, Mosbach EH (1969) Bacterial 7-dehydroxylation of cholic acid and allocholic acid. J Lipid Res 10:421–426
Canzi E, Ceccarelli A, Ferrari A, Fesce E, Pacini N (1985) Effect of lincomycin treatment on intestinal microflora composition and its bile-acid-metabolizing activity. Curr Microbiol 12:1–4
Edenharder R, Slemrova J (1976) Die Bedeutung des bakteriellen Steroidabbaus für die Ätiologie des Dickdarmkrebses. IV. Spaltung von Glykocholsäure, Oxydation und Reduktion von Cholsäure durch saccharolytische Bacteroides-Arten. Zbl Bakt Hyg I, Abt Orig B 162:350–373
Ferrari A, Beretta L (1977) Activity on bile acids of aClostridium bifermentans cell-free extract. FEBS Lett 75:163–165
Ferrari A, Pacini N, Canzi E (1980) A note on bile acids transformations by strains of Bifidobacterium. J Appl Bacteriol 49:193–197
Gustafsson BE, Midtvedt T, Norman A (1966) Isolated fecal microorganisms capable of 7α-dehydroxylating bile acids. J. Exp Med 123:413–432
Gustafsson BE, Gustafsson J-Å, Carlstedt-Duke B (1977) Prolonged induction of germfree bile acid pattern in conventional rats by antibiotics. Acta Med Scand 201:155–160
Hayakawa S, Hattori T (1970) 7α-dehydroxylation of cholic acid byClostridium bifermentans strain ATCC 9714 andClostridium sordellii strain NCIB 6929. FEBS Lett 6:131–133
Hill MJ (1985) Clostridia and human colorectal cancer. In: Borriello P (ed) Clostridia in gastrointestinal disease. Florida: CRC Press, pp 165–176
Hill MJ, Drasar BS, Aries V, Crowther JS, Hawksworth G, Williams REO (1971) Bacteria and aetiology of cancer of large bowel. Lancet 1:95–100
Hirano S, Nakama R, Tamaki M, Masuda N, Oda H (1981) Isolation and characterization of thirteen intestinal microorganisms capable of 7α-dehydroxylating bile acids. Appl Environ Microbiol 41:737–745
Hofmann AF (1977) Bile acids, diarrhea and antibiotics: data, speculation and a unifying hypothesis. J Infect Dis 135 suppl: S126-S132
Hylemon PB, Glass TL (1983) Biotransformation of bile acids and cholesterol by the intestinal microflora. In: Hentges DJ (ed) Human intestinal microflora in health and disease. New York: Academic Press, pp 189–213
Hylemon PB, Cacciapuoti AF, White BA, Whitehead TR, Fricke RJ (1980) 7α-Dehydroxylation of cholic acid by cell extracts ofEubacterium species VPI 12708. Am J Clin Nutr 33:2507–2510
Midtvedt T (1967) Properties of anaerobic gram-prositive rods capable of 7α-dehydroxylating bile acids. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand 71:147–160
Midtvedt T (1974) Microbial bile acid transformation. Am J Clin Nutr 27:1341–1347
Midtvedt T, Carlstedt-Duke B, Høverstad T, Lingaas E, Norin KE, Saxerholt H, Steinbakk M (1986) Influence of peroral antibiotics upon the biotransformatory activity of the intestinal microflora in healthy subjects. Eur J Clin Invest 16:11–17
Shaw R, Elliott WH (1978) Bile acids. LV. 2,2-dimethoxypropane: an esterifying agent preferred to diazomethane for chenodeoxycholic acid. J Lipid Res 19:783–787
Stellwag EJ, Hylemon PB (1979) 7α-dehydroxylation of cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid byClostridium leptum. J. Lipid Res 20:325–333
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andréasson, K., Norin, K.E. & Midtvedt, T. Influence of ampicillin, clindamycin or metronidazole upon the 7α-dehydroxylation of bile acids in the human intestine. Current Microbiology 16, 329–331 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01568540
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01568540