Abstract
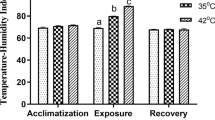
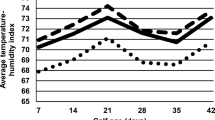
Thyroid gland activity, using the ET3-131I-U/100% Ht method, was determined on: (a) the same 12 Friesian and 8 Buffalo dry nonpregnant cows in winter (14.2°C, 58% RH), spring 23.4°C, 47% RH) and summer (26.7°C, 65% RH), keeping feed and management the same for all animals; (b) 3 Friesian and 3 Buffalo female calves exposed successively to the natural outdoor climate of 14.6°C, 53% RH, a controlled climate of 29.0°C, 50% RH and a controlled climate of 42.0°C, 50% RH for 3 days at each exposure. ET3U was higher in winter than spring in Friesians (p < 0.01), not Buffaloes; and in winter than in summer in both species (p < 0.01). Values in spring were higher than in summer in both species (p < 0.01). The per cent decline in ET3U was more pronounced at high than at low ambient temperature and relative humidity. The thyroid activity at high ambient temperature took at least 72 hours to reach minimum level. Buffaloes showed less decline than Friesians from winter to summer (9.4% for Buffaloes and 23.7% for Friesians) and from 14.6° to 29.0°C (4.29% for Buffaloes and 10.31% for Friesians), suggesting that Buffaloes are more heat tolerant than Friesians. Within each species, a greater variation in the percentage decline in thyroid activity was observed in Friesians than Buffaloes.
Zusammenfassung
Die Schilddrüsenaktivität wurde untersucht von (a) 12 friesischen Rindern und 8 Wasserbüffeln (alle trocken und nicht trächtig) im Winter (14,2°C, 58% RF), Frühling (23,4°C, 47% RF) und Sommer (26.7°C, 65% RF) und von (b) 3 friesischen und 3 weiblichen Büffelkälbern, die jeweils 3 Tage in natürlichem Klima aussen bei 14,4°C, 53% RF und in künstlichem Klima bei 29,0° und 42.0°C, 50% RF, lebten. Futter und Haltung war bei allen Tieren gleich. Bestimmt wurde die Erythrozyten131Jod-trijodthyronin-Aufnahme, korrigiert über den Hämatokrit (ET3U). Die ET3U war bei beiden Tierarten im Winter höher als im Frühling (p < 0.01) und Sommer. Die Frühlingswerte waren höher als die Sommerwerte (p < 0.01). Die prozentuale Senkung der ET3U war deutlicher bei hoher als bei niedriger Temperatur und relativer Feuchtigkeit. Die Minimalwerte wurden frühestens nach 72 Stunden erreicht. Bei den Wasserbüffeln war die Senkung der ET3U zwischen Winter und Sommer geringer als bei den friesischen Rindern, als Zeichen dafür, dass sie Hitze besser ertragen.
Resume
On a examiné l'activité de la glande thyroïde de bovins en utilisant la méthode ET3-131IU/100% HT. Le premier essai concernait 12 vaches frisonnes et 8 buffles femelles toutes sèches et non portantes. Ces animaux ont été gardés dans des conditions identiques pour tous (étable, alimentation et soins) en hiver (14,2°C et 58% HR), au printemps (23,4°C et 47% HR) et en été (26,7°C et 65% HR). Dans un second essai, 3 génisses frisonnes et 3 jeunes buffles femelles furent d'abord gardés 3 jours à l'extérieur (14,6°C et 53% HR), puis placées 3 jours en climat contrôlé (29,0°C et 50% HR, respectivement 42,0°C et 50% HR). La valeur de ET3U est plus élevée en hiver qu'au printemps et plus élevée en hiver qu'en été (p < 0,01) et cela pour les deux races. Les valeurs du printemps dépassent celles de l'été (p < 0,01) dans les 2 cas également. Le taux d'abaissement de ET3U a été plus accentué par températures et humidités élevées que par températures et humidités basses. Les valeurs minimales ne furent atteintes que 72 heures au moins après le changement de climat. Les buffles présentent un abaissement moins prononcé de l'activité thyroïdienne que les frisonnes et cela aussi bien de l'hiver à l'été (9,4% pour les buffles et 23,7% pour les frisonnes) que de 14,6° à 29,0°C (4,29% pour les buffles et 10,31% pour les frisonnes). On en peut conclure que les buffles présentent une plus grande tolérance à la chaleur que les frisonnes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ASPLUND, R.O., McLAREN, G.A., HENDERSON, H.O. and PORTERFIELD, I.D. (1959): Unusual magnitude and variation of plasma protein bound iodine values of dairy cattle. J.Dairy Sci., 42: 1718–1723.
BLINCOE, C. and BRODY, S. (1955): The influence of ambient temperature, air velocity, radiation intensity and starvation on thyroid gland activity and iodide metabolism in cattle. Mo. Agric. Exp. Sta. Res. Bull. 576.
BRANTON, C., GANGWAR, P.C., BANERJEE, M.R., BREIDENSTEIN, C. and GUIDRY, A.J. (1964): Adaptive responses of Holstein heifers to controlled and natural climatic conditions. J.Dairy Sci., 47: 691.
HAMOLOSKY, M.W., STEIN, M. and FREEDBERG, A.S. (1957): The thyroid hormone-plasma protein complex in man. II. A new in vitro method for study of uptake of labelled hormone components by human erythrocytes. J.clin.Endocr., 17: 33–44.
JOHNSON, H.D. and KAMAL, T.H. (1958): Effect of rising environmental temperature (35° – 90°F) on thyroxine-I-131 utilization of young dairy calves. J.Animal Sci., 17: 1228.
JOHNSON, H.D. and KIBLER, H.H. (1963): Temperature humidity effects on thyroxine-I-131 disappearance rates in cattle. J.appl.Physiol., 18: 73–76.
JOHNSON, H.D. and RAGSDALE, A.C. (1960): The effect of rising environmental temperature (35°–95°F) on thyroid I-131 release rate of Holstein, Brown Swiss and Jersey heifers. J.Agric.Sci., 54: 421–426.
KAMAL, T.H. (1964): Physiological reactions of cows to hot environmental conditions. FAO/IAEA Symposium on Radioisotopes in Animal Nutrition and Physiology. Prague, November 23–27.
KAMAL, T.H., JOHNSON, H.D. and RAGSDALE, A.C. (1959): The effect of long exposure of environmental temperature of 50° and 80°F on glutathione, BEI-131, and growth rate of dairy calves. Mo.Agric.Exp.Sta.Res.Bull. 710.
KAMAL, T.H. and SEIF, S.M. (1969): Effect of natural and controlled climates of the Sahara on virtual tritium space in Friesians and Water Buffaloes. J.Dairy Sci., 52: 1657–1663.
LEWIS, R.C., LODGE, J.R. and REINEKE, E.P. (1957): The thyroxine secretion rate of dairy calves estimated by the extrapolation technique. J.Animal Sci., 16: 1063.
LEWIS, R.C. and RALSTON, N.P. (1953): Protein-bound iodine levels in dairy cattle plasma. J.Dairy Sci., 36: 33–38.
LODGE, J.R., LEWIS, R.C. and REINEKE, E.P. (1957): Estimating the thyroid activity of dairy heifers. J.Dairy Sci., 40: 209–215.
LODGE, J.R., LEWIS, R.C., REINEKE, E.P. and McGILLIARD, L.D. (1958): Thyroidal uptake of I-131 by dairy calves. J. Dairy Sci., 41: 641–646.
MEITES, J. and WOLTERINK, L.F. (1950): Uptake of radioactive iodine by the thyroids of underfed rats. Science, 111: 175–176.
MORRISON, F.E. (1945): Feeds and Feeding. 22nd Ed., Itacha, N.Y., Morrison Publishing House, 1027–1034.
MOUSTGAARD, J., NIELSEN, P.B. and SORENSEN, P.H. (1959): Roy. Vet. Agric.Coll.Sterility Res.Inst.Ann.Rep. 173.
PIPES, G.W., BAUMAN, T.R., BROOKS, J.R., COMFORT, J.E. and TURNER, C.W. (1963): Effect of season, sex and breed on the thyroxine secretion rate of beef cattle and a comparison with dairy cattle. J.Animal Sci., 22: 476–480.
PREMACHANDRA, B.N., PIPES, G.W. and TURNER, C.W. (1958): Variation in the thyroxine secretion rate of cattle. J.Dairy Sci., 41: 1609–1615.
PREMACHANDRA, B.N., PIPES, G.W. and TURNER, C.W. (1959): Thyroid function of mono- and dizygous cattle twins. J.Dairy Sci., 42: 1346–1350.
SATO, M., SHIMIZU, H. and TAKEUCHI, S. (1960): On the thyroid gland activity of ruminant. I. The seasonal changes of serum protein-bound iodine in the dairy cattle. Tokohu J.Agric.Res., 11: 329–339.
SNEDECOR, J.W. (1962): Statistical methods. 5th Ed., Iowa State College Press, Ames, Iowa, Pp. 85.
SWETT, W.W., MATHEWS, C.A. and FOHRMAN, M.H. (1955): Weight of thyroid in dairy cows from different geographical areas within the United States. Tech.Bull. US Dept.Agric. No. 1123.
SZABO, K.T., MIXNER, J.P. and MATHER, R.E. (1963): The in vitro uptake of radioactive triiodothyronine by red blood cells as a measure of thyroidal activity in dairy cattle. J. Dairy Sci., 46: 1175.
THOMPSON, R.D., JOHNSTON, J.E., BREIDENSTEIN, C.P., GUIDRY, A.J. and BANERJEE, M.R. (1963): Effect of hot conditions on adrenal cortical, thyroidal and other metabolic responses of dairy heifers. J.Dairy Sci., 46: 227–231.
YENS, W. (1963): In vitro studies of thyroid function with erythrocyte uptake of I-131-labelled triiodothyronine. Acta. Endocr. (Kbh.),42: 1, Suppl. 76.
YOUSEF, M.K. and JOHNSON, H.D. (1964): Effect of thyroxine and high environmental temperature on some blood constituents of dairy cattle. J.Dairy Sci., 47: 693.
YOUSEF, M.K. and JOHNSON, H.D. (1965): Time course of thyroxine I-131 disappearance rates in cattle during exposure to hot and cold environments. Life Sciences, 4: 1531–1543.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamal, T.H., Ibrahim, I.I. The effect of the natural climate of the sahara and controlled climate on thyroid gland activity in friesian cattle and water buffaloes. Int J Biometeorol 13, 287–294 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01553036
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01553036