Summary
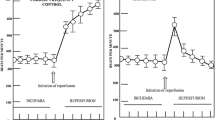
In order to examine the question, whether improved digitalis tolerance by Spirolactone may be partially a result of antagonism on myocardial potassium balance, 6 patients without clinical signs of heart failure were given 400 mg, 3 were given 200 or 300 mg Spirolactone orally daily and 6 patients received placebo during a 5 to 7 days period. During cardiac catheterization hemodynamics and serum potassium concentrations were determined repeatedly prior to and following intravenous administration of 0,375 to 0,625 mg Strophanthin. Injection of Strophanthin resulted in a significant drop in left ventricular enddiastolic pressure and a rise indp/dt max. In the control group a significant increase in arterial and coronary sinus potassium concentration was observed. Myocardial potassium balance was definitely negative from the third to the eighth minute. Values in the group receiving Spirolactone did not differ significantly from the placebo group. It is suggested that therapeutic doses of Strophanthin result in a loss of potassium from the myocardium by inhibition of the Na+, K+ membrane ATPase not influenced by pretreatment with Spirolactone.
Zusammenfassung
Zur Prüfung der Frage, ob eine Verbesserung der Digitalistoleranz unter Spirolactone durch eine gegensinnige Beeinflussung der myokardialen Kaliumbilanz mitbedingt wird, erhitelen 6 klinisch nicht kardial dekompensierte Patienten 5–7 Tage hindurch täglich 400 mg, 3 Patienten 200 bzw. 300 mg Spirolactone oral und 6 Patienten Placebo. Im Rahmen eines diagnostischen Herzkatheterismus wurden hämodynamische Messungen und multiple Serumkaliumbestimmungen vor und nach Gabe von 0,375–0,625 mg Strophanthin intravenös durchgeführt. Nach Strophanthin kam es zu einem signifikanten Abfall des enddiastolischen Drucks und zu einem Anstieg desdp/dt max im linken Ventrikel. In der Kontrollgruppe war ein signifikanter Anstieg der Kaliumspiegel im arteriellen und Koronarsinusblut zu beobachten, es bestand eine negative myokardiale Kaliumbilanz von der 3. bis zur 8. min nach Strophanthin. Die entsprechenden Werte nach Spirolactonevorbehandlung unterschieden sich von jenen der Kontrollgruppe nicht signifikant. Es wird geschlossen, daß nicht toxische Dosen von Strophanthin beim Menschen durch Hemmung der Natrium-Kalium-Membran ATPase zu einem myokardialen Kaliumverlust führen, der durch orale Vorbehandlung mit Spirolactone nicht sicher verändert wird.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Abshagen, U.: Effects of pretreatment with spirolactone on pharmacokinetics of 4′″-methyldigoxin in rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol.278, 91 (1973)
Akera, T., Larsen, F.S., Brody, T.M.: The effect of ouabain on sodium- and potassium-activated adenosine triphospatase from the hearts of several mammalian species. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.170, 17 (1969)
Baskin, S.I., Akera, T., Puckett, C.R., Brody, S.L., Brody, T.M.: Effects of potassium caurenoate on cardiac functions and (Na++K+) — activated ATPase. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol.143, 495 (1973)
Bliss, H.A., Adolph, R.J.: Effect of experimental congestive heart failure and acetyl strophanthidin on myocardial electrolyte and water content. Circ. Res.13, 207 (1963)
Brennan, F.J., McCans, J.L., Chiong, M.A., Parker, J.O.: Effects of ouabain on myocardial potassium and sodium balance in man. Circulation14, 107 (1972)
Buck, S.H., Lage, G.L.: Possible mechanism of the prevention of digitoxin toxicity by spirolactone in the mouse. Arch. int. Pharmacodyn.189, 192 (1971)
Calhoun, J.A., Harrison, T.R.: Studies in congestive heart failure: IX. The effect of digitalis on the potassium content of the cardiac muscle of dogs. J. clin. Invest.10, 139 (1931)
Cattell, M., Goodell, H.: On the mechanism of the action of digitalis glucosides on muscle. Science86, 106 (1937)
Clarke, N.E., Mosher, R.E.: The water and electrolyte content of the human heart in congestive heart failure with and without digitalization. Circulation5, 907 (1952)
Dittrich, H.: Untersuchungen über den Kalium-, Natrium- und Wassergehalt an Leichenherzen bei Herzinsuffizienz und Myokardinfarkt. Beitr. path. Anat.121, 426 (1959)
Glynn, I.M.: The action of cardiac glycosides on sodium and potassium movements in human red cells. J. Physiol.136, 148 (1957)
Glynn, I.M.: The action of cardiac glycosides on ion movements. Pharmacol. Rev.16, 381 (1964)
Gonlubol, F., Siegel, A., Bing, R.J.: Effect of a cardiac glycoside (Cedilanid) on the sodium ant potassium balance of the human heart. Circ. Res.4, 298 (1956)
Harrison, T.R., Pilcher, C., Ewing, G.: Studies in congestive heart failure. IV. The potassium content of skeletal and cardiac muscle. J. clin. Invest.8, 325 (1930)
Hochrein, H.: Experimentelle und klinische Gesichtspunkte zur Digitaliswirkung. Münch. med. Wschr.111, 1294 (1969)
Johnson, J.A.: Influence of ouabain, strophanthidin and dihydrostrophanthidin on sodium and potassium transport in frog sartorii. Amer. J. Physiol.187, 328 (1956)
Klein, W.: Elektrolytprobleme bei chronischen Herzerkrankungen unter Digitalis- und Diuretikatherapie. Vortrag: Symposium: „Langzeittherapie mit Diuretika unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der Elektrolytverschiebungen“ Wien, 1974
Krämer, K.D., Ghabussi, P., Hochrein, H.: Klinische Prüfung der subtoxischen Vollwirk- und Erhaltungsdosis von Digoxin unter dem Einfluß von Spironolaktone. Arzneimittel- Forsch. (Drug Res.)23, 508 (1973)
Ku, D., Akera, A., Pew, C.L., Brody, T.M.: Cardiac glycosides: Correlations among Na+, K+-ATPase, sodium pump and contractility in the guinea pig heart. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol.285, 185 (1974)
Kukovetz, W.R.: Kalziumabhängige Funktionen des Herzmuskels. Wien. klin. Wschr.83, 616 (1971)
Lown, B., Whipple, G.H., Shoemaker, W.C., Craig, L.C., Levine, S.A.: Role of the liver in digitalis-induced electrolyte shifts. Circulation18, 753 (1958)
Lüllmann, H., Holland, W.: Influence of ouabain on an exchangeable calcium fraction, contractile force, and resting tension of guinea-pig atria. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.137, 186 (1962)
Mason, D.T., Braunwald, E.: Digitalis: New facts about an old drug. Amer. J. Cardiol.22, 151 (1968)
Nielsen, C.J., Lucchesi, B.R.: Inability of potassium canrenoate to convert experimentally induced ouabain arrhythmias in the canine heart. Circ. Res.84, 635 (1974)
Paimer, R.F., Posey, V.A.: Ion effects on calcium accumulation by cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. J. Gen. Physiol.50, 2085 (1967)
Regan, T.J., Christenson, R.C., Wada, T., Talmers, F.N., Hellems, H.K.: Myocardial response to acetyl strophantidin in congestive heart failure: A study of electrolytes and carbohydrate substrates. J. clin. Invest.38, 306 (1959)
Repke, K., Portius, H.J.: Über die Identität der Ionenpumpen-ATPase in der Zellmembran des Herzmuskels mit einem Digitalis-Rezeptorenzym. Experientia19, 452 (1963)
Savoie, L., Krajny, M., Kleiman, B.: Digitoxin induced cardiac necrosis and its inhibition. Cardiologia54, 287 (1969)
Schatzmann, H.J.: Herzglykoside als Hemmstoffe für den aktiven Kalium-und Natriumtransport durch die Erythrocytenmembran. Helv. physiol. Pharmac. Acta11, 346 (1953)
Schaumann, W., Koch, K., Mattern, H.R.: Extarenal actions of Aldosterone antagonists in Guinea pigs. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol.279, 9 (1973)
Schröder, R., Schüren, K.P., Biamino, Meyer, V., Sadée, W.: Positiv-inotrope Herzwirkung von Aldadien-Kalium (Aldactone pro injectione). Klin. Wschr.49, 1093 (1971)
Schwartz, A., Allen, J.C., Harigaya, S.: Possible involvement of cardiac Na+, K+-adenosine triphosphatase in the mechanism of action of cardiac glycosides. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.168, 31 (1969)
Selye, H., Krajny, M., Savoie, L.: Digitoxin poisoning: Prevention by spironolactone. Science164, 842 (1969)
Selye, H., Mandeville, R., Yeghiayan, E.: On the catatoxic effect of antimineralcorticoids. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol.266, 34 (1970)
Selye, H., Mécs, I., Tamura, T.: Effect of spironolactone and norbolethone on the toxicity of digitalis compounds in the rat. Brit. J. Pharmacol.37, 485 (1969)
Strauer, B.E.: The influence of the aldosterone-antagonist spironolactone on myocardial contractility. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. Ther.201, 59 (1973)
Tourniaire, A., Blum, Guyot, R., Madignier, M.: L'hyperexcitabilité myocardique des cardiopathies decompensées. Effet de la Spironolactone. Sem. Hôp. Paris45, 1388 (1969/II)
Vöhringer, H.F., Weller, L., Rietbrock, N.: Influence of spironolactone pretreatment on pharmacokinetics and metabolism of digitoxin in rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol.287, 129 (1975)
Wiener, L., Dwyer, E.M., Cox, J.W.: Left ventricular hemodynamics in exercise-induced angina pectoris. Circulation38, 240 (1968)
Yeh, B.K., Saha, A.K., Sung, P.K., Samet, P.: Soldactone (Sc-14, 266): Suppression of digitalis-induced arrhythmias. Fed. Proc.30, 228 (1971)
Yeh, B.K., Sung, P.K., Saha, A.K.: Use of potassium-canrenoate to suppress ouabain-induced ventricular arrhythmias in dogs. Circ. Res.31, 915 (1972)
Yeh, B.K., Lazzara, R.: Reversal of ouabain-induced electrophysiological effects by potassium canrenoate in canine Purkinje fibers. Circ. Res.32, 501 (1973)
Yeh, B.K., Sung, P.K., Lazzara, R.: The specifity of potassium canrenoate. A steroidal antidysrhythmic drug. 7th World Cong. of Cardiol. 188 (1974)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Slany, J., Mösslacher, H. Einfluß von Spirolactone auf die myokardiale Kaliumbilanz unter Strophanthin beim Menschen. Klin Wochenschr 54, 671–676 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01469147
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01469147