Summary
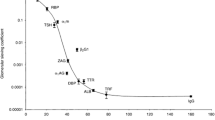
The urinary protein pattern following tubular damage is different from other proteinurias. The tubular proteinuria consists of micromolecular proteins of MW 10-70000. The disturbed tubular function probably leads to a diminished reabsorption of these microproteins from the tubular fluids. By determining the molecular weight of the urinary proteins by SDS-PAA- electrophoresis tubular proteinurias may be distinguished from glomerular and extrarenal forms. Tubular proteinurias are found in inflammatory, degenerative and vascular tubulopathies. The course of acute tubular diseases reveals proteinurias of different micromolecular composition depending of the improving tubular function; this supports the concept of a selective tubular reabsorption of microproteins. Tubular proteinurias are associated with normal as well as with impaired glomerular filtration, which, in part, might influence the amount of microproteins excreted.
Zusammenfassung
Eine besondere Form der Urinproteinausscheidung wird bei tubulären Schädigungen gefunden und als tubuläre Proteinurie bezeichnet. Sie besteht aus kleinmolekularen Proteinen von MG 10-70000, die infolge der gestörten tubulären Funktion aus dem Primärharn nicht rückresorbiert werden können. Ihr niedriges Molekulargewicht erlaubt nach Trennung an der SDS-PAA-Elektrophorese die Differenzierung der tubulären Proteinurie von glomerulären und extrarenalen Formen.
Entzündliche, degenerative und vasculär bedingte Tubulusveränderungen gehen mit einer tubulären Proteinurie einher, die somit ein wichtiger diagnostischer Hinweis sein kann. Bei Verlaufsbeobachtungen akuter tubulärer Schädigungen finden sich unterschiedlich zusammengesetzte tubuläre Proteinurien, die eine selektive tubuläre Resorption der Mikroproteine wahrscheinlich machen. Auch bei normaler glomerulärer Filtration finden sich tubuläre Proteinurien, deren Größe in der Niereninsuffizienz durch die verminderte Mikroproteinfiltration beeinflußt wird.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Berggard, I.: Plasma proteins in normal human urine, p. 7–19 in: 16
Boesken, W.H., Kopf, K., Schollmeyer, P.: Differentiation of proteinuric diseases by discelectrophoretic molecular weight analysis of urinary proteins. Clin. Nephrol.1, 311 (1973)
Boesken, W.H., Schmidt, M., Jontofsohn, R., Heinze, V.: Proteinuria as diagnostic marker after human kidney transplantation. Proc. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Ass. (EDTA) Tel Aviv (1974) (im Druck)
Bonomo, L., Schena, F.P.: Patterns of proteinuria in chronic pyelonephritis. The pseudoglomerular pattern. Clin. chim. Acta23, 295 (1969)
Butler, E.A., Flynn, F.V.: The proteinuria of renal tubular disorders. Lancet1958II, 978
Cohen, A.M., Walker, W.G.: The use of renal clearances of enzymes as an indicator of selective permeability of the renal glomerulus. J. Lab. clin. Med.70, 571 (1967)
Friberg, L.: Health hazards in the manufacture of alkaline accumulators with special reference to the chronic cadmium poisoning. Acta med. scand. 138, Suppl.240, 1 (1950)
Gerard, P.: Comparative histophysiology of the vertebrate nephron. J. Anat. (Lond.)70, 345 (1936)
Germann, H.J., Hoppe-Seyler, G., Boesken, W.H.: Akutes Nierenversagen nach Rifampicin. Dtsch. med. Wschr.99, 1454 (1974)
Hardwicke, J., Cameron, J.S., Harrison, J.F., Hulme, B., Soothill, J.F.: Proteinuria, studied by clearances of macromolecules, p. 11–52 (1970) in: 16
Lambert, P.P.: Sur les potentialites de resorption des tube contourne chez les urodeles. C.R. Soc. Biol. (Paris)110, 114 (1932)
Lambert, P.P., Gassee, J.P., Askenasi, R.: Physiological basis of protein excretion, p. 67–82 (1970) in: 16
Harrison, J.F., Blainey, J.D.: Low molecular weight proteinuria in chronic renal disease. Clin. Sci.33, 381 (1967)
Laterre, E.C., Heremans, J.F.: Proteins peculiar to normal urine and other secretions, p. 45–58 (1970) in: 16
Laterre, E.C., Manuel, Y.: Tubular proteinuria. Biochemical assay, p. 172–187 (1970) in: 16
Manuel, Y., Revillard, J.P., Bethuel, H. (ed.): Proteins in normal and pathological urine. Basel: S. Karger 1970
Manuel, Y., Revillard, J.P.: Study of urinary proteins by zone electrophoresis, p. 153–171 (1970) in: 16
Pesce, A.J., Boreisha, I., Pollack, V.E.: Papid differentiation of glomerular and tubular proteinuria by SDS-polyacrylamidgel electrophoresis. Clin. chim. Acta40, 27 (1972)
Petersson, P.A., Evrin, P.E., Vahlquist, A., Wibell, L., Bergard, I.: Characterization of proteins in tubular proteinuria. Scand. J. clin. Lab. Invest. 29, Suppl.126, abstr. 2.3 (1972)
Ravnskov, U.: Proteinuria after human renal transplantation. Scand. J. Urol. Nephrol.8, 37 (1974)
Revillard, J.P., Manuel, Y., Francois, R., Traeger, J.: Renal diseases associated with tubular proteinuria, p. 209–219 (1970) in: 16
Rohrer, Th., Fischer, L., Fuhrmann, Ch., Hodler, J.: Über die Selektivität der Eiweißausscheidung im Harn von Patienten mit chronischen parenchymatösen Nephropathien. Schweiz. med. Wschr.103, 131 (1973)
Squire, J.R., Blainey, J.D., Hardwicke, J.: Proteinuria, p. 213 in: Black, Renal diseases. Oxford: Blackwell 1962
Thoenes, W., Langer, K.H., Pfeiffer, U., Romen, W.: Eiweißtropfen und Lysosomen im proximalen Tubuluskonvolut der Ratte. Virchows Arch. Abt. B5, 124 (1970)
Virella, G., Pires, M.T., Marques Coelho, I.: Analytical characterization of the urinary proteins from 60 patients with monoclonal gammopathies. Clin. chim. Acta50, 63 (1974)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Mit Unterstützung der Deutschen Forschungsgemeinschaft (Bo 378/6).
Unter technischer Assistenz von Anita Mamier.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boesken, W.H. Die tubuläre Proteinurie. Klin Wochenschr 53, 473–479 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01468633
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01468633