Abstract
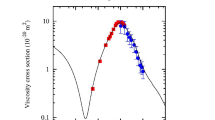
Reliable values of the viscosity in thermal argon plasmas are most important for our understanding of the momentum transfer and for realistic modeling of various plasma applications. Despite numerous attempts to determine reliable viscosity values over the last three decades, discrepancies still exist among the data reported by different authors. In this paper, a critical analysis is undertaken of calculated and experimental data of the argon viscosity based on recent publications. Our recalculation of viscosities in thermal argon plasmas are performed by using Lennard-Jones, Morse, Aziz, and exponential repulsive potentials for Ar-Ar atom interactions in different temperature ranges from 300 to 20,000 K. The contributions of elastic collisions of e-Ar, e-Ar+, and Ar+-Ar, as well as charge exchange of Ar+-Ar, to the viscosity become important with increasing temperature and degree of ionization in argon plasmas. Based on a critical analysis and recalculations, improved values of the argon viscosity are recommended, covering temperatures from 300 to 20,000 K. Polynomial expressions have been developed for calculating argon viscosities, which will be useful for numerical work and other applications of thermal argon plasmas at atmospheric pressure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. R. Lide and H. V. Kehiaian,CRC Handbook of Thermophysical and Thermochemical Data, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida (1994).
G. C. Maitland and E. B. Smith,J. Chem. Eng. Data 17, 150 (1972).
E. Bich, J. Millat, and E. Vogel,J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 19, 1289–1305 (1990).
N. B. Vargaftik,Handbook of Physical Properties of Liquids and Gases: Pure Substances and Mixtures, 2nd edn., Hemisphere Publishing Corp., Washington, New York, London (1983).
M. I. Boulos, P. Fauchais, and E. Pfender,Thermal Plasmas, Fundamentals and Applications, Vol. 1, Plenum Press, New York (1994).
R. A. Dawe and E. B. Smith,J. Chem. Phys. 52, 693 (1970).
M. N. Bahadori and S. L. Soo,Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 9, 17 (1966).
E. I. Ansinovskii and E. P. Pakhomov,High Temp. 5, 859 (1967).
S. V. Dresvin,Physics and Technology of Low-Temperature Plasmas, The Iowa State University Press, Ames, Iowa (1977).
A. Kanzawa and I. Kimura,AIAA J. 5, 1315 (1967).
D. P. Aeschliman and A. B. Cambel,Phys. Fluids 13, 2466 (1970).
R. S. Devoto,Phys. Fluids 18, 616 (1973).
A. A. Clifford, P. Gray, and N. Platts,J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 73, 381 (1977).
J. A. Kunc,J. Chem. Phys. 99, 4705 (1993).
B. Pateyron, M.-F. Elchinger, G.Delluc, and P. Fauchais,Plasma Chem. Plasma Process.12, 421 (1992).
A. B. Murphy and C. J. Arundell,Plasma Chem. Plasma Process.14, 451 (1994).
J. O. Hirschfelder, C. F. Curtiss, and R. B. Bird,Molecular Theory of Gases and Liquids, 2nd edn., Wiley, New York (1964).
S. Chapman and T. G. Cowling,Mathematical Theory of Non-uniform Gases, 3rd edn., Cambridge University Press, London (1970).
L. A. Viehland, A. R. Janzen, and R. A. Aziz,J. Chem. Phys. 102, 5444 (1995).
W. L. T. Chen, J. Heberlein, E.Pfender, B. Pateyron, G. Delluc, M.-F. Elchinger, and P. Fauchais,Plasma Chem. Plasma Process.15, 559 (1995).
G. C. Maitland, M. Rigby, E. B. Smith, and W. A. Wakeham,Intermolecular Forces, Clarendon Press, Oxford (1981).
R. A. Aziz, “Interatomic potentials for rare-gases: pure and mixed interaction,”Inert Gases, Springer Series in Chemical Physics, L. Klein, ed., Springer-Verlag, Berlin (1984), Vol. 34, pp. 5–86.
E. A. Mason and E. W. McDaniel,Transport Properties of Ions in Gases, Wiley, New York (1988).
W. Aretz, S. Metz, and H. Wilhelmi, “Thermodynamic and transport properties of dissociating combustion gases,” private communication, November (1993).
R. A. Aziz and H. H. Chen,J. Chem. Phys. 67, 5719 (1977).
R. A. Aziz and M. J. Slaman,J. Chem. Phys. 92, 1030 (1990).
R. A. Aziz,J. Chem. Phys. 99, 4518 (1993).
G. Sejkora, P. Girstmair, H. C. Bryant, and T. D. Mark,Phys. Rev. A29, 3379 (1984).
J. Aubreton and P. Fauchais,Rev. Phys. Appl. 18, 51 (1983).
J. Aubreton, C. Bonnefoi, and M. Mexmain,Rev. Phys. Appl. 21, 365 (1986).
J. T. Moseley, R. P. Saxon, B. A. Huber, P. C. Cosby, R. Abouaf, and M.Tadjeddine,J. Chem. Phys. 67, 1659 (1977).
H. H. Michels, R. B. Hobbs, and W. A. Wright,J. Chem. Phys. 69, 5151 (1978).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, W.L.T., Heberlein, J. & Pfender, E. Critical analysis of viscosity data of thermal argon plasmas at atmospheric pressure. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 16, 635–650 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01447012
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01447012