Summary
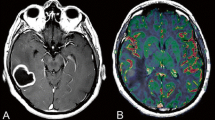
Seventeen patients with intracranial mass lesions underwent rCBF measurements with the xenon-133 carotid injection technique. In 11 patients remote areas of hyperaemia were found. There was a relation between location of the remote hyperaemia and the site of the mass lesion. In 10 of 11 patients with remote hyperaemia autoregulation was focally lost, and in 5 of 7 patients there was focal impairment of arterial pCO2-reactivity. In 8 of 11 patients with remote hyperaemia false localizing signs were found, related to the hyperaemic areas. It is suggested that the remote hyperaemic areas may be the result of brain bulk shifting due to the mass lesion and represent the initial stage of brain herniation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beks, J. W. F., Effects of increased supratentorial pressure in cats. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat.37 (1974), 627–630.
Brock, M., Experimental “luxury perfusion” in the cerebral cortex of the cat. Prog. Brain Res.30 (1968), 125.
Endo, H., Larsen, B., Lassen, N. A., Regional cerebral blood flow alterations from the site of intracranial tumors. J. Neurosurg.46 (1977), 271–281.
Gelmers, H. J., Regional cerebral blood flow. Thesis, van Gorcum, Assen, 1978.
—, Measurement of regional cerebral blood flow. Neurosurg. Rev.2 (1979), 133–141.
Hoedt-Rasmussen, K., Sveinsdottir, E., Lassen, N. A., Regional cerebral blood flow in man determined by intra-arterial injection of radioactive inert gas. Circ. Res.3 (1966), 237–247.
Langfitt, T. W., Weinstein, J. D., Kassell, N. F., Simeone, F. A., Transmission of increased intracranial pressure I. J. Neurosurg.21 (1964), 989–997.
Olesen, J., The effect of intracarotid epinephrine, norepinephrine and angiotensine on the regional cerebral blood flow in man. Neurology22 (1972), 978–987.
—, Paulson, O. B., Lassen, N. A., Regional cerebral blood flow in man determined by the initial slope of the clearance of intra-arterially injected133Xe. Stroke2 (1971), 519–539.
Palvölgyi, R., Regional cerebral blood flow in patients with intracranial tumors. J. Neurosurg.31 (1969), 149–163.
Pia, H. W., Die Schädigung des Hirnstammes bei den raumfordernden Prozessen des Gehirns. Acta neurochir. (Wien) Suppl. 4 (1957).
Roland, P. E., Larsen, B., Focal increase of cerebral blood flow during stereognostic testing in man. Arch. Neurol.33 (1976), 551–558.
Schneider, R. C., Remote cerebral hemisphere symptoms from surgically treated patients with posterior fossa brain tumors. Clin. Neurosurg.25 (1978), 57–95.
Seeger, W., Atemstörungen bei intrakraniellen Massenverschiebungen. Acta neurochir. (Wien) Suppl. 17 (1968).
Sveinsdottir, E., Larsen, B., Rommer, P., Lassen, N. A., A multidetector scintillation camera with 254 channels. J. Nucl. Med.18 (1977), 168–174.
Zülch, K. J., Über die Entstehung und Lokalisation der Hirninfarkte. Zbl. Neurochir.21 (1961), 158–178.
- Mennel, H. D., Zimmerman, V., Intracranial hypertension. In: Handbook of Clinical Neurology, Vol.16 (Vinken, P. J., Bruyn, G. W., eds.), pp. 89–149.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gelmers, H.J., Beks, J.W.F. Relation of false localizing signs and remote hyperaemia in patients with intracranial mass lesions. Acta neurochir 60, 81–89 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01401753
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01401753