Summary
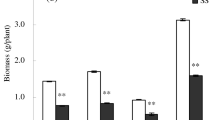
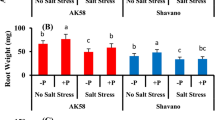
Significant Mg — Na interactions were found to govern the uptake and distribution of potassium and calcium by cotton. Contrary to the generally accepted views of cation antagonisms, it was found that under certain conditions sodium increased the potassium and calcium contents of plants. The effect of sodium was even more pronounced when magnesium was limiting.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appling, E. D., and Giddens, J., Differences in sodium and potassium content of various parts of the cotton plant at four stages of growth. Soil Sci.78, 1119–1203 (1954).
Cooper, H. P., and Garman, W. H., Effect of applications of sodium on the composition and yield of cotton at different levels of potash fertilization. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc.7, 331–338 (1942).
Cooper, H. P., Paden, W. R., and Phillippe, M. M., Effect of applications of sodium fertilizer on yields and composition of the cotton plant. Soil Sci.76, 19–28 (1953).
Cope, J. T. Jr., Bradfield, R., and Peech, M., Effect of sodium fertilization on yield and cation content of some field crops. Soil Sci.76, 65–74 (1953).
Holt, M. E., and Volk, N. J., Sodium as a plant nutrient and substitute for potassium. J. Am. Soc. Agron.37, 821–827 (1945).
Joham, H. E., The calcium and potassium nutrition of cotton as influenced by sodium. Plant Physiol.30, 4–10 (1955).
Lancaster, J. D., Andrews, W. B., and Jones, U. S., Influence of sodium on yield and quality of cotton lint and seed. Soil Sci.76, 29–40 (1953).
Larson, W. E., and Pierre, W. H., Interaction of sodium and potassium on yield and cation composition of selected crops. Soil Sci.76, 51–64 (1953).
Marshall, J. G., and Sturgis, M. B., Effects of sodium fertilizers on yield of cotton. Soil Sci.76, 75–79 (1953).
Mathews, E. D., Evidence of the value of the sodium ion in cotton fertilizers. Georgia Exp. Sta. Circ.127 (1927).
Thenabadu, M. W., Magnesium nutrition of cotton as influenced by sodium. Nature209, 165–167 (1966).
Troug, E., Berger, K. C., and Attoe, O. J., Magnesium-phosphorus relationships in plant nutrition. Soil Sci.63, 19–25 (1947).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thenabadu, M.W. Magnesium-sodium interactions effecting the uptake and distribution of potassium and calcium by cotton. Plant Soil 29, 132–143 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01393917
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01393917