Summary
-
1.
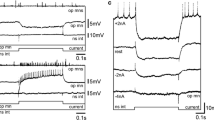
Breathing activity continued in isolated brain-velum-gill preparations of larval lampreys,Petromyzon marinus andLampetra aepyptera (Fig. 1). Periodic discharges were recorded extracellularly in the lateral fifth motor nucleus and from the fifth nerve (Fig. 2); these discharges preceded the contractions of the velum. Later in the respiratory cycle, discharges corresponding to the contractions of the branchial muscle were recorded in the tenth motor nucleus. Evidence is presented that discharges from both fifth and tenth nucleus were produced by motoneurons.
-
2.
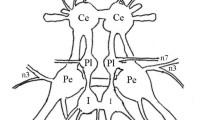
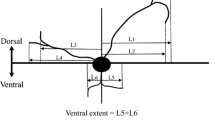
Velar motoneurons were identified by physiological criteria. Intracellular stimulation of these cells produced one-to-one movements in ipsilateral velar muscles and one-to-one electromyographio potentials (Fig. 4A). Motoneurons were confirmed as such by antidromic stimulation and collision. Velar motoneurons were located in the lateral part of the fifth motor nucleus (Fig. 3). Branchial motoneurons were also identified in the tenth motor nucleus.
-
3.
During intracellular recordings velar motoneurons exhibited periodic bursts of excitatory synaptic potentials (Fig. 4B), probably produced by unidentified pacemakers in the vicinity of the fifth motor nucleus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nieuwenhuys, R.: Topographical analysis of the brain stem of the lamprey,Lampetra fluviatilis. J. comp. Neurol.145, 165–178 (1972)
Rovainen, C. M.: Respiratory motoneurons in lampreys. J. comp. Physiol.94, 57–68 (1974)
Rovainen, C. M., Birnberger, K. L.: Identification and properties of motoneurons to fin muscle of the sea lamprey. J. Neurophysiol.34, 974–982 (1971)
Rovainen, C. M., Schieber, M. H.: Ventilation of larval lampreys. J. comp. Physiol.104, 185–203 (1975)
Teräväinen, H., Rovainen, C. M.: Fast and slow motoneurons to body muscle of the esa lamprey. J. Neurophysiol.34, 990–998 (1971)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by USPHS grant NS 09367. — The author expresses his sincere thanks to Dr. C. M. Rovainen for introducing this problem, valuable suggestions throughout the work and reading and correcting the manuscript, and to Dr. Y. Fukami for reading the manuscript. Larval sea lampreys were kindly provided by E. Louis King, Jr., and John H. Howell of the US Bureau of Sport Fisheries. Photomicrographic assistance was provided by Jennifer Arndt.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Homma, S. Velar motoneurons of lamprey larvae. J. Comp. Physiol. 104, 175–183 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01379458
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01379458