Summary
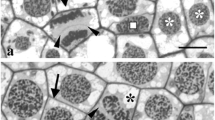
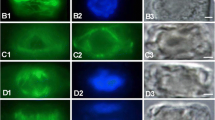
The junction between the plasma membrane and the cell wall in the subapical region of tip-growing protonemata of the fernAdiantum capillus-veneris was visualized by plasmolyzing the cells with a 1 M solution of NaCl. When the protonemata were treated with this solution, cells were rapidly plasmolyzed and the plasma membrane became detached from the cell wall around the entire periphery of the cell, with the exception of the subapex. In the subapical region, the connection between the cell wall and the plasma membrane remained undisturbed, whereas the membrane in other regions, as well as at the apex, was detached from the cell wall. As a result, the protoplasm appeared to adhere to the wall by a ringlike band of plasma membrane at the subapex. The location of the junction coincided with that of a circular array of microtubules (MTs) and microfilaments (MFs) at the cell cortex. The “subapical junction” disappeared when protonemata were treated with colchicine, cytochalasin B (CB), and blue-light irradiation, all of which are known to disrupt circular arrays of MTs. CB and blue light also disrupt the array of MFs but colchicine does not. Thus, the junction depends on the cortical MTs and not on the MFs. This finding indicates that the junction between the plasma membrane and the cell wall is sustained by a cortical array of MTs and suggests the presence of a specific and localized transmembrane structure.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CB:
-
cytochalasin B
- MF:
-
microfilament
- MT:
-
microtubule
References
Akashi T, Shibaoka H (1991) Involvement of transmembrane proteins in the association of cortical microtubules with the plasma membrane in tobacco BY-2 cells. J Cell Sci 98: 169–174
—, Kawasaki S, Shibaoka H (1990) Stabilization of cortical microtubules by the cell wall in cultured tobacco cells: effects of extensin on the cold-stability of cortical microtubules. Planta 182: 363–369
Giddings TH, Staehelin LA (1988) Spatial relationship between microtubules and plasma-membrane rosettes during the deposition of primary wall microfibrils inClosterium sp. Planta 173: 22–30
— — (1991) Microtubule-mediated control of microfibril deposition: a re-examination of the hypothesis. In: Lloyd CW (ed) The cytoskeletal basis of plant growth and form. Academic Press, London, pp 85–99
Kadota A, Wada M (1989 a) Enzymatic isolation of protoplasts from fern protonemal cells stainable with a fluorescent brightener. Plant Cell Physiol 30: 1107–1113
— — (1989 b) Circular arrangement of cortical F-actin around the subapical region of a tip-growing fern protonemal cell. Plant Cell Physiol 30: 1183–1186
— — (1992 a) The circular arrangement of cortical microtubules around the subapex of tip-growing fern protonemata is sensitive to cytochalasin B. Plant Cell Physiol 33: 99–102
— — (1992 b) Reorganization of the cortical cytoskeleton in tipgrowing fern protonemal cells during phytochrome-mediated phototropism and blue light-induced apical swelling. Protoplasma 166: 35–41
Murata T, Wada M (1989 a) Organization of cortical microtubules and microfibril deposition in response to blue light-induced apical swelling in a tip-growingAdiantum protonema cell. Planta 178: 334–341
— —, (1989 b) Effects of colchicine and amiprophos-methyl on microfibril arrangement and cell shape inAdiantum protonemal cells. Protoplasma 151: 81–87
—, Kadota A, Hogetsu T, Wada M (1987) Circular arrangement of cortical microtubules around the subapical part of a tip-growing fern protonema. Protoplasma 141: 135–138
Pennell RI, Knox JP, Scofield GN, Selvendran RR, Roberts K (1989) A family of abundant plasma membrane-associated glycoproteins related to the arabinogalactan protein is unique to flowering plants. J Cell Biol 108: 1967–1977
Quaranta V, Jones JCR (1991) The internal affairs of an integrin. Trends Cell Biol 1: 2–4
Sanders LC, Wang CS, Walling LL, Lord EM (1991) A homolog of the substrate adhesion molecule vitronectin occurs in four species of flowering plants. Plant Cell 3: 629–635
Schindler M, Meiners S, Cheresh DA (1989) RGD-dependent linkage between plant cell wall and plasma membrane: consequences for growth. J Cell Biol 108: 1955–1964
Wada M, Murata T (1991) The cytoskeleton in fern protonematal growth in relation to photomorphogenesis. In: Lloyd CW (ed) The cytoskeletal basis of plant growth and form. Academic Press, London, pp 277–288
—, Staehelin LA (1981) Freeze-fracture observations on the plasma membrane, the cell wall and cuticle of growing protonemata ofAdiantum capillus-veneris L. Planta 151: 462–468
— —, Shibata M (1990) Changes in microtubule and microfibril arrangement during polarotropism inAdiantum protonemata. Bot Mag Tokyo 103: 391–401
Wayne R, Staves MP, Leopold AC (1992) The contribution of the extracellular matrix to gravisensing in characean cells. J Cell Sci 101: 611–623
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kagawa, T., Kadota, A. & Wada, M. The junction between the plasma membrane and the cell wall in fern protonemal cells, as visualized after plasmolysis, and its dependence on arrays of cortical microtubules. Protoplasma 170, 186–190 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01378793
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01378793