Summary
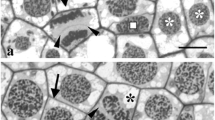
The endomembrane system of the chlamydomonad flagellate,Gloeomonas kupfferi (Chlorophyta), is complex. It consists of a proliferating ER network, a perinuclear complex of 14–18 dictyosomes and 8–12 vacuoles and an anterior contractile vacuole complex. The ER network extends from the nuclear envelope outwards, ensheafhs a dictyosome, extends out through a lobe of the chloroplast and terminates in the thin zone of peripheral cytoplasm between the chloroplast and plasmamembrane. The individual dictyosome is polar with distinct cis- and trans-faces. The cis-face is closely associated with transition vesicles emerging from the adjacent ER. Large vesicles emerge from peripheral swellings of terminal cisternae. The dictyosome-associated ER is connected to the peripheral vacuolar system. During cell division and cytokinesis, changes in the endomembrane system occur. Dictyosomes divide and quickly separate to form perinuclear complexes around the daughter nuclei. Each dictyosome undergoes morphological changes during this wall precursor-producing stage. ER lines the furrow zone and is closely associated with phycoplast microtubules. A discussion of the endomembrane system in membrane flow mechanics is provided.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ER:
-
endoplasmic reticulum
- OsFeCN:
-
Osmium ferricyanide
References
Catt JW, Hills GJ, Roberts K (1976) A structural glycoprotein containing hydroxyproline, isolated from the cell wall ofChlamydomonas reinhardii. Planta 131: 165–171
Cerenius L, Rennie P, Fowke LC (1988) Endocytosis of cationized ferritin by zoospores of the fungusAphanomyces euteiches. Protoplasma 144: 119–124
Domozych DS (1987) Cell division inCarteria crucifera (Chlorophyta): The role of the endomembrane system and phycoplast. Protoplasma 136: 170–182
—, Stewart KD, Mattox KR (1981 a) Development of the cell wall inTetraselmis: role of the Golgi apparatus and extracellular wall assembly. J Cell Sci 52: 351–371
—, Mattox KR, Stewart KD (1981 b) The role of microtubules during the cytokinetic events of cell wall ontogenesis and papilla development inCarteria crucifera. Protoplasma 106: 193–204
Dunphy WG, Rothman JE (1985) Compartmental organization of the Golgi stack. Cell 42: 13–21
Goodenough UW, Heuser JE (1988) Molecular organization of the cell wall and cell wall crystals fromChlamydomonas eugametos. J Cell Sci 90: 735–750
Grief C, Shaw PJ (1987) Assembly of cell wall glycoproteins ofChlamydomonas reinhardii: oligosaccharides are added in medial and trans Golgi compartments. Planta 171: 302–312
Gruber HE, Rosario B (1979) Ultrastructure of the Golgi apparatus and contractile vacuole inChlamydomonas reinhardi. Cytologia 44: 505–526
Hausmann K, Patterson DJ (1981) Involvement of smooth and coated vesicles in the function of the contractile vacuole complex of some cryptophycean flagellates. Exp Cell Res 135: 449–453
Hepler PK (1981) The structure of the endoplasmic reticulum revealed by osmium tetroxide-potassium ferricyanide staining. Eur J Cell Biol 26: 102–110
— (1982) Endoplasmic reticulum in the formation of the cell plate and plasmodesmata. Protoplasma 111: 121–133
Hillmer S, Depta H, Robinson DG (1986) Confirmation of endocytosis in higher plant protoplasts using lectin-gold conjugates. Eur J Cell Biol 41: 142–149
Iyengar Mop, Desikachary TV (1981) Volvocales. Hoe and Co, Madras, India, pp 532
McFadden GI, Melkonian M (1986) Golgi apparatus activity and membrane flow during scale biogenesis in the green flagellateScherffelia dubia (Prasinophyceae) I: Flagellar regeneration. Protoplasma 130: 186–198
Moestrup O, Thomassen HA (1974) An ultrastructural study of the flagellatePyramimonas orientalis with partial emphasis on Golgi apparatus activity and the flagellar apparatus. Protoplasma 81: 247–269
—, Walne PL (1979) Studies on scale morphogenesis in the Golgi apparatus ofPyramimonas tetrarrhyncus (Prasinophyceae). J Cell Sci 36: 437–459
Morré DJ (1987) The Golgi apparatus. Int Rev Cytol [Suppl] 17: 211–253
Nichols HW (1973) Growth media-freshwater. In: Stein JR (ed) Handbook of phycological methods. Culture methods and growth measurements. Cambridge University Press, New York, pp 123–154
Patterson DJ, Hausmann K (1981) The behaviour of contractile vacuole complexes of cryptophycean flagellates. Br Phycol J 16: 429–439
Picton JM, Steer MW (1983) Membrane recycling and the control of secretory activity in pollen tubes. J Cell Sci 63: 303–310
Quader H, Vankempen R, Stelzer R, Robinson DG (1983) Studies on the contractile vacuole ofPoterioochromonas malhamensis Peterfi. II. Antimonate stains the contractile vacuole ofPoterioochromonas. Eur J Cell Biol 30: 283–287
Roberts K, Hills GJ, Shaw PJ (1982) The structure of algal cell walls. In: Harris J (ed) Electron microscopy of proteins, vol 3. Academic Press, London, pp 1–40
Robinson DG, Kristen U (1982) Membrane flow via the Golgi apparatus of higher plant cells. Int Rev Cytol 77: 89–127
— (1985) Plant membranes: endo and plasmamembranes of plant cells. Wiley, New York (Cell biology monographs, vol 3)
Staehelin LA, Chapman RL (1987) Secretion and membrane recycling in plant cells, novel intermediary structures visualized in ultrarapidly frozen sycamore and carrot suspension-culture cells. Planta 171: 43–51
Tanchak MA, Fowke LC (1987) The morphology of multivesicular bodies in soybean protoplasts and their role in endocytosis. Protoplasma 138: 173–187
—, Griffing LR, Mersey BG, Fowke LC (1984) Endocytosis of cationized ferritin by coated vesicles of soybean protoplasts. Planta 162: 481–486
Wessel G, Robinson DG (1979) Studies on the contractile vacuole ofPoterioochromonas malhamensis Peterfi. I. The structure of alveolate vesicles. Eur J Cell Biol 19: 60–66
Zhang Y-H, Robinson DG (1986) The endomembranes ofChlamydomonas reinhardii: a comparison of the wildtype with the wall mutants CW2 and CW15. Protoplasma 133: 186–194
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Domozych, D.S. The endomembrane system and mechanism of membrane flow in the green alga,Gloeomonas kupfferi (Volvocales, Chlorophyta) I. An ultrastructural analysis. Protoplasma 149, 95–107 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01322982
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01322982