Abstract
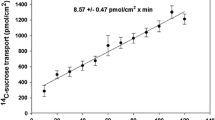
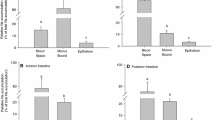
Only recently has it been appreciated that intestinal uptake is influenced by the dimensions of the unstirred water layer (UWL) as well as by the characteristics of the underlying microvillus membrane. This study was undertaken to compare the unidirectional flux rate (Jd) of a homologous series of saturated fatty acids (FA) into everted sacs, disks, and full thickness biopsies prepared from the jejunum and ileum of adult rabbits, under conditions selected to vary the effective resistance of the UWL. When the resistance of the UWL was low, Jd was much higher for sacs than for biopsies or for disks. The change in incremental free energy of transfer ζΔFw→1 was similar in disks and biopsies from the jejunum and ileum; ζΔFw→1 was higher in sacs than in disks or biopsies of jejunum and was higher in sacs of jejunum than in sacs of ileum. When the bulk phase was unstirred and UWL resistance was high, Jd of all fatty acids was lower, and the difference in Jd between the stirred and unstirred conditions increased with longer fatty acid chain lengths; for each FA Jd was higher in sacs than in biopsies or disks. These results suggest that (1) the higher Jd into everted jejunal sacs than into disks or biopsies is due to a difference in the permeability properties of the membrane resulting from the method of preparation of the everted sacs; (2) differences in Jd of FA at different sites along the intestine are due to a greater functional surface area of the membrane of the jejunum than of the ileum; and (3) variations in the effective resistance of the UWL have a profound effect on Jd into intestinal sacs, disks, and biopsies. It is concluded that thereaare qualitative as well as quantitative differences in the rate of uptake of saturated fatty acids into differentin vitro preparations, and that comparisons of Jd between different techniques may be invalid.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parsons DS: Methods for investigation of intestinal absorption.In: Handbook of Physiology, Alimentary Canal, Section 6, Volume III, CF Code (ed). American Physiological Society, Bethesda, MD, 1968, pp 1177–1216
Sladen GE: Methods of studying intestinal absorption in man.In: Intestinal Absorption in Man. I McColl, GEG Soden (eds). New York, Academic Press, 1975, pp 1–49
Mishkin S, Kessler JI: The uptake and release of bile salt and fatty acid by hamster jejunum. Biochim Biophys Acta 202:222–224, 1970
Mishkin S, Yalovsky M, Kessler JI: Thein vitro uptake and kinetics of release of palmitic acid and taurodeoxycholate from hamster small intestinal segments. Biochim Biophys Acta 225:335–346, 1971
Naupert C, Rommel K: Absorption of short and medium chain fatty acids in the jejunum of the rat. Z Klin Chem Klin Biochem 13:553–562, 1975
Ockner RK, Pittman JP, Yager JL: Differences in the intestinal absorption of saturated and unsaturated long chain fatty acids. Gastroenterology 62:981–992, 1972
Salle VL, Wilson FA, Dietschy JM: Determination of unidirectional uptake rates for lipids across the intestinal brush border. J Lipid Res 13:184–192, 1972
Diamond JM, Wright EM: Biological Membranes: The physical basis of ion and non-electrolyte selectivity. Annu Rev Physiol 31:581–646, 1969
Dietschy JM: Mechanisms of bile acid and fatty acid absorption across the unstirred water layer and brush border of the intestine. Helv Med Acta 37:89–102, 1973
Dietschy JM, Westergaard H: The effect of unstirred water layers on various transport processes in the intestine.In Intestinal Absorption and Malabsorption. TZ Csaky (ed). New York, Raven Press, 1975, pp 197–207
Dietschy JM: General principles governing the movement of lipids across biological membranes.In: Disturbances in Lipid and Lipoprotein Metabolism. JM Dietschy, JA Ontko (eds). Clinical Physiology Series, American Physiological Society, Bethesda, MD, 1978, pp 1–28
Ho NFH, Higguchi WI: Theoretical model studies of intestinal drug absorption. IV: bile acid transport at premicellar concentrations across diffusion-layer membrane barrier, J Pharm Sci 63:686–690, 1974
Hoyumpa HM, Nichols S, Schenker S, Wilson FA: Thiamine transport in thiamine-deficient rats: Role of the unstirred water layer. Biochim Biophys Acta 436:438–447, 1976
Lukie BE, Westergaard H, Dietschy JM: Validation of a chamber that allows measurement of both tissue uptake rates and unstirred layer thickness in the intestine under conditions of controlled stirring. Gastroenterology 67:652–661, 1971
Wilson FA, Sallee VL, Dietschy JM: Unstirred water layers in intestine: Rate determinant of fatty acid absorption from micellar solutions. Science 174:1031–1033, 1971
Wilson FA, Dietschy JM: The intestinal unstirred layer: Its surface area and effect on active transport kinetics. Biochim Biophys Acta 363:112–126, 1974
Westergaard H, Dietschy JM: Delineation of the dimensions and permeability characteristics of the two major diffusion barriers to passive mucosal uptake in the rabbit. J Clin Invest 54:718–732, 1974
Thomson ABR: Intestinal absorption of lipids: Influence of the unstirred water layer and bile acid micelle.In Disturbances in Lipid and Lipoprotein Metabolism. JM Dietschy, AM Gotto, and JA Ontko, Clinical Physiology Series, American Physiological Series, Bethesda, MD, 1978, pp 29–55
Hingson DS, Diamond JM: Comparison of non-electrolyte permeability patterns in several epithelia. J Membr Biol 10:93–135, 1972
Diamond JM, Wright EM: Molecular forces governing non-electrolyte permeation through cell membranes. Proc R Soc London Biol Sci 172:273–316, 1969
Wright EM, Prather JW: The permeability of the frog chorid plexus to non-electrolytes. J Membr Biol 2:127–149, 1970
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
With the technical assistance of B. Philips, M. Chung, and K. Marshall.
Supported by a grant from the Medical Research Council and the Medical Services Research Foundation of Alberta; B. D. O'Brien is a member of Her Majesty's Armed Forces (Canada).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thomsom, A.B.R., O'Brien, B.D. Uptake of a homologous series of saturated fatty acids into rabbit intestine using threein vitro techniques. Digest Dis Sci 25, 209–215 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01308141
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01308141