Summary
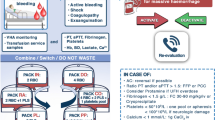
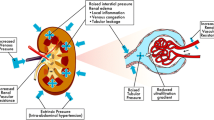
Mediators from the coagulation system, the complement system, the kallikrein-kinin system and the arachidonic acid metabolism are made responsible for the pathogenesis of organ failure (ARDS) following sepsis. Products from these systems influence, directly or indirectly, vascular tone and permeability, especially in the pulmonary circulation. Besides these mediators, toxic oxygen species and proteases released from activated granulocytes and macrophages injure endothelial cells and provoke vascular leakage.
Zusammenfassung
Für die Entwicklung von Organkomplikationen im Rahmen einer Sepsis werden Mediatoren aus dem Gerinnungs-, dem Komplement-, dem Kallikrein-Kinin-System und aus dem Arachidonsäure-Metabolismus verantwortlich gemacht. Produkte aus diesen Systemen beeinflussen teils direkt, teils indirekt über Zielzellen, den Gefässtonus und die Gefässpermeabilität vor allem in der Lungenstrombahn. Neben diesen Mediatoren wirken insbesondere die aus aktivierten Granulocyten und Makrophagen liberierten toxischen Sauerstoffprodukte und Proteasen endothelschädigend und permeabilitätssteigernd.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Baird BR, Cheronis JC, Sandhaus RA, Berger EM, White CW, Repine JE (1986) O2, metabolites and neutrophil elastase synergistically cause edematous injury in isolated rat lungs. J Appl Physiol 61:2224–2229
Barnhart MI, Chien S (1978) Platelet-vessel wall dynamics. Thromb Haemost 63:301–317
Brigham KL, Meyrick B (1984) Interactions of granulocytes with the lungs. Circ Res 54:623–635
Cohen AB (1979) The effects in vivo and in vitro of oxidative damage to purified a,-antitrypsin and to the enzyme-inhibiting activity of plasma. Am Rev Respir Dis 1219:953–960
Colman RW, Osbahr AJ, Morris RE (1967) New vasoconstrictor, bovine peptide B, released during blood coagulation. Nature 215:292–293
Fletcher JR, Ramwell PW, Herman CM (1976) Prostaglandins and the hemodynamic course of entotoxin shock. J Surg Res 20:589
Fritz H, Jochum M, Duswald KH, Dittmer H, Kortmann H (1984) Granulocyte proteinases as mediators of unspecific proteolysis in inflammation: A review. In: Goldberg DM, Werner M (eds) Selected topics in clinical enzymology, Vol 2. de Gruyter, Berlin, pp 305–328
Gerdin B, Belew M, Lindquist O, Saldeen T (1979) Effect of fibrin derived peptide on pulmonary microvascular permeability. In: Saldeen T (ed) The microembolism syndrome. Almquist and Wiksell, Stockholm, pp 233–239
Johnson D, Travis J (1979) The oxidative inactivation of human a,-proteinase inhibitor. J Biol Chem 254:4022–4026
Lough J, Moore S (1975) Endothelial injury induced by thrombin or thrombi. Lab Invest 33:130–135
Manwarning D, Curreri PW (1982) Platelet and neutrophil sequestration after fragment D-induced respiratory distress. Circ Shock 9:75–80
McDonald JA, Baum BJ, Rosenberg DM, Kelman JA, Brin SC, Crystal RG (1979) Destruction of a major extracellular adhesive glycoprotein (fibronectin) of human fibroblasts by neutral proteases from polymorphonuclear leukocyte granules. Lab Invest 40:350–357
Mittermayer Ch, Riede UN, Bleyl U, Herzog H, von Wichert P, Riesner K (1978) Schocklunge. Verh Dtsch Ges Pathol 62:11–65
Neuhof H (1984) Zur pathogenetischen Bedeutung der klassischen Kaskadensysteme und des Arachidonsäure-Metabolismus. Med Welt 35:1457–1462
Neuhof H, Seeger W, Wolf HRD (1986) Generation of mediators by limited proteolysis during blood coagulation and fibrinolysis - its pathogenetic role in the adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Resuscitation 14:23–32
Neuhof H (1987) Mediatoren in der Pathogenese des akuten Atemnotsyndroms (ARDS). In: Lawin P (Hrsg) Aktuelle Aspekte und Trends der respiratorischen Therapie. Springer, Berlin, pp 87 -100
Oettinger W, Seifert J (1982) Pathophysiologische Bedeutung der Prostanoide im septischen Schock. Fortschr Med 46:21–69
Ogletree ML, Brigham KL (1979) Indomethacin augments endotoxin induced increased lung vascular permeability in sheep. Rev Respir Dis 119:383
Riede UN, Mittermayer Ch, Rohrbach R, Joh K, Vogel W, Fringes B (1982) Mikrothrombosierung der Endostrombahn als Ursache schockbedingter Organkomplikationen (unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der Schocklunge). Haemostasiologie 2:3–24
Rietschel ET, Zähringer U, Wollenweber H-W, Miragliotta G, Musehold J, Lüderitz T, Schade U (1984) Bacterial endotoxins: chemical structure and biologic activity. Am J Emerg Med 2:60
Schlag GH, Redl H (1980) Die Leukostase in der Lunge beim hypovoldmisch-traumatischen Schock. Anaesthesist 29:606–612
Seeger W, Wolf H, Stähler G, Neuhof H, Róka L (1982) Increased pulmonary vascular resistance and permeability due to arachidonate metabolism in isolated rabbit lungs. Prostaglandins 23:157–173
Seeger W, Stöhr G, Wolf HRD, Neuhof H (1985) Alteration of surfactant function due to protein leakage: special interaction with fibrin monomer. J Appl Physiol 58:326–338
Seeger W, Suttorp N, Hellwig A, Bhakdi S (1986) Noncytolytic terminal complement complexes may serve as calcium gates to elicit leukotriene B4 generation in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Immunol 137:1286–1293
Seeger W, Walmrath D, Neuhof H, Lutz F (1986) Pulmonary microvascular injury induced by pseudomonas aeruginosa cytotoxin in isolated rabbit lungs. Infect Immunol 52:846–852
Slotman GJ, Burchard KW, Williams JJ, D'Arezzo A, Yellin SA (1986) Interaction of prostaglandins, activated complement, and granulocytes in clinical sepsis and hypotension. Surgery 99:744- 750
Sprung CL, Schultz DR, Marcial E, Caralis PV, Gelbard MA, Arnold PI, Long WM (1986) Complement activation in septic shock patients. Crit Care Med 14:525–528
Suttorp N, Simon LM (1982) Enhancement of polymorphonuclear leukocyte-mediated cytotoxicity in lung cells exposed to sustained in vitro hyperoxia. J Clin Invest 70:342–350
Suttorp N, Seeger W, Lutz F, Bhakdi S (1985) Stimulation der Leukotrien-B4-Bildung in Granulozyten and Prostazyklinbildung in Endothelzellen durch porenbildende bakterielle Toxine. Med Welt 36:1238–1244
Tate RM, Vanbenthuysen KM, Shasby DM, McMurtry IF, Repine JE (1982) Oxygen-radical-mediated permeability edema and vasoconstriction in isolated perfused rabbit lungs. Am Rev Respir Dis 126:802–806
Varani J, Fligiel SEG, Till GO, Kunkel RG, Ryan US, Ward PA (1985) Pulmonary endothelial cell killing by human neutrophils: Possible involvement of hydroxyl radical. Lab Invest 53:656–663
Yamamoto T, Cochrane CG (1981) Guinea pig Hageman factor as a vascular permeability enhancement factor. Am J Pathol 105:164–175
Zaslow MC, Clark RA, Stone PJ, Calore JD, Snider GL, Franzblau C (1983) Human neutrophil elastase does not bind to alpha,-protease inhibitor that has been exposed to activated human neutrophils. Am Rev Respir Dis 128:434–439
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neuhof, H. 3. Ursachen und Therapie von Organversagen: Mediatoren, ihr Stellenwert und therapeutische Implikationen am Beispiel des septischen Patienten. Langenbecks Arch Chiv 372, 43–47 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01297787
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01297787