Abstract
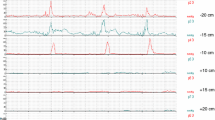
The colon motor response to a meal consisting of 100 mM of sodium oleate was assessed before and after neodecortication in male Sprague-Dawley rats. Recording probes were anchored surgically in the ascending and descending colon. Pressure changes were recorded on a dynograph using a low-compliance perfusion system. A motility index took into account the amplitude, duration, and frequency of contractions. Neodecortication increased the motility index of the distal colon in the fasting state. However, removal of the cerebral cortex did not affect significantly the colon motor response to a meal. Meal stimulation increased the motility index before and after neodecortication. These findings suggest that (1) resting colonic motor activity is increasea after neodecortication, probably through the loss of an inhibitory influence of the central nervous system; and (2) the cerebral cortex is not required for the colon response to a meal in the rat.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kerlin P, Zinsmeister A, Phillips S: Motor responses to food of the ileum, proximal colon, and distal colon of healthy humans. Gastroenterology 84:762–770, 1983
Loening-Baucke V, Anuras S: Effects of a meal on the motility of the sigmoid colon and rectum in healthy adults. Am J Gastroenterol 78:398–397, 1983
Snape WJ, Wright SH, Battle WM, Cohen S: The gastrocolic response: Evidence for a neural mechanism. Gastroenterology 77:1235–1240, 1979
Snape WJ Jr, Matarazzo SA, Cohen S: Effect of eating and gastrointestinal hormones on human colonic myoelectrical and motor activity. Gastroenterology 75:373–378, 1978
Welgan P, Meshkinpour H, Hoehler F: The effect of stress on colon motor and electrical activity in irritable bowel syndrome. Psychosomat Med 47:139–149, 1985
Narducci F, Snape WJ, Battle WM, London R, Cohen S: Stimulation of colonic myoelectric activity by emotional stress in healthy subjects and the irritable bowel syndrome: Effect of pretreatment with Librium. Gastroenterology 82:1137, 1982
Rostad H: Colonic motility in the cat. V: Influence of telencephalic stimulation and the peripheral pathways mediating the effects. Acta Physiol Scand 89:169–181, 1973
Deller DJ, Wangel AG: Intestinal motility in man. I. A study combining the use of intraluminal pressure recording and cine radiography. Gastroenterology 48:45–57, 1965
Bloom AA, LoPresi P, Gawar JT: Motility of the intact human colon. Gastroenterology 54:232–240, 1968
Wright SH, Snape WJ, Battle W, Cohen S, London RL: Effect of dietary components on gastrocolonic response. Am J Physiol 238:228–232, 1980
Sillen LF, Schulte SJ, Woods JH, Cowles VE, Condon RE, Bass P: Electromotor feeding responses of primate ileum and colon. Am J Surg 137:99–105, 1979
Sun EA, Snape WJ, Cohen S, Renny A: The role of opiate receptors and cholinergic neurons in the gastrocolonic response. Gastroenterology 82:689–693, 1982
Watts JW, Fultron JF: Intussusception—the relation of the cerebral cortex to intestinal motility in the monkey. N Engl J Med 210:883–896, 1934
Spiegel EA, Weston K, Oppenheimer MJ: Postmofor foci influencing the gastrointestinal tract and their descending pathways. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2:a45–53, 1943
Meshkinpour H, Harmon D, Thompson R, Yu J: Effects of thoracic spinal cord transection on colonic motor activity in rats. Paraplegia 23:272–276, 1985
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meshkinpour, H., Harmon, D., Thompson, R. et al. Impact of neodecortication on colon motor response to a meal in the rat. Digest Dis Sci 32, 743–746 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01296141
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01296141