Abstract
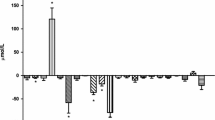
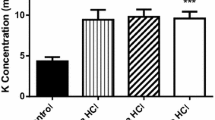
The contribution of hyperammonemia to plasma amino acid imbalance in patients with liver disease was assessed in 10 subjects with chronic hepatitis and in 17 advanced cirrhotics. Insulin, glucagon, and plasma amino acids were determined both in the basal state and 45 min after oral ammonium chloride, at doses used in the ammonia-tolerance test. In cirrhotics, ammonia increased to 3 times basal values, in association with a rise in insulin and, more marked, in glucagon. Aromatic amino acids and free tryptophan further increased, while a significant fall in branched-chain amino acids and glutamate was observed. The increase in ammonia levels strongly correlated with the increase in glucagon (r=0.707). Two patients, with large esophageal varices, showed signs of disturbed consciousness, in association with a marked rise in ammonia and in the ratio of free tryptophan to the sum of neutral amino acids. In patients with chronic hepatitis, whose ammonia levels rose slightly, minor variations in pancreatic glucoregulatory hormones and plasma amino acids were observed, as also happened in 10 healthy subjects following ammonium chloride ingestion. Our data fit with the hypothesis that the plasma amino acid imbalance of cirrhotics may be partly due to ammonia-induced changes in pancreatic hormones.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zieve L: Hepatic encephalopathy: Summary of present knowledge with an elaboration on recent developments.In Progress in Liver Diseases, Vol VI, H Popper, F Schaffner (eds.). New York, Grune & Stratton, 1979, pp 327–341
James JH, Jeppson B, Ziparo V, Fischer JE: Hyperammonaemia, plasma amino acid imbalance, and blood-brain amino acid transport: A unified theory of portal-systemic encephalopathy. Lancet 2:772–775, 1979
Soeters PB, Fischer JE: Insulin, glucagon, amino acid imbalance, and hepatic encephalopathy. Lancet 2:880–882, 1976
Conn HO: Ammonia tolerance as an index of portal-systemic collateral circulation in cirrhotics. Gastroenterology 41:97–106, 1961
Zoli M, Marchesini G, Angiolini A, Dondi C, Bianchi FB, Pisi E: Plasma amino acids as markers of liver dysfunction in cirrhotics. Scand J Gastroenterol 16:689–692, 1981
Paquet KJ, Albrecht M, Kliems G: Sclerotherapy of the oesophageal varices—prophylactically—with acute bleeding—at intervals?In Operative Endoskopie 1979, L Demling, W Rösch (eds). Berlin, Acron Verlag, 1979, pp 33–46
Conn HO: Ammonia tolerance in liver disease. J Lab Clin Med 55:855–861, 1960
Seligson D, Hirahara K: The measurement of ammonia in whole blood, erythrocytes, and plasma. J Lab Clin Med 49:962–974, 1957
Marchesini G, Forlani G, Zoli M, Angiolini A, Scolari MP, Bianchi FB, Pisi E: Insulin and glucagon levels in liver cirrhosis: Relationship with the plasma amino acid imbalance of chronic hepatic encephalopathy. Dig Dis Sci 24:594–601, 1979
Berger M, Zimmermann-Telschow H, Berchtold P, Drost H, Muller WA, Gries FA, Zimmermann H: Blood amino acid levels in patients with insulin excess (functioning insulinoma) and insulin deficiency (diabetic ketosis). Metabolism 27:793–799, 1978
Fischer JE, Baldessarini RJ: Pathogenesis and therapy of hepatic coma.In Progress in Liver Diseases, Vol V, H Popper, F Schaffner (eds.). New York, Grune & Stratton, 1976, pp 363–397
Mashford ML, Mahon WA, Chalmers TC: Studies of the cardiovascular system in the hypotension of liver failure. N Engl J Med 267:1071–1074, 1962
Dodsworth JM, James JH, Cummings MG, Fischer JE: Depletion of brain norepinephrine in acute hepatic coma. Surgery 75:811–820, 1974
Fischer JE, Baldessarini RJ: False neurotransmitters and hepatic failure. Lancet 2:75–79, 1971
Lam KC, Tall AR, Goldstein GB, Mistilis SP: Role of a false neurotransmitter, octopamine, in the pathogenesis of hepatic and renal encephalopathy. Scand J Gastroenterol 8:465–472, 1973
Cangiano C, Calcaterra V, Cascino A, Rossi-Fanelli F, Capocaccia L: The role of the false neurotransmitters, octopamine and phenylethanolamine, in human hepatic encephalopathy. Rendic Gastroenterol 9:189–193, 1977
Knell AJ, Davidson AR, Williams R, Kantamaneni BD, Curzon G: Dopamine and serotonin metabolism in hepatic encephalopathy. Br Med J 1:549–551, 1974
Baldessarini RJ, Karobath M: Biochemical physiology of central synapses. Annu Rev Physiol 35:273–304, 1973
Bessman SP, Bessman AW: The cerebral and peripheral uptake of ammonia in liver disease with a hypothesis for the mechanism of hepatic coma. J Clin Invest 34:622–628, 1955
Berl S: Cerebral amino metabolism in hepatic coma. Exp Biol Med 4:71–84, 1971
Strombeck DR, Rogers Q, Stern JH: The effects of intravenous ammonia infusion on plasma levels of amino acids, glucagon and insulin in dogs. Gastroenterology 74:1165, 1978 (abstract)
Doeffel M, Schlienger JL, Bockel R: Lack of correlation between insulin, glucagon and plasma amino acid imbalance in alcoholic cirrhosis. Proceedings of the 15th Meeting of the European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL), Belgrade, Sava Centar, 1980, p 30 (abstract)
Marchesini G, Zoli M, Dondi C, Cecchini L, Angiolini A, Bianchi FB, Pisi E: Prevalence of subclinical hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotics and relationship to plasma amino acid imbalance. Dig Dis Sci 25:763–768, 1980
Sherwin R, Joshi P, Hendler R, Felig P, Conn HO: Hyperglucagonemia in Laennec's cirrhosis. The role of portalsystemic shunting. N Engl J Med 290:239–242, 1974
Sherwin RS, Fischer M, Bessoff J, Snyder N, Hendler R, Conn HO, Felig P: Hyperglucagonaemia in cirrhosis: Altered secretion and sensitivity to glucagon. Gastroenterology 74:1224–1228, 1978
Rosen HM, Yoshimura N, Hodgman JM, Fischer JE: Plasma amino acid patterns in hepatic encephalopathy of differing etiology. Gastroenterology 72:483–487, 1977
Cascino A, Cangiano C, Calcaterra V, Rossi-Fanelli F, Capocaccia L: Plasma amino acid imbalance in patients with liver disease. Am J Dig Dis 23:591–598, 1978
White LP, Phear EA, Summerskill WHJ, Sherlock S: Ammonium tolerance in liver disease: Observations based on catheterization of the hepatic veins. J Clin Invest 34:158–168, 1955
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marchesini, G., Zoli, M., Dondi, C. et al. Ammonia-induced changes in pancreatic hormones and plasma amino acids in patients with liver cirrhosis. Digest Dis Sci 27, 406–412 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01295648
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01295648