Summary
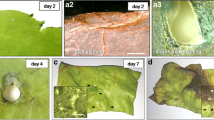
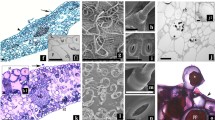
Quantitative electron micrograph analytical techniques were used to study cytological changes associated with the process of dedifferentiation and redifferentiation in mature, specialized cells of the stipe in the brown algaSargassum filipendula following wounding. Early cytological changes associated with this process appear to be those involved with formation of a protective layer of material at the wound surface. An increase in the volume of cytoplasm occupied by mitochondria, dictyosomes, and type A and B vesicles was evident by three days postwound. Cytoplasmic volume occupied by chloroplasts decreased during the early stages of wound reaction while the development of internal membranes (thylakoids) in these organelles increased. Cells at the cut surface eventually differentiated into one of two types of tissues: 1. A wound surface epidermal layer similar in cytological aspect to the epidermal layers of the intact and regenerated plant. 2. A meristematic “regeneration bud” from which developed the blade-like regeneration growth. The morphology and anatomy of the tissues of the regeneration blade resembled those of the blade of the intact plant rather than those of the stipe from which it originated. Percent difference values were obtained by comparing cytological features of the tissues from the regeneration blade with those of the intact stipe and blade. The comparisons supported previously obtained data indicating that the regeneration blade should be considered as a typical blade organ rather than a morphological variant of the stipe. Results of this study raises questions about possible physiological differences which may exist between stipe and blade organs in this plant.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dawes, C. J., 1971: Biological techniques m electron microscopy, 193 p. New York: Barnes and Noble, Inc.
Evans, L. V., andM. S. Holligan, 1972: Correlated light and electron microscope studies on brown algae. I. Localization of alginic acid and sulphated polysaccharides inDictyota. New Phytol.71, 1161–1172.
Fagerberg, W. R., 1975: A light and electron microscopic investigation of wound regeneration and differentiation inSargassum filipendula. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of South Florida. Diss. Abstr. Int. Xerox Univ. Microfilms. Ann Arbor, Mich. #76–10, 578. 239 p.
—, andC. J. Dawes, 1976: Studies onSargassum. I. A light microscopic examination of the wound regeneration process in mature stipes ofS. filipendula. Amer. J. Bot.63, 110–119.
Fletcher, R. L., 1975: Studies on the recently introduced brown algaSargassum muticum (Yendo) Fensholt. II. Regenerative ability. Bot. Mar.18, 157–162.
Floc'h, J.-Y., etM. Penot, 1976: Etude comparative du transport a longue distance de differents radioelements dans le thalle deLaminaria digitata (Linne) Lamouroux. C. R. Acad. Sci. (Paris)282 (Serie D), 989–992.
French, J. C., andD. J. Paolillo, Jr., 1975: The effect of the calyptra on the plane of guard cell mother cell division inFunaria andPhyscomitrium capsules. Ann. Bot.39, 233–236.
—, 1976: Effect of the calyptra on intercalary meristematic activity in the sporophyte ofFunaria (Musci). Amer. J. Bot.63, 492–498.
Fritsch, F. E., 1945: The structure and reproduction of the algae. II.Phaeophyceae, Rhodophyceae, Myxophyceae, pp. 322–396. London: Cambridge University Press.
Fulcher, G. R., andM. E. McCully, 1969: Histological studies on the genusFucus. IV. Regeneration and adventive embrony. Canad. J. Bot.47, 1643–1649.
—, 1971: Histological studies on the genusFucus. V. An autoradiographic and electron microscopic study of the early stages of regeneration. Canad. J. Bot.49, 161–165.
Lintilhac, P. M., 1974: Differentiation, organogenesis, and the tectonics of cell wall orientation. III. Theoretical considerations of cell wall mechanics. Amer. J. Bot.61, 230–237.
McCully, M. E., 1968: Histological studies on the genusFucus. III. Fine structure and possible functions on the epidermal cells of the vegetative thallus. J. Cell Sci.3, 1–16.
Moss, B., 1961: Wound healing and regeneration inFucus vesiculosus L. In: Fourth International Seaweed Symposium (Devirille, D., andJ. Felman, eds.), pp. 117–122. New York: The Macmillan Co. 1964.
—, 1964: Growth and regeneration ofFucus vesiculosus in culture. Brit. phycol. Bull2, 377–380.
Nicholson, N. L., andW. R. Briggs, 1972: Translocation of photosynthate in the brown algaNereocystis. Amer. J. Bot.59, 97–106.
Normindin, D. K., 1973: Direct deposition at high resolution of specific metals from solutions at radioactive sites in tissue sections. Trans. amer. microsc. Soc.92, 381–398.
O'Brien, T. P. O., andM. E. McCully, 1969: Plant structure and development: A pictorial and physiological approach, 114 p. New York: The Macmillan Co.
Parker, B. C., 1963: Translocation in the giant kelpMacrocystis. Science140, 891–892.
—, 1965: Translocation in the giant kelp Macrocystis. I. Rates, direction and quantity of14C labelled organic products and fluorescein. J. Phycol.1, 41–46.
Schmitz, K., andL. M. Srivastava, 1974: Fine structure and development of sieve tubes inLaminaria groenlandica Rosenv. Cytobiol.10, 66–87.
Thompson, D'Arcy, 1917: An growth and form, abridged edition. 1971 (Bonner, J. T., ed.), 328 p. London: Cambridge Univ. Press.
Underwood, E. E., 1970: Quantitative stereology, 274 p. Reading, Mass.: Addison-Wesley Publishing Co.
van Went, J. L., A. C. Aelst, andP. M. L. Tammes, 1973: Transverse connections between cortex and translocating medulla inLaminaria digitata. Acta Bot. (Neerl.)23, 77–78.
Weibel, E. R., 1969: Stereological principles for morphometry in electron microscope cytology. Int. Rev. Cytol.26, 235–299.
—, andR. P. Bolender, 1973: Stereological techniques for electron microscopic morphometry. In: Principles and techniques of electron microscopy: Biological applications, Vol. 3 (Hayat, M. A., ed.), pp. 237–296. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold Co.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fagerberg, W.R., Dawes, C.J. Studies onSargassum II. Quantitative ultrastructural changes in differentiated stipe cells during wound regeneration and regrowth. Protoplasma 92, 211–227 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01279459
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01279459