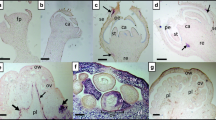
Abstract
To clone cDNAs of mRNA specifically expressed at the infection sites, we applied the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) combined with pricking microinjection to barley coleoptile epidermis inoculated with powdery mildew pathogen. In essence, first-strand cDNAs were synthesized in situ the needle-pricked epidermal cells in which fungal haustoria had formed, and were subsequently amplified by PCR with synthetic primers. The amplified DNAs were subcloned into a plasmid vector for the construction of a cDNA library. The antisense RNAs were in vitro-transcribed from subcloned DNAs, labelled, and introduced into pathogen-invaded coleoptile epidermal cells by pricking microinjection. Target cell-specific cDNAs were identified by a specific in situ hybridization in the pathogen-invaded cells. This technique was also applied to the amplification and identification of cDNAs which were reverse-transcribed from mRNAs of targeted infection structures of the powdery mildew pathogens inoculated onto barley coleoptile epidermis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apte AN, Siebert PD (1993) Anchor-ligated cDNA libraries: a technique for generating a cDNA library for the immediate cloning of the 5′ ends of mRNAs. BioTechniques 15:890–893.
Belyavsky A, Vinogradova T, Rajewsky K (1989) PCR-based cDNA library construction: general cDNA libraries at the level of a few cells. Nucleic Acids Res 17:2919–2932
Bushnell WR, Dueck J, Rowell JB (1967) Living haustoria and hyphae ofErysiphe graminis f. sp.hordei with intact and partly dissected host cells ofHordeum vulgare. Can J Bot 45:1719–1732
Chirgwin JM, Przybbyla AE, MacDonald RJ, Rutter WJ (1979) Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry 18:5294–5299
Edwards JBDM, Delort J, Mallet J (1991) Oligodeoxyribonucleotide ligation to single-stranded cDNAs: a new tool for cloning 5′ ends of mRNAs and for constructing cDNA libraries by in vitro amplification. Nucleic Acids Res 19:5227–5232
Forster AC, McInnes JL, Sklingel DC, Symons RH (1985) Non-radioactive hybridization probes prepared by the chemical labelling of DNA and mRNA with a novel reagent, photobiotin. Nucleic Acids Res 13:745–761
Frohman MA, Dush MK, Martin GR (1988) Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:8998–9002
Harvey RL, Darlison MG (1991) Random-primed cDNA synthesis facilitates the isolation of multiple 5′-cDNA ends by RACE. Nucleic Acids Res 19:4002
Karrer EE, Lincoln JE, Hogenhout A, Bennett AB, Bostock R, Marteau B, Lucas WJ, Gilchrist DG, Alexander D (1995) In situ isolation of mRNA individual plants cells: creation of cell-specific cDNA libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:3814–3818
Matsuda Y, Toyoda H, Ouchi S (1989) Application of microinjection to appressorium and haustoria ofEysiphe graminis f. sp.hordei. Ann Phytopathol Soc Jpn 55:67–68
Matsuda Y, Toyoda H, Nogi Y, Tamai T, Ouchi S (1992) Foreign gene expression in barley coleoptile epidermis: an improved system for gene transfer and in situ detection of gene expression by dual microinjection. Plant Tissue Cult Lett 9:154–163
Matsuda Y, Toyoda H, Morita M, Ikeda S, Tamai T, Nishiguchi T, Ouchi S (1994) A novel method for in situ hybridization in fungal cells based on pricking microinjection of photobiotin labelled probes. J Phytopathol 141:133–142
Ohara O, Dorit RL, Gilbert W (1989) One-side polymerase chain reaction: the amplification of cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:5673–5677
Ruano G, Fenton W, Kidd KK (1989) Biphasic amplification of very dilute DNA samples via ‘booster’ PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 17:5407
Sambrook J, Fritsch FF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning 2. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR (1977) DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:5463–5467
Toyoda H, Matsuda Y, Shoji R, Ouchi S (1987) A microinjection technique for conidia ofErysiphe graminis f. sp.hordei. Phytopathol 77:815–818
Toyoda H, Yamaga T, Matsuda Y, Ouchi S (1990) Transient expression of theβ-glucuronidase gene introduced into barley coleoptile cells by microinjection. Plant Cell Rep 9:299–302
Toyoda H, Matsuda Y, Yamaga T, Ikeda S, Morita M, Tamai T, Ouchi S (1991) Suppression of the powdery mildew pathogen by chitinase microinjected into barley coleoptile epidermal cells. Plant Cell Rep 10:217–220
Troutt AB, McHeyzer-Williams MG, Pulendran B, Nossal GJV (1992) Ligation-anchored PCR: a simple amplification technique with single-side specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:9823–9825
Yanisch-Perron CV, Messing J (1985) Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of M13mpl8 and pUC19 vectors. Gene 33:103–119
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. M. Widholm
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsuda, Y., Toyoda, H., Kurita, A. et al. In situ PCR technique based on pricking microinjection for cDNA cloning in single cells of barley coleoptile and powdery mildew pathogen. Plant Cell Reports 16, 612–618 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01275501
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01275501