Summary
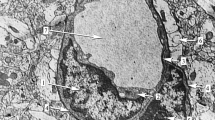
Morphological investigations on the permeability of intercellular junctions between ependymal cells and between capillary endothelial cells in the subcommissural organ (SCO) of the guinea pig have been carried out using freeze-fracturing and tracer experiments with horseradish peroxidase (HRP). The ependymal junction reveals a moderately developed network of tight junctional strands surrounding the tall ependymal cell. The apical portion of this junctional network tends to form nearly complete strands, whereas the basal portion usually shows irregular, fragmented strands often arranged in hairpin-like structures. The passage of intraventricularly infused HRP is blocked, leaving unstained areas, at the level of membrane fusions. At the same time the lateral intercellular space below the junction is densely stained, probably due to invasion from the basal side through adjacent ordinary ependymal junctions. The SCO capillary endothelium shows a high distribution density of pinocytotic vesicles. Vesicular transport of intravascularly injected HRP is observed, but no HRP penetration occurs through the endothelial junction. The active participation of vesicles in tracer movement is shown in preparations fixed before administration of HRP. Extravasation of this tracer is indicated to some degree in the SCO capillary, but permeability here appears to be comparable to that of ordinary brain capillaries. Accordingly, the SCO ependymal tight junction seems to form an effective barrier not to blood plasma or similar materials but to apically secreted substances, preventing them from spreading back into SCO intercellular spaces.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bomhard, K. Von., Kohl, W., Schinko, I. &Wetzstein, R. (1974) Feinbau und Passageverhalten der Capillaren in Subkommissuralorgan der Ratte.Zeitschrift für Anatomie und Entwicklungsgeschichte 144, 101–22.
Brightman, M. W., Prescott, L. &Reese, T. S. (1975) Intercellular junctions of special ependyma. InBrain-Endocrine Interaction II (edited byKnigge, K. M., Scott, D. E., Kobayashi, H. &Ishii, S.), pp. 146–165. Basel: Karger.
Brightman, M. W. &Reese, T. S. (1969) Junctions between intimately apposed cell membranes in the vertebrate brain.Journal of Cell Biology 40, 648–77.
Broadwell, R. D. &Brightman, M. W. (1976) Entry of peroxidase into neurons of the central and peripheral nervous systems from extracerebral and cerebral blood.Journal of Comparative Neurology 166, 257–84.
Chen, I-Li, Lu, K. -S. &Lin, H. -S. (1973) Electron microscopic and cytochemical studies of the mouse subcommissural organ.Zeitschrift für Zellforschung und mikroskopische Anatomie 139, 217–36.
Claude, P. &Goodenough, D. A. (1973) Fracture faces of zonulae occludentes from ‘tight’ and ‘leaky’ epithelia.Journal of Cell Biology 58, 390–400.
Deurs, B. Van (1977) Vesicular transport of horseradish peroxidase from brain to blood in segments of the cerebral microvasculature in adult mice.Brain Research 124, 1–8.
Deurs, B. Van &Koehler, J. K. (1979) Tight junctions in the choroid plexus epithelium. A freeze-fracture study including complementary replicas.Journal of Cell Biology 80, 662–73.
Gotow, T. &Hashimoto, P. H. (1979) Fine structure of the ependyma and intercellular junctions in the area postrema of the rat.Cell and Tissue Research 201, 207–25.
Gotow, T. &Hashimoto, P. H. (1980) Fine structure of the ependymal cysts in and around the area postrema of the rat.Cell and Tissue Research 206, 303–18.
Gotow, T. &Hashimoto, P. H. (1981) Graded differences in tightness of ependymal intercellular junctions within and in the vicinity of the rat median eminence.Journal of Ultrastructure Research 76, 293–311.
Gotow, T. &Hashimoto, P. H. (1982) Intercellular junctions between specialized ependymal cells in the subcommissural organ of the rat.Journal of Neurocytology 11, 363–79.
Hashimoto, P. H. &Hama, K. (1968) An electron microscope study on protein uptake into brain regions devoid of the blood-brain barrier.Medical Journal of Osaka University 18, 331–46.
Kimble, J. E. &Møllgard, K. (1973) Evidence for basal secretion in the subcommissural organ of the adult rabbit.Zeitschrift für Zellforschung und mikroskopische Anatomie 142, 223–39.
Kimble, J. E., Sørensen, S. C. &Møllgard, K. (1973) Cell junctions in the subcommissural organ of the rabbit as revealed by use of ruthenium red.Zeitschrift für Zellforschung und mikroskopische Anatomie 137, 375–86.
Madsen, J. K. &Møllgard, K. (1979) The tight epithelium of the Mongolian gerbil subcommissural organ as revealed by freeze-fracturing.Journal of Neurocytology 8, 481–91.
Møllgard, K. &Wiklund, L. (1979) Serotoninergic synapses on ependymal and hypendymal cells of the rat subcommissural organ.Journal of Neurocytology 8, 445–67.
Murakami, M., Shimada, T., Oribe, T. &Hiraki, T. (1972) An electron microscopic study on the subcommissural organ of the monkey,Macacus fuscatus.Archivum histologicumjaponicum 34, 61–72.
Oksche, A. (1969) The subcommissural organ.Journal ofNeuro-Visceral Relations 9, 111–39.
Papacharalampous, N. X., Schwink, A. &Wetzstein, R. (1968) Elektronen-mikroskopische Untersuchungen am Subkommissuralorgan des Meerschweinchens.Zeitschrift für Zellforschung und mikroskopische Anatomie 90, 202–29.
Rodríguez, E. M. (1969) Ependymal specializations. I. Fine structure of the neural (internal) region of the toad median eminence, with particular reference to the connections between the ependymal cells and the subependymal capillary loops.Zeitschrift für Zellforschung und mikroskopische Anatomie 102, 153–71.
Rodríguez, E. M. (1970) Ependymal specializations, II. Ultra structural aspects of the apical secretion of the toad subcommissural organ.Zeitschrift für Zellforschung und mikroskopische Anatomie 111, 15–31.
Stanka, P., Schwink, A. &Wetzstein, R. (1964) Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchung des Subkommissuralorgans der Ratte.Zeitschrift für Zellforschung und mikroskopische Anatomie 63, 277–301.
Sterba, G., Ermisch, A., Freyer, K. &Hartmann, G. 1967 Incorporation of Sulphur-35 into the subcommissural organ and Reissner's fibre.Nature 216, 504.
Sterba, G., Kleim, I., Naumann, W. &Petter, H. (1981) Immunocytochemical investigation of the subcommissural organ in the rat.Cell and Tissue Research 218, 659–62.
Tani, E., Yamagata, S. &Ito, Y. (1977) Freeze-fracture of capillary endothelium in rat brain.Cell and Tissue Research 176, 157–65.
Weindl, A. &Joynt, R. J. (1973) Barrier properties of the subcommissural organ.Archives of Neurology 29, 16–22.
Westergaard, E. &Brightman, M. W. (1973) Transport of proteins across normal cerebral arterioles.Journal of Comparative Neurology 152, 17–44.
Wiklund, L., Lundberg, J. J. &Møllgard, K. (1977) Species differences in serotoninergic innervation and secretory activity of rat, gerbil, mouse and rabbit subcommissural organ.Acta physiologica scandinavica 452, 27–30.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gotow, T., Hashimoto, P.H. Fine structural studies on ependymal paracellular and capillary transcellular permeability in the subcommissural organ of the guinea pig. J Neurocytol 11, 447–462 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01257988
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01257988