Summary
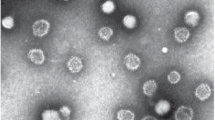
The viruses of equine arteritis, rubella, bovine viral diarrhea and hog cholera have been concentrated and purified. In preparations negatively stained with uranyl acetate they appeared as roughly spherical particles about 60 nm across. Within their envelopes isometrical cores were detected after spontaneous disruption or upon pretreatment; they are considered to be the viral nucleocapsids. The lower coefficients of variation calculated for the nucleocapsids as compared with those of the respective virus particles indicate that the pronounced heterogeneity in virion size must be attributed to the envelope. Ringlike morphological subunits observed on the surface of the spherical nucleocapsids and the presence of centra] core components suggest that the four viruses should be classified as togaviruses (lipid-containing RNA viruses with cubic symmetry of the nucleocapsid), together with arbo-A-viruses. The bovine viral diarrhea and hog cholera viruses differ from the other viruses studied in their lower sedimentation and density values, their lesser nucleocapsid diameters and an unusual “rosary” envelope structure. A further subdivision of the togavirus group is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aaslestad, H. G., E. J. Hoffman, andA. Brown: Fractionation of EEE virus by density gradient centrifugation in CsCl. J. Virol.2, 972–978 (1968).
Andrewes, C. H.: Generic names of viruses of vertebrates. Virology40, 1070–1071 (1970).
Auletta, A. E., C. L. Gitnick, C. E. Whitmire, andJ. L. Sever: An improved diluent for rubella hemagglutination and hemagglutination-inhibition tests. Appl. Microbiol.16, 691–694 (1968).
Aynaud, J. M.: Etude de la multiplicationin vitro d'un clone de virus de la peste porcine. Rech. Vét.1, 25–36 (1968).
Von Bonsdorff, C. H., P. Saikku, andN. Oker Blom: The inner structure of Uukuniemi and two Bunyamwera supergroup arboviruses. Virology39, 342–344 (1969).
Cusumano, C. L.: Density gradient centrifugation studies of rubella virus. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N.Y.)122, 461–465 (1966).
Darbyshire, J. H.: A serological relationship between swine fever and mucosal disease of cattle. Vet. Rec.72, 331 (1960).
Dinter, Z.: Relationship between bovine virus diarrhoea virus and hog cholera virus. Zbl. Bakt. I. Abt. Orig.188, 475–486 (1963).
Fernelius, A. L.: Characterization of bovine viral diarrhoea viruses. I. Determination of buoyant density. Arch. ges. Virusforsch.25, 211–218 (1968).
Hafez, S. M., K. Petzoldt, andE. Reczko: Morphology of bovine viral diarrhoea virus. Acta virol.12, 471–473 (1968).
Hermodsson, S., andZ. Dinter: Properties of bovine virus diarrhoea virus. Nature (Lond.)194, 893–894 (1962).
Holmes, J. H., C. M. Wark, andM. F. Warburton: Is rubella an arbovirus? II. Ultrastructural morphology and development. Virology37, 15–25 (1969).
Horzinek, M.: Characterization of hog cholera virus. I. Determination of buoyant density. J. Bact.92, 1723–1726 (1966).
Horzinek, M.: Characterization of hog cholera virus. II. Determination of sedimentation coefficient. Arch. ges. Virusforsch.21, 447–453 (1967).
Horzinek, M., E. Reczko, andK. Petzoldt: On the morphology of hog cholera virus. Arch. ges. Virusforsch.21, 475–478 (1967).
Horzinek, M., andM. Mussgay: Studies on the nucleocapsid structure of a group A arbovirus. J. Virol.4, 514–520 (1969).
Horzinek, M., M. Mussgay, andA. Adam: Studies on the substructure of togaviruses. I. Effect of urea, deoxycholate and saponin on the Sindbis virion. Arch. ges. Virusforsch.33, 296–305 (1971).
Hyllseth, B.: Buoyant density studies on equine arteritis virus. Arch. ges. Virusforsch., in press. (1970).
Kakefuda, T., andJ. P. Bader: Electron microscopical observations on the RNA of murine leukemia virus. J. Virol.4, 460–474 (1969).
Laufs, R., andR. Thomssen: Inhibition der Rubellavirus-Hämagglutination. I. Eigenschaften eines in fetalem Kälberserum vorkommenden Inhibitors der Rubellavirus-Hämagglutinationin vitro. Arch. ges. Virusforsch.24, 181–191 (1968).
Maess, J., E. Reczko undH. O. Böhm: Das Pferdearteriitisvirus (Equine arteritis virus): Seine Vermehrung in BHK 21-Zellen, die Bestimmung der Flotationsdichte und die elektronenoptische Darstellung. Arch. ges. Virusforsch.30, 47–58 (1970).
Magnusson, P., andP. Skaaret: Purification studies of rubella virus. Arch. ges. Virusforsch.20, 374–382 (1967).
Miller, H. K., andR. W. Schlesinger: Differentiation and purification of influenza viruses by adsorption on aluminium phosphate. J. Immunol.75, 155–160 (1955).
Mussgay, M., andR. Rott: Studies on the structure of a hem agglutinating component of a group A arbovirus (Sindbis). Virology23, 573–581 (1964).
Nicoli, J., etP. Acker: Les inhibiteurs sériques de l'hémagglutination par les arbovirus. Ann. Inst. Pasteur108, 22–32 (1965).
Porterfield, J. S., andC. E. Rowe: Hemagglutination with arthropod-borne viruses and its inhibition by certain phospholipids. Virology11, 765–770 (1960).
Ritchie, A. E., andA. L. Fernelius: Characterization of bovine viral diarrhoea viruses. V. Morphology of characteristic particles studied by electron microscopy. Arch. ges. Virusforsch.28, 369–389 (1969).
Salminen, A.: Chemistry of nonspecific inhibitors of hemagglutination by arthropod-borne viruses. Virology16, 201–203 (1962).
Stewart, G. L., P. D. Parkman, H. E. Hopps, R. D. Douglas, J. P. Hamilton, andH. M. Meyer: Rubella virus hemagglutination-inhibition test. New Engl. J. Med.276, 554–557 (1967).
Thomssen, R., R. Laufs undJ. Müller: Physikalische Eigenschaften und Partikelgröße des Rubellavirus. Arch. ges. Virusforsch.23, 332–345 (1968).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported in part by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, Bad Godersberg, BRD.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horzinek, M., Maess, J. & Laufs, R. Studies on the substructure of togaviruses. Archiv f Virusforschung 33, 306–318 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01254687
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01254687