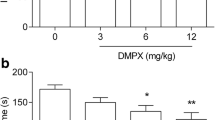
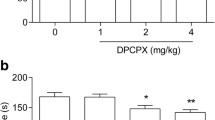
Summary
The compound EXP 561 (1-amino-4-phenylbicyclo-[2, 2, 2]-octane), an inhibitor of the noradrenaline (NA), 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) and dopamine (DA) uptake, a potential antidepressant agent, was studied in tests for evaluation of antidepressant drugs (AD). In most experiments (the apomorphine and reserpine hypothermia, the behavioural despair test, the blood pressure increases induced by NA and 5-HT) EXP 561 revealed similar activities as tricyclic AD. EXP 561 evoked stimulation of the hind limb flexor reflex in spinal rats, blocked by prazosin, metergoline and clomipramine. EXP 561 administered repeatedly in mice (twice daily for 14 days) did not evoke the adaptive changes induced by AD inhibiting the amine uptake, i.e. it did not enhance the amphetamine locomotor hyperactivity, did not potentiate the clonidine aggressiveness (at a lower dose, while at a higher one it acted less potently than when given acutely) or did not change the reserpine effect on the locomotor activity. EXP 561 showed a poor affinity toα 1-adrenoceptor (IC50 was 135,000 nM).
The results indicate that the inability to induce adaptive changes is a feature which differentiates EXP 561 from tricyclic AD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andén N-E, Ross B-E, Werdinius B (1964) Effects of chlorpromazine, haloperidol and reserpine on the levels of phenolic acids in rabbit corpus striatum. Life Sci (Part 2) 3: 149–158
Campbell IC, Todrick A (1973) On the pharmacology and biochemistry of the amine-uptake mechanism in human blood platelets. Br J Pharmacol 49: 279–287
Charney DS, Menkes DB, Heninger GR (1981) Receptor sensitivity and the mechanism of action of antidepressant treatment. Arch Gen Psychiatry 38: 1160–1180
Cheng Y-C, Prusoff WH (1973) Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 percent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol 22: 3099–3108
Fuller RW, Snoddy HD, Perry KW (1976) Inhibition of amine uptake by 4-phenyl-bicyclo(2, 2, 2)octan-1-amine hydrochloride monohydrate (EXP 561) in rats. Biochem Pharmacol 25: 1409–1410
Gershon S, Hekimian LJ, Floyd A (1968) Non-correlation of preclinical-clinical evaluation of a proposed anti-depressant 4-phenyl-bicyclo(2, 2, 2)octan-1-amine hydrochloride monohydrate (EXP 561). Arzneimittelforschung 18: 243–245
Glowinski J, Axelrod J (1965) Effects of drugs on the uptake, release, and metabolism of3H-norepinephrine in the rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 149: 43–49
Hall H, ögren S-O (1981) Effects of antidepressant drugs on different receptors in the brain. Eur J Pharmacol 70: 393–407
Juorio AV, Sharman DF, Trajkov T (1966) The effect of drugs on the homovanillic acid content of the corpus striatum of some rodents. Br J Pharmacol Chemother 26: 385–392
Koe BK (1976) Molecular geometry of inhibitors of the uptake of catecholamines and serotonin in synaptosomal preparations of rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 199: 649–661
Maj J (1984) Mechanism of action of antidepressant drugs given repeatedly: changes in the responses mediated by noradrenaline (α 1) and dopamine receptors. In: Proceedings of 9th IUPHAR international congress of pharmacology, vol 3. London, pp 137–143
Maj J (1986) Repeated treatment with antidepressant drugs: responses mediated by brain dopamine receptors. In: Hippius H, Klerman GL, Matussek N (eds) New results in depression research. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo, pp 90–98
Maj J, Palider W, Baran L (1976) The effects of serotoninergic and antiserotoninergic drugs on the flexor reflex of spinal rat: a proposed model to evaluate the action of the central serotonin receptor. J Neural Transm 38: 131–147
Maj J, Rogoż Z, Skuza G, Sowinska H (1983) Reserpine-induced locomotor stimulation in mice chronically treated with typical and atypical antidepressants. Eur J Pharmacol 87: 469–474
Maj J, Przegalinski E, Mogilnicka E (1984 a) Hypotheses concerning the mechanism of action of antidepressant drugs. In: Reviews of physiology, biochemistry, and pharmacology, vol 100. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo, pp 1–74
Maj J, Rogoz Z, Skuza G, Sowinska H (1984 b) Repeated treatment with anti-depressant drugs potentiates the locomotor response to (+)-amphetamine. J Pharm Pharmacol 36: 127–130
Maj J, Wedzony K, Skuza G (1985) Subsensitivity of presynaptic and supersensitivity of postsynaptic dopaminergic receptors as a result of repeated administration of antidepressant drugs. In: Advances in pharmacological research and practice. Proceedings of 4th congress of the Hungarian pharmacological society, Budapest 1985. Pergamon, Akadémia Kiadó, vol 2, pp 47–55
Mogilnicka E, Wcedzony K, Klimek V, Nowak G (1985) The importance of timing for the action ofα 1 orΒ-agonists: possible relationship with the density of [3H]-prazosin and [3H]-dihydroalprenolol binding sites. Eur J Pharmacol 113: 279–282
Ozawa H, Miyauchi T, Sugawara K (1975) Potentiating effect of lithium chloride on aggressive behaviour induced in mice by nialamide plus L-dopa and clonidine. Eur J Pharmacol 34: 169–179
Porsolt RD, Le Pichon M, Jalfre M (1977) Depression: a new animal model sensitive to antidepressant treatments. Nature 266: 730–732
Wong DT, Molloy BB, Bymaster FP (1977) Blockade of monoamine uptake by 1-amino-4-phenylbicyclo[2,2,2]octane (EXP 561) in rat brain and heart. Neuropharmacology 16: 11–15
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maj, J., Skuza, G., Sowińska, H. et al. Pharmacological properties of EXP 561, a potential antidepressant drug. J. Neural Transmission 70, 81–97 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01252511
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01252511