Summary
The effects of acute and chronic administration of nefiracetam, a pyrrolidone derivative, on monoaminergic neurotransmitter systems in the mouse hippocampus, frontal cortex, hypothalamus, and striatum were studied. The levels of monoamines and of their metabolites were measured by high performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection on the first, 7th, and 14th days after nefiracetam was given. The neurochemical effects of nefiracetam were compared with those of oxiracetam and indeloxazine.
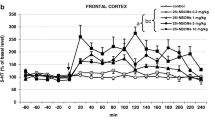
Acute administration of nefiracetam (10 mg/kg, po) and oxiracetam (10 mg/ kg, po) had no effect on the levels of noradrenaline (NA), dopamine (DA), or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), or on the levels of their metabolites, 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylglycol (MHPG), 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC), homovanillic acid (HVA), and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA), in any of the regions examined. In contrast, a single dose of indeloxazine (10 mg/kg, po) decreased the levels of MHPG, DOPAC, and 5-HIAA in all regions examined.
After chronic administration of nefiracetam (10 mg/kg, po, once daily), the levels of MHPG, DOPAC, and 5-HIAA were higher than control in all regions on the 14 th day only. Oxiracetam (10 mg/kg, po, once daily) similarly increased the levels of MHPG, DOPAC, and 5-HIAA in the hippocampus, frontal cortex, and striatum, but not in the hypothalamus. Conversely, indeloxazine (10 mg/ kg, po, once daily) decreased the levels of MHPG and 5-HIAA in all regions and the levels of DOPAC and HVA in the hippocampus and striatum as measured on the 7 th and 14 th days.
These results show that nefiracetam has a delayed effect on brain monoaminergic metabolism, and that its effects are similar to those of oxiracetam, but clearly different from those of indeloxazine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe E (1991) Reversal effect of DM-9384 on scopolamine-induced acetylcholine depletion in certain regions of the mouse brain. Psychopharmacology 105: 310–315
Bjerkenstedt L, Edoman G, Flyckt L (1985) Clinical and biochemical effects of citalopram, a selective 5-HT reuptake inhibitor — a dose-response study in depressed patients. Psychopharmacology 87: 253–259
Brozoski TJ, Brown RM, Rosvold HE, Goldman PS (1979) Cognitive deficit caused by regional depletion of dopamine in prefrontal cortex of rhesus monkey. Science 205: 929–932
Flood JF, Cherkin A (1987) Fluoxetine enhances memory processing in mice. Psychopharmacology 93: 36–43
Gottfries CG (1985) Alzheimer's disease and senile dementia: biochemical characteristics and aspects of treatment. Psychopharmacology 86: 245–252
Gottfries CG (1989) Pharmacological treatment strategies in dementia disorders. Pharmacopsychiatry 22: 129–134
Gottfries CG (1990) Neurochemical aspects of dementia disorders. Dementia 1: 56–64
Hollander ER, Mohs C, Davis KE (1986) Cholinergic approaches to the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Br Med Bull 42: 97–100
Kawajiri S, Sakurai T, Ojima H, Hatanaka S, Yamasaki T, Kojima H, Akashi A (1988) Effect of DM-9384, a new pyrrolidone derivative, on learning behaviour and cerebral choline acetyltransferase activity in rats. Psychopharmacology 96 [Suppl]: 306
Kawajiri S, Taniguchi K, Sakurai T, Kojima H, Yamasaki T (1990) Effect of DM-9384 on extracellular acetylcholine in the rat frontal cortex measured with microdialysis. Eur J Pharmacol 183: 928
Murai S, Saito H, Masuda Y, Itoh T (1988) Rapid determination of norepinephrine, dopamine, serotonin, their precursor amino acids, and related metabolites in discrete brain areas of mice within ten minutes by HPLC with electrochemical detection. J Neurochem 50: 473–479
Murasaki M, Miura S, Ishigooka J, Watanabe H, Uchiumi M, Fukuyama Y, Mochizuki Y, Sumiyoshi A (1988) Phase I study of DM-9384. Psychopharmacology 96 [Suppl]: 301
Nabeshima T, Noda Y, Tohyama K, Itoh J, Kameyama T (1990) Effects of DM-9384 in a model of amnesia based on animals with GABAergic neuronal dysfunctions. Eur J Pharmacol 178: 143–149
Nabeshima T, Noda Y, Tohyama K, Itoh J, Kameyama T (1991) Effects of DM-9384, a cyclic derivative of GABA, on amnesia and decreases in GABAA and muscarinic receptors induced by cycloheximide. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 257: 271–275
Nyth AE, Gottfries CG (1990) The clinical efficacy of citalopram in treatment of emotional disturbances in dementia disorders. A nordic multicentre study. Br J Psychiatry 157: 894–901
Oreland L, Gottfries CG (1986) Platelet and brain monoamine oxidase in aging and in dementia of Alzheimer's type. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiary 10: 533–540
Reinikainen KL, Soininen H, Riekkinen PJ (1990) Neurotransmitter changes in Alzheimer's disease: implications to diagnostics and therapy. J Neurosci Res 27: 576–586
Sakurai T, Ojima H, Yamasaki T, Kojima H, Akashi A (1989) Effects of N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-2-(2-oxo-l-pyrrolidinyl)acetamide (DM-9384) on learning and memory in rats. Jpn J Pharmacol 50: 47–53
Slotnick BM, Leonard CM (1975) A stereotaxic atlas of the albino mouse forebrain. US department of health, education, and welfare. Public health service. Alcohol, drug abuse, and mental health administration, Rockville, Maryland
Spignoli G, Pepeu G (1986) Oxiracetam prevents electroshock-induced decrease in brain acetylcholine and amnesia. Eur J Pharmacol 126: 253–257
Spignoli G, Pepeu G (1987) Interactions between oxiracetam, aniracetam and scopolamine on behavior and brain acetylcholine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 27: 491–495
Tachikawa S, Harada M, Maeno H (1979) Pharmacological and biochemical studies on a new compound, 2-(7-indenyloxymethyl)morpholine hydrochloride (YM-08054-1), and its derivatives with potential antidepressant properties. Arch Int Pharmacodyn 238: 81–95
Watabe T, Yamaguchi H, Ashida S, Yoshii M (1991) DM-9384, a new cognition enhancing agent, is a potent facilitator of neuronal Ca channel activity as compared with other pyrrolidone derivatives. Soc Neurosci Abstr 29: 17
Yamamoto N, Shimizu M (1987) Effects of indeloxazine hydrochloride (YM-08054) on anoxia. Arch Int Pharmacodyn 286: 272–281
Yamaguchi T, Harada M, Nagano H (1985) Effects of indeloxazine hydrochloride (YM-08054) on monoamines and their metabolites in rat brain. Biogenic Amines 3: 21–32
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abe, E., Murai, S., Saito, H. et al. Effects of nefiracetam, a novel pyrrolidone derivative, on brain monoamine metabolisms in mice. J. Neural Transmission 90, 125–136 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01250794
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01250794