Summary
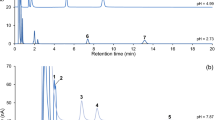
CSF was removed at a constant flow rate of 1μl/min from the third ventricle of anesthetized rats. Fiveμl CSF samples were directly injected every 15 min into a liquid Chromatographic system coupled with an amperometric detector. Mean CSF values for free dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC), homovanillic acid (HVA) and 5-hydroxyindolacetic acid (5-HIAA) were 1.4, 0.9, and 2.6×10−6M respectively. High doses of probenecid resulted in a linear increase of acidic metabolite concentrations which gave an index of the fractional turnover rates related to the resorption by the weak organic acid carrier. Accumulation rates were 0.24, 0.87, and 1.58μmol/l/h for DOPAC, HVA and 5-HIAA respectively. This route of elimination was predominant for 5-HIAA while it represented only a small part of total turnover for DOPAC. A high elimination rate constant for HVA validates the use of control levels of this metabolite as an indication of fractional HVA turnover dependent upon probenecid-sensitive carrier.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aizenstein, M. L., Korf, J.: Aspects of influx and efflux of homovanillic acid of rat cerebrospinal fluid. Brain Res.149, 129–140 (1978).
Ashcroft, G. W., Dow, R. C., Moir, A. T. B.: The active transport of 5-hydroxyindol-3-ylacetic acid and 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid from a recirculatory perfusion system of the cerebral ventricles of the unanesthetized dog. J. Physiol. (London)199, 397–425 (1968).
Barkai, A. I.: Serotonin turnover in the intact rabbit brain: relationship to extracellular proteins and modification by pentobarbital or haloperidol. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.208, 44–48 (1979).
Cespuglio, C. R., Faradji, H., Riou, F., Buda, M., Gonon, F., Pujol, J. F., Jouvet, M.: Differential pulse voltammetry in brain tissue. II. Detection of 5-hydroxyindolacetic acid in the rat striatum. Brain Res.223, 299–311 (1981).
Cheifetz, S., Warsh, J. J.: Occurrence and distribution of 5-hydroxytryptophol in the rat. J. Neurochem.34, 1093–1099 (1980).
Cserr, H. F., Van Dyke, D. H.: 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid accumulation by isolated choroid plexus. Am. J. Physiol.220, 718–723 (1971).
Danguir, J., Le Quan-Bui, K. H., Elghozi, J. L., Devynck, M. A., Nicolaidis, S.: LCEC monitoring of 5-hydroxyindolic compounds in the cerebrospinal fluid of the rat related to sleep and feeding. Brain Res. Bull.8, 293–297 (1982).
Dedek, J., Baumes, R., Tien-Duc, N., Gomeni, R., Korf, J.: Turnover of free and conjugated (sulphonyloxy) dihydroxyphenylacetic acid and homovanillic acid in rat striatum. J. Neurochem.33, 687–695 (1979).
Fernström, J. D., Wurtman, R. J.: Brain serotonin content: physiological regulation by plasma neutral amino acids. Science178, 414–416 (1972).
Forn, J.: Active transport of 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid by the rabbit choroid plexusin vitro: blockade by probenecid and metabolic inhibitors. Biochem. Pharmacol.21, 619–624 (1972).
Growdon, J. H., Melamed, E., Logue, M., Hefti, F., Wurtman, R. J.: Effects of oral L-tyrosine administration on CSF tyrosine and homovanillic levels in patients with parkinson's disease. Life Sci.30, 827–832 (1982).
Knott, P. J., Curzon, G.: Free tryptophan in plasma and brain tryptophan metabolism. Nature239, 452–453 (1972).
Korf, J., Van Praag, H. M.: Amine metabolism in the human brain: further evaluation of the probenecid test. Brain Res.35, 221–230 (1971).
Le Quan-Bui, K. H., Elghozi, J. L., Devynck, M. A., Meyer, P.: Rapid liquid Chromatographic determination of 5-hydroxyindoles and dihydroxyphenylacetic acid in cerebrospinal fluid of the rat. European J. Pharmacol.81, 315–320 (1982).
Mann, J. D., Butler, A. B., Rosenthal, J. E., Maffeo, C. J., Johnson, R. N., Bass, N. H.: Regulation of intracranial pressure in rat, dog, and man. Ann. Neurol.3, 156–165 (1978).
Meek, J. L., Neff, N. H.: Acidic and neutral metabolites of norepinephrine: their metabolism and transport from brain. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.181, 457–462 (1972).
Mignot, E., Laude, D., Elghozi, J. L., Le Quan-Bui, K. H., Meyer, P.: Central administration of yohimbine increases free 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylglycol in the cerebrospinal fluid of the rat. European J. Pharmacol.83, 135–138 (1982).
Mignot, E., Laude, D., Elghozi, J. L.: Kinetics of pharmacologically-induced changes in dopamine and serotonin metabolites levels in CSF of the rat. J. Neurochem. (in press).
Morot-Gaudry, Y., Hamon, M., Bourgoin, S., Ley, J. P., Glowinsky, J.: Estimation of the rate of 5-HT synthesis in the mouse brain by various methods. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol.282, 223–238 (1974).
Neff, N. H., Tozer, T. N., Brodie, B. B.: Application of steady state kinetics to studies of the transfer of 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid from brain to plasma. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.158, 214–218 (1967).
Nielsen, J. A., Moore, K. E.: Measurement of metabolites of dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine in cerebroventricular perfusates of unanesthetized, freely-moving rats: selective effects of drugs. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav.16, 131–137 (1982).
Palfreyman, M. G., Huot, S., Wagner, J.: Value of monoamine metabolite determinations in CSF as an index of their concentrations in rat brain following various pharmacological manipulations. J. Pharmacol. Methods8, 183–196 (1982).
Renaud, B., Mouret, J., Michel, D., Chazot, G., Laurent, B., Quincy, C.: Exploration pharmacologique du métabolisme des monoamines cérébrales par le test au probénécide: intérêt et limites. In: Les Neuromédiateurs du Tronc Cérébral (Schott, B., Chazot, G., eds.), pp. 217–231. Paris: Sandoz. 1980.
Sarna, G. S., Hutson, P. H., Tricklebank, M. D., Curzon, G.: Determination of brain 5-hydroxytryptamine turnover in freely moving rats using repeated sampling of cerebrospinal fluid. J. Neurochem.40, 383–388 (1983).
Van Wijk, M., Sebens, J. B., Korf, J.: Probenecid-induced increase of 5-hydroxytryptamine synthesis in rat brain, as measured by formation of 5-hydroxytryptophan. Psychopharmacol.60, 229–235 (1979).
Weiner, I. M.: Transport of weak acids and bases. In: Handbook of Physiology, Section 8: Renal Physiology (Orloff, J., Berliner, R. W., eds.), pp. 521–554. Washington: American Physiological Society. 1973.
Westerink, B. H. C., Korf, J.: Turnover of acid dopamine metabolites in striatal and mesolimbic tissue of the rat brain. European J. Pharmacol.37, 249–255 (1976).
Westerink, B. H. C., Spaan, S. J.: Estimation of the turnover of 3-methoxytyramine in the rat striatum by HPLC with electrochemical detection: implications for the sequence in the cerebral metabolism of dopamine. J. Neurochem.38, 342–347 (1982).
Wightman, R. M., Strope, E., Plotsky, P., Adams, R. N.:In vivo voltammetry: monitoring of dopamine metabolites in CSF following release by electrical stimulation. Brain Res.159, 55–68 (1978).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elghozi, J.L., Mignot, E. & Le Quan-Bui, K.H. Probenecid sensitive pathway of elimination of dopamine and serotonin metabolites in CSF of the rat. J. Neural Transmission 57, 85–94 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01250050
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01250050