Abstract
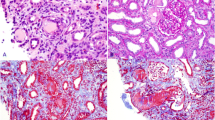
Immunoscintigraphy with technetium-99m labelled BW 250/183, a murine monoclonal antibody specific for granulocytes, yielded a false-positive result in a patient suspected of having an abscess in his renal graft. To substantiate the presumption that diathesis and unspecific accumulation of the antibody may have caused this result, ten selected patients were investigated who presented with chronic vascular graft rejection but without signs of bacterial infection. Scintiscans were recorded 4 and 24 h after administration of99mTc-labelled BW 250/183. Graft-background ratios (GBRs) were calculated for each transplant. These were compared with the mean of physiological kidney-background ratios (KBRs) and with bone marrow-background ratios (BMBRs). After removal, the grafts were examined with pathological and immunohistological methods. Seven transplants demonstrated 4-h GBRs (mean: 3.9±1.1,P <0.001) significantly outside the range of normal KBRs while three were within the normal range (mean: 1.8±0.4). The relation between 4-h and 24-h GBRs varied. After 24 h five GBRs still remained increased (mean: 3.2±1.4,P <0.05). By contrast the BMBRs decreased uniformly by 18%±5%. After graft removal, histopathology demonstrated no dominant granulocyte accumulations but various degrees of chronic vascular and tubulo-interstitial rejection. Immunohistochemical studies did not indicate cross-reactivity of BW 250/183. Increased GBRs of longstanding renal allografts indicate the passage of the antibody through injured vascular walls rather than the presence of granulocyte accumulations. Therefore, variability of GBRs with time reflects changes in transitory concentrations of99mTc-labelled BW 250/183 in the tissues.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Joseph K, Höffken H, Bosslet K, Schorlemmer HU. In vivo labelling of granulocytes with Tc-99m-anti-NCA monoclonal antibodies for imaging inflammation.Eur J Nucl Med 1988; 14:367–373.
Lind P, Langsteger W, Költringer P, Dimai HP, Passl R, Eber O. Immunoscintigraphy of inflammatory processes with a technetium-99m-labeled monoclonal antigranulocyte antibody (MAb BW 250/183).J Nucl Med 1990; 31: 417–423.
Duncker CM, Carrió I, Bernd L, et al. Radioimmune imaging of bone marrow in patients with suspected bone metastases from primary breast cancer.J Nucl Med 1990; 31: 1450–1455.
Becker W, Dölkemeyer U, Gramatzki M, Schneider MU, Scheele J, Wolf F. Use of immunoscintigraphy in the diagnosis of fever of unknown origin.Eur J Nucl Med 1993; 20: 1078–1083.
Becker W, Borst U, Fischbach W, Pasurka B, Schäfer R, Börner W. Kinetic data of in-vivo labeled granulocytes in humans with a murine Tc-99m-labelled monoclonal antibody.Eur J Nucl Med 1989; 15: 361–366.
Becker W, Goldenberg DM, Wolf F. The use of monoclonal antibodies and antibody fragments in the imaging of infectious lesions.Semin Nucl Med 1994; 24: 142–153.
Corstens FHM, Oyen WJG, Becker WS. Radioimmunoconjugates in the detection of infection and inflammation.Semin Nucl Med 1993; 23: 148–164.
Steinsträßer A, Berberich R, Kuhlmann L, Zabori S, Schwarz A. Binding of the monoclonal antibody BW 250/183 to human granulocytes.Nucl Med 1992; 31: 57–63.
Wirnsberger GH, Becker H, Ziervogel K, Holler H. Diagnostic immunchistochemistry of neuroblastic tumors.Am J Surg Pathol 1992; 16: 49–57.
Thakur ML, Segal AW, Louis L, Welch MJ, Hopkins J, Peters TJ. Indium-111-labeled cellular blood components: mechanism of labeling and intracellular location in human neutrophils.J Nucl Med 1977; 18: 1022–1025.
Rojas-Burke J. Health officials reactions to infection mishaps.J Nucl Med 1992; 33: 13N-27N.
Torregrosa JV, Bassa P, Lomena FJ, et al. The usefulness of 111-In-labeled platelet scintigraphy in the diagnosis of patients with febrile syndrome and a nonfunctioning renal graft.Transplantation 1994; 57: 1732–1735.
Khanuja PS, Taylor D, Toledo-Prereyra LH, Mittal VK. Diagnostic value of indium-111 leucocyte scans for localizing infective foci in renal or combined renal and pancreatic transplant patients.Dialysis Transplant 1993; 22: 90–100.
Bosslet K, Lüben G, Schwarz A, et al. Immunohistochemical localization and molecular characteristics of the three monoclonal antibody-defined epitopes detectable on the carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA).Int J Cancer 1985; 36: 75–84.
Bosslet K, Schorlemmer HU, Steinstraeβer A, Schwarz A, Sedlacek HH. Molecular and functional properties of the granulocyte specific Mab 250/183 suited for the immunoscintigraphic localization of inflammatory processes. In: Höfer R, ed.Radioactive isotopes in clinical medicine and research. New York: Schattauer; 1988: 15–20.
Mason J. Renal side-effects of cyclosporine.Transplant Proc 1990; 22: 1280–1283.
Moore LC, Mason J, Feld L, van Liew JB, Kaskel FJ. Effect of cyclosporine on endothelial albumin leakage in rats.J Am Soc Nephrol 1992; 3: 51–57.
Corstens FHM, Claessens RAMJ. Imaging inflammation with human polyclonal immunoglobulin: not looked for but discovered.Eur J Nucl Med 1992; 19: 155–158.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lipp, R.W., Wirnsberger, G.H., Ratschek, M. et al. The influence of vascular diathesis on the localization of inflammatory foci in renal allografts with a specific antigranulocyte antibody. Eur J Nucl Med 23, 395–400 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01247367
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01247367