Summary
A Computer Model for Stress-Volume Relationships of Porous Rocks with Various Saturations
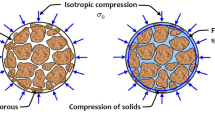
A model has been developed that predicts the hydrostatic and one-dimensional strain, stress-volume relationship for porous rocks with various fluid contents. The model uses spherical and penny-shaped pores and includes distributions in both size and separations of these pores. Some of the pores are interconnected to allow the passage of fluid as the porosity changes. The model is calibrated to the dry hydrostatic pressure-volume relationship and is then used to predict the stress-volume relationships for saturated or partially saturated rocks. The model predictions are compared to the experimental results for Mt. Helen tuff.
Zusammenfassung
Ein Computer-Modell für die Beziehungen zwischen Spannung und Volumen poröser Gesteine mit verschiedenen Sättigungsgraden
Es wurde ein Modell zur Vorhersage des Verhältnisses von hydrostatischer Spannung bzw. durch eindimensionale Verformung erzeugter Spannung zu Volumen poröser Gesteine mit unterschiedlichem Flüssigkeitsgehalt entwickelt. Das Modell benutzt kugelförmige und münzenförmige Poren und berücksichtigt sowohl verschiedene Größen- als auch Abstandsverteilungen dieser Poren. Zwischen einigen der Poren bestehen Verbindungen, die bei wechselnder Porosität das Durchfließen von Flüssigkeit ermöglichen. Das Modell wird auf das Verhältnis von hydrostatischer Spannung zu Volumen im Trockenzustand geeicht und dann zur Vorhersage des Spannungs-Volumen-Verhältnisses des gesättigten oder teilweise gesättigten Gesteins benutzt. Die Modellvorhersagen werden mit den experimentellen Ergebnissen für einen Tuff des Mt. Helen verglichen.
Résumé
Computer-Modèle pour les relations entre contrainte et volume de roches poreuses de saturation différente
On a établi un modèle qui permet de prédire la relation entre la contrainte hydrostatique et la contrainte résultante de la déformation unidimensionnelle, d'une part, et, d'autre part, le volume de diverses roches poreuses ayant diverses teneurs en fluides. Le modèle prévoit des pores sphériques et des pores en forme de disques et comporte des répartitions à la fois suivant la taille des pores et suivant qu'ils sont séparés ou non. Certains pores sont reliés entre eux pour permettre le passage du fluide lorsque la porosité se trouve modifiée. Le modèle est calibré par rapport à la relation à sec entre la contrainte hydrostatique et le volume; il est ensuite utilisé pour prédire les relations entre contraintes et volume de roches saturées ou partiellement saturées. Les prédictions du modèle sont comparées aux résultats expérimentaux obtenus avec le tuf de Mount Helen.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bridgman, P. W.: Freezing and Compression of Twenty-One Substances to 500,000 kg/cm2. Proc. Am. Acad. Arts Sci.74, 399–424 (1942).
Butkovich, T. R.: A Technique for Generating Pressure-Volume Relationships and Failure Envelopes for Rocks. UCRL-51411. Livermore, California: Lawrence Livermore Laboratory 1973.
Carrol, M. M., Holt, A. C.: Suggested Modifications of thep-α Relation for Porous Materials. J. Appl. Phys.43, 759–761 (1972).
Heard, H. C., Bonner, B. P., Duba, A. G., Schock, R. N., Stephens, D. R.: High Pressure Mechanical Properties of Mt. Helen, Nevada, Tuff. UCID-16261. Livermore, California: Lawrence Livermore Laboratory 1973.
Herrman, W.: Constitutive Equation for Dynamic Compaction of Ductile Porous Materials. J. Appl. Phys.40, 2490–2499 (1969).
Morland, L. W., Hastings, C. R.: A Void-Collapse Model for Dry Porous Tuffs. Engineering Geology7, 81–97 (1973).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Work performed under the auspices of theU. S. Department of Energy by theLawrence Livermore Laboratory under contract number W-7405-ENG-48.
With 7 Figures
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abey, A.E. A computer model for stress-volume relationships of porous rocks with various saturations. Rock Mechanics 13, 235–244 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01243534
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01243534