Abstract
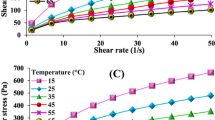
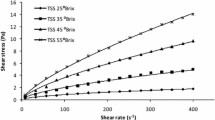
The feasibility of using apparent viscosity (ηa) as a method for detecting the occurrence of previous irradiation of pepper was studied. Apparent viscosity of heat-treated suspensions of white and black pepper, nonirradiated or irradiated with different doses of ionising radiation (γ), was measured under different “shear rates”. Results of previous research were therefore expanded and their usefulness examined; low shear rate conditions were found to be preferable for the detection and semi-quantitative evaluation of irradiation doses. The experimental methodology for semi-quantitative estimation was developed and its scope and limitations are presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
IAEA (1989) International document on food irradiation. In: Proceedings of the International Conference of Acceptance Control and Trade in Irradiated Food, STI/PUB/788/IAEA. International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, pp 135–143
Farkas J, Koncz A, Sharif MM (1990) Identification of irradiated dry Ingredients on the basis of starch damage. Radiat Phys Chem 35: 324–328
Heide L, Nurnberger E, Bögl KW (1990) Investigations on the detection of irradiated food by measuring the viscosity of suspended spices and dried vegetables. Radiat Phys Chem 36: 613–619
Farkas J, Sharif MM, Barabássy S (1990) Analytical studies into radiation-induced starch damage in black and white peppers. Acta Alimentaria 19: 273–279
Farkas J, Sharif MM, Koncz Á (1990) Detection of some irradiated spices on the basis of radiation induced damage of starch. Radiat Phys Chem 36: 621–627
Schreiber GA, Helle N, Bögl KW (1993) Detection of irradiated food — methods and routine applications. Int J Radiat Biol 63: 105–130
Schreiber GA, Leffke A, Mager M, Helle N, Bögl KW (1994) Viscosity of alkaline suspensions of ground black and white pepper samples: an indication or an identification of high dose radiation treatment? Radiat Phys Chem 44: 467–472
Heide L, Mohr E, Wichmann G, Bögl KW (1988) Are viscosity measurements a suitable method for the identification of irradiated spices? In: Health impact, identification, and dosimetry of irradiated foods. ISH-Heft 125. Institut für Sozialmedizin und Epidemiologie des Bundesgesundheitsamtes, pp 176–189
Heide L, Bögl KW (1990) Detection methods for irradiated food - luminescence and viscosity measurements. Int J Radiat Biol 57: 201–219
Sharif MM, Farkas J (1993) Analytical studies into radiationinduced starch damage in black and white peppers. Radiat Phys Chem 42: 383–386
Polónia MID (1994) Detection of irradiated condiments (peppers) (in Portuguese). Masters Thesis, Technical University of Lisbon
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Esteves, P., Polónia, I., Andrade, M.E. et al. Alteration of apparent viscosity of irradiated pepper — a tool for semi-quantitative estimation of irradiation dose. Z Lebensm Unters Forch 201, 351–354 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01192731
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01192731