Conclusions
-
1.
The regularities of change in the normalized histogram of the correlation of impulse trains of disynaptically linked neurons, in the presence of changes in efficiency of interneuronal, monosynaptic links, in the excitability of neurons, and in the summated effect upon them of independent, irregular, afferent, synaptic inputs, were studied, using a mathematical model of neuronal interaction.
-
2.
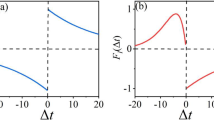
The amplitude of the basic maximum (minimum) of the normalized histogram of disynaptically linked neurons (meaning also the degree of dependence of their impulse trains) increases both with increase in the amplitude of the postsynaptic potentials which allow for a functional link between these neurons, and with decrease in the frequency of discharges of any of them (but not of the interneuron) which is conditional upon a decrease in the sweep of the irregular, exogenous oscillations of its membrane potenital or an increase in the threshold of generation of the impulse.
-
3.
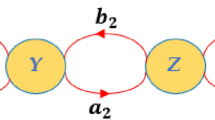
In the case of an excitatory, disynaptic link between the neurons, the increase in the degree of dependence of their impulse trains has a limit, determined by the greatest of the mean frequencies of the discharges of the pre- and postsynaptic neurons.
-
4.
It is impossible only by the character of the modification of the cross-over-correlational histogram of the impulse trains of polysynaptically linked neurons to establish the true physiological cause of this modification. It is necessary also to take into account the character of the mean frequency of the discharges of the neurons studied.
-
5.
The increase in the amplitude of the basic maximum (if the link is excitatory), or of the basic minimum (if the link is inhibitory), of the normalized cross-over-correlational histogram of their impulse trains, which accompanies the increase in the mean frequency of the discharges (the decrease in mean interspike intervals) of both neurons, is an unambiguous indicator of an increase in the efficiency of the disynaptic link between neurons (as a result of modification of synapses or change in the functional state of the interneuron).
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
A. G. Galashina and A. V. Bogdanov, “Conditioned reflex changes in the functional links between adjacent and remote cortical neurons,” Zh. Vyssh. Nervn. Deyat. im. I. P. Pavlova,31, No. 3, 497 (1981).
U. G. Gasanov, Systematic Activity of Cortical Neurons during Training [in Russian], Nauka, Moscow (1981).
V. A. Zosimovskii, “Physiological interpretation of the statistical indicators of the dependence of the impulse trains of interacting neurons,” Zh. Vyssh. Nervn. Deyat. im. I. P. Pavlova,32, No. 4, 676 (1982).
V. A. Zosimovskii, “The reflection of the plastic properties of the simplest neuronal junctions in the statistical characteristics of their elements. Monosynaptically linked neurons,” Zh. Vyssh. Nervn. Deyat. im. I. P. Pavlova,34, No. 6, 1149 (1984).
V. A. Zosimovskii, “The features of the form of the histograms of the auto- and cross-correlations of the impulse trains of polysynaptically linked neurons,” Zh. Vyssh. Nervn. Deyat. im. I. P. Pavlova,35, No. 3, 544 (1985).
S. V. Karnup and M. N. Zhadin, “Autocorrelational analysis of the background impulsization of cortical neurons during training,” Zh. Vyssh. Nervn. Deyat. im. I. P. Pavlova,30, No. 4, 738 (1980).
S. V. Karnup and M. N. Zhadin, “Interaction of background-active cortical neurons in the development of a conditioned defense reflex,” Zh. Vyssh. Nervn. Deyat. im. I. P. Pavlova,30, No. 5, 971 (1980).
M. N. Livanov, “Neuronal mechanisms of memory,” Usp. Fiz. Nauk,6, No. 3, 66 (1975).
G. Kh. Merzhanova, S. A. Varashkevich and V. B. Dorokhov, “Statistical analysis of interneuronal functional links in the development of conditioned reflexes,” Zh. Vyssh. Nervn. Deyat. im. I. P. Pavlova,31, No,5, 950 (1981).
R. M. Meshcherskii, The Analysis of Neuronal Activity [in Russian], Nauka, Moscow (1972).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Zhurnal Vysshei Nervnoi Deyatel'nosti imeni I. P. Pavlova, Vol. 36, No. 2, pp. 368–374, March–April, 1986.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zosimovskii, V.A. The reflection of the plastic properties of the simplest neuronal junctions in the statistical characteristics of the impulse activity of their elements. Polysynaptically linked neurons. Neurosci Behav Physiol 17, 20–26 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01186802
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01186802