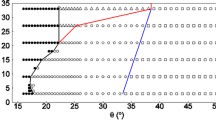
Summary
The mechanics of flowing granular materials such as coal, sand, metal ores, etc., and their flow characteristics have received considerable attention in recent years as it has relevance to several important technological problems. In a number of instances, these materials are also heated prior to processing, or cooled after processing. The governing equations for the flow of granular materials, taking into account the heat transfer mechanism by conduction, are derived using a continuum model (cf. Goodman and Cowin [1], [2], Rajagopal and Massoudi [3]). For a fully developed flow of these materials down an inclined plane, the equations reduce to a system of coupled non-linear ordinary differential equations. The resulting boundary value problem is solved numerically and the results are presented for cases where the viscosity and thermal conductivity are assumed to be functions of the volume fraction. It is shown that the equations admit multiple solutions for certain values of the parameters.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- D :
-
Symmetric part of the velocity gradient
- K :
-
thermal conductivity
- L :
-
velocity gradient
- T :
-
Cauchy stress tensor
- b :
-
body force
- h :
-
characteristic height
- q :
-
heat flux
- r :
-
radiating heat
- u :
-
velocity vector
- α:
-
angle of inclination of the inclined plane with the horizontal
- ɛ:
-
specific internal energy
- γ:
-
distributed mass density
- Θ:
-
temperature
- ν:
-
volume fraction
- ϱ:
-
bulk mass density
References
Goodman, M. A., Cowin, S. C.: Two problems in the gravity flow of granular materials. J. Fluid Mech.45, 321–339 (1971).
Goodman, M. A., Cowin, S. C.: A continuum theory for granular materials. Arch. Rat. Mech. Anal.44, 249–266 (1972).
Rajagopal, K. R., Massoudi, M.: A method for measuring material moduli of granular materials: flow in an orthogonal rheometer. Topical Report U.S. Department of Energy DOE/PETC/TR-90/3 (1990).
Patton, J. S., Sabersky, R. H., Brennen, C. E.: Convective heat transfer to rapidly flowing, granular materials. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer29, 1263–1269 (1986).
Uhl, V. W., Root, W. L.: Heat transfer to granular solids in agitated units. Chem. Eng. Prog.63, 81–92 (1967).
Sullivan, W. N., Sabersky, R. H.: Heat transfer to flowing granular media. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer18, 97–107 (1975).
Spelt, J. K., Brennen, C. E., Sabersky, R. H.: Heat transfer to flowing granular material. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer25, 791–796 (1982).
Reynolds, O.: Experiment showing dilatancy a property of granular material, possibly connected with gravitation. Proc. Roy. Inst. Gr. Britain11, 354–363 (1886).
Reiner, M.: A mathematical theory of dilatancy. Am. J. Math.67, 350–362 (1945).
Cowin, S. C.: A theory for the flow of granular material. Power Tech.9, 61–69 (1974).
Cowin, S. C.: Constitutive relations that imply a generalized Mohr-Coulomb criterion. Acta Mech.20, 41–46 (1974).
Savage, S. B.: Gravity flow of cohesionless granular materials in chutes and channels. J. Fluid Mech.92, 53–96 (1979).
Ahmadi, G.: A generalized continuum theory for granular materials. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech.17, 21–33 (1982).
McTigue, D. F.: A non-linear constitutive model for granular materials: applications to gravity flow. J. Appl. Mech.49, 291–296 (1982).
Nunziato, J. W., Passman, S. L., Thomas Jr., J. P.: Gravitational flows of granular materials with incompressible grains. J. Rheol.24, 395–420 (1980).
Passman, S. L., Nunziato, J. W., Bailey, P. B., Thomas Jr., J. P.: Shearing flows of granular materials. J. Eng. Mech. Div. ASCE106, 773–783 (1980).
Boyle, E. J., Massoudi, M.: Kinetic theories of granular materials with applications to fluidized beds. Technical Note, U.S. Department of Energy DOE/METC-89/4088 (1988).
Boyle, E. J., Massoudi, M.: A theory for granular materials exhibiting normal stress effects based on Enskog's dense gas theory. Int. J. Eng. Sci.28, 1261–1275 (1990).
Hutter, K., Szidarovszky, F., Yakowitz, S.: Plane steady shear flow of a cohesionless granular material down an inclined plane: a model for flow avalanches. Part I. Theory. Acta Mech.63, 87–112 (1986).
Hutter, K., Szidarovszky, F., Yakowitz, S.: Plane steady shear flow of a cohesionless granular material down an inclined plane: a model for flow avalanches. Part II. Numerical results. Acta Mech.65, 239–261 (1986).
Johnson, P. C., Jackson, R.: Frictional-collisional constitutive relations for granular materials with application to plane shear. J. Fluid Mech.176, 67–93 (1987).
Rajagopal, K. R., Troy, W. C., Massoudi, M.: Existence of solutions to the equations governing the flow of granular materials. Eur. J. Mech. B/Fluids11, 265–276 (1992).
Johnson, G., Massoudi, M., Rajagopal, K. R.: Flow of a fluid-solid mixture between flat plates. Chem. Eng. Sci.46, 1713–1723 (1991).
Johnson, G., Massoudi, M., Rajagopal, K. R.: Flow of a fluid infused with solid particles through a pipe. Int. J. Eng. Sci.29, 649–661 (1991).
Walton, O. R., Braun, R. L.: Stress calculations for assemblies of inelastic spheres in uniform shear. Acta Mech.63, 73–86 (1986).
Schlünder, E. U.: Heat transfer to moving spherical packing at short contact times. Int. Chem. Eng.20, 550–554 (1980).
Wunschmann, J., Schlünder, E. U.: Heat transfer from heated surfaces to spherical packings. Int. Chem. Eng.20, 555–563 (1980).
Schlünder, E. U.: Particle heat transfer. In: Proc. Seventh Int. Heat Trans. Conf. Munich, vol. 1 (Grigull, U., Hahne, E., Stephan, K., Straub, J., eds.), pp. 195–211. New York: Hemisphere Pub. 1982.
Buggisch, B., Löffelmann, G.: Theoretical and experimental investigations into local granulate mixing mechanisms. Chem. Eng. Process.26, 193–200 (1989).
Bashir, Y. M., Goddard, J. D.: Experiments on the conductivity of suspensions of ionically-conductive spheres. AIChE J.36, 387–396 (1990).
Batchelor, G. K., O'Brien, R. W.: Thermal or electrical conduction through a granular material. Proc. R. Soc. London Ser.A355, 313–333 (1977).
Hui, K., Haff, P. K., Unger, J. E., Jackson, R.: Boundary conditions for high-shear grain flows. J. Fluid Mech.145, 223–233 (1984).
Johnson, P. C., Nott, P., Jackson, R.: Frictional-collisional equations of motion of particular flows and their application to chutes. J. Fluid Mech.210, 501–535 (1990).
Ascher, U., Christianson, J., Russel, R. D.: Collocation software for boundary value ODE's. ACM Trans. Math. Software7, 209–222 (1981).
Ahn, H.: Experimental and analytical investigation of granular materials. Ph.D. Thesis, Caltech. 1989.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gudhe, R., Rajagopal, K.R. & Massoudi, M. Fully developed flow of granular materials down a heated inclined plane. Acta Mechanica 103, 63–78 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01180218
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01180218