Abstract
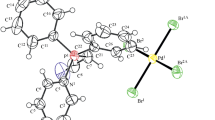
(SP-4-4)-chloro[2-(di-tert-butylphosphino)-2-methylpropyl-C,P] (triphenylarsine)palladium(II), C30H41ClPAsPd, has been characterized by single-crystal X-ray diffraction data. It crystallizes in the monoclinic space groupP21 witha=9.611(2),b=14.335(2),C=11.953(1) Å,β=111.97(1)° andZ=2. The phasing model was determined by direct methods and the full-matrix least-squares refinement of 302 structural parameters yielded a reliability factor of 0.039 for 2269 unique reflections withI> 3σ(I). The square planar geometry about the Pd atom is angularly distorted due to the steric bulk of the ligands and the formation of the four-membered ring, Pd-P-C(2)-C(1), which is severely distorted. The arsine and phosphine ligands are orientedtrans across the square-planar geometry with an As-Pd-P angle of 163.5(1)°. Details of the structural content and selected bond lengths and angles are discussed. The phenyl rings are planar and in a staggered orientation. Steric bulk illustrations from “ligand profile” calculations (θ/2 vs φ) about the arsine and phosphine ligands are presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alyea, E. C., Dias, S. A., Ferguson, G., and Restivo, R. J. (1977).Inorg. Chem. 16, 2329.
BIDICS (1969–1981).Institute for Materials Research, Hamilton, Canada.
Chow, A., Clark, H. C., Fraenkel, G., Grossie, D. A., Hampden-Smith, M. J., Mullica, D. F., and Ruegger (1991).Organometallics, submitted for publication.
Clark, H. C. (1977).Israel J. Chem. 15, 210.
Howells, E. R., Phillips, D. C., and Rogers, D. (1950).Acta Crystallogr. 3, 210.
Ibers, J. A., and Hamilton, W. C. (1974).International Tables for X-ray Crystallography, Vol. IV, Kynoch Press, Birmingham.
Leschnitzer, D. H. (1989). Thesis, Baylor University, Waco, Texas.
Mullica, D. F., Oliver, J. D., and Grossie, D. A. (1987).Acta Crystallogr. C 43, 591.
Mullica, D. F., Oliver, J. D., Sappenfield, E. L., and Grossie, D. A. (1986).Acta Crystallogr. C 42, 1695.
Mullica, D. F., Sappenfield, E. L., and Hampden-Smith, M. J. (1991).Polyhedron,10, 867.
Richardson, J. F., and Payne, N. C. (1977).Canad. J. Chem. 55, 3203.
Shelxtl-pc (1989).Siemens Analytical X-ray Instruments, Madison, Wisc.
Smith, J. D., and Oliver, J. D. (1978).Inorg. Chem. 17, 2585.
Tolman, C. A. (1970).J. Am. Chem. Soc. 92, 2956.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mullica, D.F., Sappenfield, E.L. & Leschnitzer, D.H. Crystal and molecular structure of chloro(tri-t-butylphosphino-C,P)triphenylarsinepalladium(II). Journal of Crystallographic and Spectroscopic Research 21, 675–679 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01179912
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01179912