Conclusions
-
1.
We investigated the specific characteristics of cast microconductors from the liquid phase with use of solid solutions of copper with Ag, Si, Ga, In, Zn, Ge, Sn, Cr, Mn, Ni, Pd, and Fe. We determined the variation of CER and the resistivity with composition. At concentrations corresponding to the solid solution the value of CER is inversely proportional to the atomic number of the element dissolved in the alloy.
-
2.
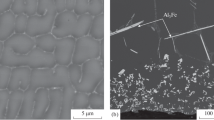
Several structural characteristics of cast microconductors of copper alloys obtained by rapid quenching from the liquid phase were investigated. It was found that the structure of microconductors 3–20 μ in diameter consists of misoriented dendrites 0.2–0.5 μ in size, with small branches. In the longitudinal direction the strand consists of oriented polycrystals with preferred orientations [100] and [111]. In microconductors of copper alloys with palladium there are sections consisting of stressed blocks of single crystals.
-
3.
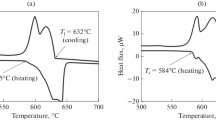
With quenching of microconductors of binary alloys of copper with gallium and indium directly from the liquid phase the region of existence of the primary solid solution in the metastable condition broadens as compared with corresponding equilibrium systems.
-
4.
Among the copper alloys investigated, the most promising systems for the development of microconductors with low CER are Cu−Mn and Cu−Ni. Low-resistance alloys have been developed on the basis of these systems, with CER<10·10−6 C−1 and linear resistance 2.5–60 kΩ/m. These alloys have been introduced in industry for the production of cast microconductors and resistance elements based on them.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
E. Ya. Badinter et al., Cast Microconductors and Their Properties [in Russian], Shtiintsa, Kishinev (1973).
M. Hansen and K. Anderko, Constitution of Binary Alloys, McGraw-Hill, New York (1959).
N. Ya. Karasik et al., Elektron. Tekh., Seriya Radiokomponenty, No. 1, 103 (1967).
I. V. Salli, Solidification at Ultra-High Cooling Rates [in Russian], Naukova Dumka, Kiev (1972), p. 14.
H. Thomas, Z. Phys.,129, 219 (1951).
N. P. Shmuilova, B. V. Farmakovskii, and V. I. Vakhrameev, Microconductors and Resistance Instruments [in Russian], No. 8, Izd. Kartya Moldovenyaske, Kishinev (1971), p. 36.
E. M. Savitskii, V. P. Polyakova, and M. A. Tylkina, Palladium Alloys [in Russian], Nauka, Moscow (1967), p. 50.
Additional information
Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 3, pp. 33–38, March, 1977.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farmakovskii, B.V., Karasik, N.Y. Structure and properties of cast microconductors of binary copper alloys. Met Sci Heat Treat 19, 200–204 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01167000
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01167000