Abstract
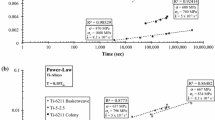
The creep behaviour of Al-10 at% Zn at 573 K is divisible into three deformation regions; low stress region, intermediate stress region and high stress region. The creep characteristics of the low stress region and intermediate stress region are consistent with dislocation climb and viscous glide, respectively. In the high stress region, the stress exponent,n increases with stress, the activation energy is higher than those observed in the other two regions, the activation area is slightly decreasing with stress and the internal stress is almost negligible. Present analysis shows that these characteristics are consistent with the thermally-activated glide motion of dislocations as a rate controlling mechanism at high stresses.[/p]
Similar content being viewed by others
References
O. D. Sherby andP. M. Burke,Prog. Mater. Sci. 13 (1968) 325.
W. R. Cannon andO. D. Sherby,Metall. Trans. 1 (1970) 1030.
F. A. Mohamed andT. G. Langdon,Acta Metall. 22 (1974) 779.
J. Weertman, in “Rate Processes in Plastic Deformation of Materials”, edited by J. C. M. Li and A. K. Mukherjee (ASM, Metal Park, Ohio, 1975) p. 315.
O. D. Sherby andC. M. Young, in “Rate Processes in Plastic Deformation of Materials”, edited by J. C. M. Li and A. K. Mukherjee (ASM, Metal Park, Ohio, 1975) p. 497.
M. F. Ashby andH. J. Frost, in “Constitutive Equations in Plasticity”, edited by A. S. Argon (MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts, 1975) p. 117.
W. D. Nix andB. Ilschner, in “Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on the Strength of Metals and Alloys”, edited by P. Haasen, E. Gerold and G. Kostorz (Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1979) p. 1503.
A. Arieli andA. K. Mukherjee, in “Creep and Fracture of Engineering Materials and Structures”, edited by B. Wilshire and D. R. J. Owen (Pineridge Press, Swansea, 1981) p. 97.
F. A. Mohamed,Mater. Sci. Eng. 38 (1979) 73.
K. L. Murty,Scripta Metall. 7 (1973) 899.
P. Yavari andT. G. Langdon,Acta Metall. 30 (1982) 2181.
M. S. Soliman andF. A. Mohamed,Metall. Trans. A15 (1984) 1893.
K. Kuchařová andJ. Čadek,Phys. Status Solidi (a) 6 (1971) 33.
H. J. Frost andM. F. Ashby, “Deformation Mechanism Maps” (Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1982) p. 8.
S. Takeuchi andA. S. Argon,J. Mater. Sci. 11 (1976) 1542.
V. I. Vladimirov, A. A. Kusov andN. N. Gorobey,Phys. Met. Metallogr. 48 (1979) 154.
V. I. Vladimirov andN. N. Gorobey,ibid.|53 (1982) 159.
J. Friedel, “Dislocations” (Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1964) p. 315.
H. W. King,J. Mater. Sci. 1 (1966) 79.
B. A. Chin, PhD thesis, Stanford University, California (1976).
M. S. Soliman, PhD thesis, University of California, Irvine (1984).
B. Burton,Phil. Mag. A 46 (1982) 607.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soliman, M.S. Breakdown of the power-law creep in a Class I Al-10 at % Zn alloy. J Mater Sci 22, 3529–3532 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01161453
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01161453