Abstract
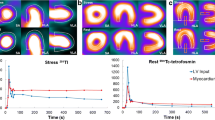
We assessed the significance of transient left ventricular dilation (TLVD) during single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) dipyridamole thallium-201 scintigraphy (DTS) in 49 patients who underwent both DTS and diagnostic coronary arteriography. Quantitative analysis of DTS images and independent review by 3 experienced observers determined that 17 patients had TLVD and 32 patients had no TLVD. Patients with TLVD were similar to patients without TLVD with respect to age, history of myocardial infarction, coronary risk factors and occurrence of chest pain or electrocardiographic changes during DTS. The frequency of three-vessel coronary artery disease (3VD) was greater in patients with TLVD than in patients without TLVD (94% vs. 16%, p<0.01). The sensitivity of TLVD was 76% and the specificity 96% for the detection of 3VD. Of the 16 patients with 3 VD who manifested TLVD, standard SPECT DTS analysis demonstrated defect or perfusion abnormalities in 14 patients and no abnormalities in 2 patients.
In conclusion, the finding of TLVD during SPECT DTS is a specific marker for severe coronary disease and can provide additive information to standard SPECT thallium-201 analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DTS:
-
dipyridamole thallium-201 scintigraphy
- TLVD:
-
transient left ventricular dilation
- SPECT:
-
single photon emission computed tomography
- 3VD:
-
three-vessel coronary artery disease
References
Leppo J, Boucher CA, Okada RD, Newell JB, Strauss HW, Pohost GM. Serial thallium-201 myocardial imaging after di-pyridamole infusion: diagnostic utility in detecting coronary stenoses and relationship to regional wall motion. Circulation 1982; 66: 649–57.
Josephson MA, Brown BG, Hecht HS, Hopkins J, Pierce CD, Petersen RB. Noninvasive detection and localization of coronary stenoses in patients: comparison of resting dipyri-damole and exercise thallium-201 myocardial perfusion imaging. Am Heart J 1982; 103: 1008–18.
Beer SG, Heo J, Iskandrian AS. Dipyridamole thallium imaging. Am J Cardiol 1991; 67: 18D-26D.
Boucher CA, Brewster DC, Darling RC, Okada RD, Strauss HW, Pohost GM. Determination of cardiac risk by dipyrida-mole-thallium imaging before peripheral vascular surgery. N Engl J Med 1985; 312: 389–94.
Leppo J, Plaja J, Gionet M, Tumolo J, Paraskos JA, Cutler BS. Noninvasive evaluation of cardiac risk before elective vascular surgery. J Am Coll Cardiol 1987; 9: 269–76.
Dash H, Massie BM, Botvinick EH, Brundage BH. The noninvasive identification of left main and three-vessel coronary artery disease by myocardial stress perfusion scintigraphy and treadmill exercise electrocardiography. Circulation 1979; 60: 276–84.
Rigo P, Bailey IK, Griffith LSC, Pitt B, Burow RD, Wagner HN, et al. Value and limitations of segmental analysis of stress thallium myocardial imaging for localization of coronary artery disease. Circulation 1980; 61: 973–81.
Stolzenberg J. Dilatation of left ventricular cavity on stress thallium scan as an indicator of ischemic disease. Clin Nucl Med 1980; 5: 289–91.
Weiss AT, Berman DS, Lew AS, Nielsen J, Potkin B, Swan HJC, et al. Transient ischemic dilation of the left ventricle on stress thallium-201 scintigraphy: a marker of severe and extensive coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 1987; 9: 752–9.
Chouraqui P, Rodrigues EA, Berman DS, Maddahi J. Significance of dipyridamole-induced transient dilation of the left ventricle during thallium-201 scintigraphy in suspected coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol 1990; 66: 689–94.
Lette J, Lapointe J, Waters D, Cerino M, Picard M, Gagnon A. Transient left ventricular cavitary dilation during dipyridamole-thallium imaging as an indicator of severe coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol 1990; 66: 1163–70.
Takeishi Y, Tonooka I, Ikeda K, Komatani A, Tsuiki K, Yasui S. Dilatation of the left ventricular cavity on dipyrida-mole thallium-201 imaging: a new marker of triple-vessel disease. Am Heart J 1991; 121: 466–75.
Maddahi J, Abdulla A, Garcia EV, Swan HJC, Berman DS. Noninvasive identification of left main and triple vessel coronary artery disease: improved accuracy using quantitative analysis of regional myocardial stress distribution and wash-out of thallium-201. J Am Coll Cardiol 1986; 7: 53–60.
Ringqvist I, Fisher LD, Mock M, Davis KB, Wedel H, Chaitman BR, et al. Prognostic value of angiographic indices of coronary artery disease from the Coronary Artery Surgery Study (CASS). J Clin Invest 1983; 71: 1854–66.
Mangano DT, London MJ, Tubau JF, Browner WS, Hollen-berg M, Krupski W, et al. Dipyridamole thallium-201 scinti-graphy as a preoperative screening test: A reexamination of its predictive potential. Circulation 1991; 84: 493–502.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zack, P.M., Ouimette, M.V., Chung, WM. et al. The significance of transient left ventricular dilation during SPECT dipyridamole thallium-201 scintigraphy. Int J Cardiac Imag 9, 265–271 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01137153
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01137153