Abstract
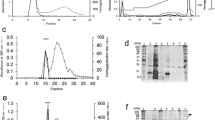
Dopamine D2 receptors , detected by [3H]spiperone Dopamine D2 receptors , detected by [3H]spiperone binding, were solubilized from bovine caudate nucleus by cholate/sodium chloride and were found to bind to wheat germ agglutinin immobilized on agarose. Specific elution could be achieved with N-acetylglucosamine whereas other sugars tested were inactive in this regard . The eluted preparation was enriched in solubilized receptors about sevenfold. The pharmaco-logical properties of the preparation were essentially unchanged by the lectin affinity purification procedure. The D2 dopamine receptor is therefore a glycoprotein. binding, were solubilized from bovine caudate nucJeus by cholate/sodium chloride and were found to bind to wheat germ agglutinin immobilized on agarose. Specific elution could be achieved with N-acetylglucosamine whereas other sugars tested were inactive in this regard . The eluted preparation was enriched in solubilized receptors about sevenfold. The pharmacological properties of the preparation were essentially unchanged by the lectin affinity purification procedure. The D2 dopamine receptor is therefore a glycoprotein.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Laduron PM & Ilien B (1982) Biochem. Pharmacol31, 2145–2151.
Strange PG (1983) Trends in Pharmacological Sciences4, 188–190.
Gioannini T, Foucaud B, Hiller J, Hatten ME & Simon EJ (1982) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.105, 1128–1134.
Hedo JA, Harrison LC & Roth J (1981) Biochemistry20, 3385–3393.
Herron GS & Schimerlik MI (1983) J. Neurochem.41, 1414–1420.
Pfeiffer FG, Graham D & Betz H (1982) J. Biol. Chem.257, 9389–9393.
Salvaterra PM, Gurd JM & Mahler HR (1977) J. Neurochem.29, 345–348.
Shirakawa O, Kuno T & Tanaka C (1983) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.115, 814–819.
Stadel JM, Shorr RGL, Limbird LE & Lefkowitz RJ (1981) J. Biol. Chem.256, 8718–8723.
Withy RM, Mayer RJ & Strange PG (1981) J. Neurochem.37, 1144–1154.
Hall JM, Frankham PA & Strange PG (1983) J. Neurochem.41, 1526–1532.
Wheatley M, Hall JM, Frankham PA & Strange PG (1984) J. Neurochem.43, 926–934.
Withy RM, Mayer RJ & Strange PG (1982) J. Neurochem.38, 1348–1355.
Wheatley M & Strange PG (1983) FEBS Lett.151, 97–101.
Berrie CP, Bloxham CA, Birdsall NJM & Hulme EC (1983) Brit. J. Pharmacol.78, 7P.
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL & Randall RJ (1951) J. Biol. Chem.193, 265–275.
Peters BP, Ebisu S, Goldstein IJ & Flashner M (1979) Biochemistry18, 5505–5511.
Lew JY & Goldstein M (1984) J. Neurochem.42, 1298–1305.
Kilpatrick BF & Caron MG (1984) Biochem. Pharmacol.33, 1981–1988.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abbott, W.M., Strange, P.G. Partial purification of dopamine D2 receptors using lectin affinity columns. Biosci Rep 5, 303–308 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01116901
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01116901