Abstract
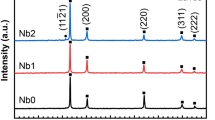
Sulfidation corrosion of 4130 steel in CH3SH was studied in the temperature range 250–550°C. The rate of sulfidation attack was found to be a function of temperature and sulfur activity. Investigations of the corrosion process led to the proposal of two mechanisms of sulfidation, dependent on temperature. Cation diffusion through the iron sulfide corrosion product is the rate-determining step at higher temperatures (>370°C), while a surface reaction was identified as the rate-limiting step at lower temperatures. The corrosion scale has preferred orientation as determined by X-ray diffraction and morphological observations. The lower-temperature corrosion product is made up of columnar grains of pyrrhotite crystals with the c-axis aligned nearly perpendicular to the steel substrate. At high temperatures, a whisker morphology developed with the whiskers having variable texture with respect to the steel substrate. A preformed-surface-oxide layer on 4130 steel does not appear to significantly reduce sulfidation corrosion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Dittrich,Die Chemische Fabrik 6, 25 (1933);10, 145 (1937).
A. Dravnieks,Ind. Eng. Chem. 43, 2897 (1951).
K. Hauffe and A. Rahmel,Z. Phys. Chem. 199, 152 (1952).
R. A. Meussner and C. E. Birchenall,Corrosion 13, 6771 (1957).
H. Arm, P. Delahay, C. Hudgins, F. Hugli, L. Hulett, and M. Qureshi,J. Electrochem. Soc. 107, 264 (1960).
M. Danielewski and S. Mrowec,J. Thermal. Anal. 29, 1025, (1984).
S. Mrowec,Bull. Acad. Polon. Sci. 15, 517 (1967).
E. T. Turkdogan,Trans. TMS-AIME 242, 1665 (1968).
E. W. Haycock, inHigh Temperature Metallic Corrosion by Sulfur and its Compounds, Z. A. Foroulis, ed. (The Electrochemical Society, 1970), p. 187.
A. Rahmel,Corros. Sci. 13, 125 (1973).
D. J. Young and W. W. Smeltzer,J. Electrochem. Soc. 123, 229 (1976).
M. Caillet, A. Galerie, and Ph. Hadjisavas,Pr. Kom. Ceram., Pol. Akad. Nauk [Ser.]Ceram. 30, 171 (1980).
E. M. Fryt, W. W. Smeltzer, and J. S. Kirkaldy,J. Electrochem. Soc. 126, 673 (1979).
D. J. Young,Rev. High Temp. Mater. 4, 299 (1980).
T. A. Ramanarayanan and S. N. Smith,Corrosion 46, 66 (1990).
Z. A. Foroulis,Werkst. Korros. 29, 385 (1978).
Z. A. Foroulis, 4th Asian-Pacific Corrosion Control Conf., Tokyo, Japan, 1985.
R. L. Piehl,Corrosion 16, 139 (1960).
C. Husen, inHigh Temperature Metallic Corrosion by Sulfur and Its Compounds, Z. A. Foroulis, ed. (The Electrochemical Society, 1970), p. 187.
E. W. Haycock,J. Electrochem. Soc. 106, 771 (1959).
V. Srinivasan, R. A. Padgett Jr., and A. Choudhray,Corrosion 47, 703 (1991).
W. L. Worrell and H. I. Kaplan, inHeterogeneous Kinetics at Elevated Temperatures, G. R. Belton and W. L. Worrell, eds. (Plenum Press, New York, 1970), p. 113.
D. F. Wilson and O. F. Devereaux, inCorrosion in Fossil Fuel Systems, I. G. Wright, ed. (The Electrochemical Society Softbound Proceeding Series, 1983), p. 247.
R. H. Condit, R. R. Hobbins, and C. E. Birchanell,Oxid. Met. 81, 409 (1974).
E. T. Turkdogen,Trans. AIME 242, 1665 (1968).
W. L. Worrell and E. T. Turkdogan,Trans. AIME 242, 1673 (1968).
L. Himmel, R. F. Mehl, and C. E. Birchenall,Trans. AIME 197, 827 (1953).
B. Gillot,Ann. Chim. Fr. 3, 209 (1978).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pareek, V.K., Ramanarayanan, T.A., Mumford, J.D. et al. The role of morphology and structure in the kinetic evolution of iron-sulfide films on Fe-base alloys. Oxid Met 41, 323–341 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01113369
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01113369