Abstract
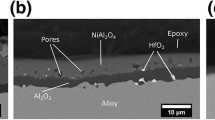
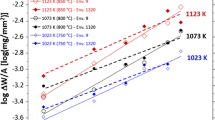
The internal oxidation of dilute Ni-Al alloys, either pure or containing small additions of tantalum or hafnium, was investigated at 1200° C in air. The advance of the precipitation zone followed a parabolic relationship at a slightly decreasing rate with increasing aluminium content. The presence of active elements had no appreciable effect on the growth rate. The precipitate shape, size and spacing depended upon the aluminium concentration and more significantly on the active element additions. The morphology varied from polyhedral crystallites and epitaxial platelets in the Ni-0.5 wt% Al alloy, to well defined cylindrical rods extending across the precipitation zone approximately normal to the reaction interface, in the alloys of higher aluminium content. An also continuous and similarly oriented plate-like morphology was observed in the active element-containing alloys. X-ray microanalysis indicated that the continuous precipitates consisted of NiAl2O4 and Al2O3. The former phase comprised approximately 65±5% of the outer region of the precipitation zone. Aluminium depletion in the alloy ahead of the precipitation front and a consequent enrichment in the form of oxide within the reaction zone inferred that growth was controlled by simultaneous outward aluminium and inward oxygen diffusion. No correlation was found between either the growth rate or oxygen permeability and the distribution of the precipitates. It was, therefore, concluded that the interfacial boundaries were ineffective in accelerating oxygen transport at this elevated temperature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. S. Wolf andE. B. Evans,Corros.-NACE 18 (1962) 129t.
W. C. Hagel,Corros. 21 (1965) 316.
F. S. Pettit,Trans. Met. Soc. AIME 239 (1967) 1296.
F. H. Stott andG. C. Wood,Corros. Sci. 17 (1977) 647.
H. Hindam andW. W. Smeltzer,J. Electrochem. Soc. 127 (1980) 1622.
W. W. Smeltzer, H. Hindam andF. A. Elrefaie, Proceedings of the NACE Conference on High Temperature Corrosion, San Diego, California, March 1981 (National Association of Corrosion Engineers, Houston, Texas).
D. P. Whittle, Y. Shida, G. C. Wood, F. H. Stott andB. D. Bastow,Phil. Mag. A, in press.
F. A. Elrefaie andW. W. Smeltzer,Oxid. Met. 18 (1982) 407.
Idem, J. Electrochem. Soc. 128 (1981) 2237.
H. Hindam, PhD thesis, “Microstructure and Growth of Al2in3 on Ni-Al Alloys”, McMaster University (1979).
“JANAF Thermochemical Tables”, 2nd edn, edited by D. R. Stall and H. Prophet (National Bureau of Standards, Washington DC, 1971).
R. Hultgren, P. D. Desai, D. T. Hawkins, M. Gleiser andK. K. Kelly, “Selected Values of the Thermodynamic Properties of Binary Alloys” (American Society for Metals, Metals Park, Ohio 1973) p. 191.
C. Wagner,Z. Elektrochem. 63 (1959) 772.
R. A. Rapp,Corrosion 21 (1965) 382.
J. H. Swisher, “Oxidation of Metals and Alloys”, edited by D. L. Douglass (American Society for Metals, 1971) p. 235.
E. E. Underwood, “Metals Handbook” Vol. 8, edited by T. Lyman, 8th edn., (American Society for Metals, Metals Park,Ohio 1973).
F. Maak,Z. Metallkunde 52 (1961) 545.
T. L. Meijering,Adv. Mater. Res. 5 (1971) 1.
J. D. Whittenberger,Met. Trans. 3 (1972) 2010.
M. M. P. Janssen,ibid. 4 (1973) 1623.
A. V. Seybolt, quoted in “Metals Reference Handbook”, edited by C. J. Smithells, 5th edn. (Butterworths, Borough Green, 1976).
C. J. Smithells andC. E. Ransley,Proc. Roy. Soc. A155 (1936) 195.
G. Böhm andM. Kahlweit,Acta Met. 12 (1964) 641.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Since the submission of this paper we have heard with regret of the death of Professor Whittle and would like to acknowledge his significant contributions to the subject of materials science.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hindam, H., Whittle, D.P. High temperature internal oxidation behaviour of dilute Ni-Al alloys. J Mater Sci 18, 1389–1404 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01111959
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01111959