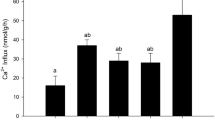
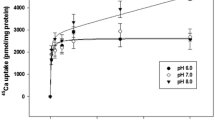
Summary
When the mulletMugil capito is transferred to medium lacking Ca++ (either Ca++-free seawater or distilled water) the passive permeability of the gill to Na+ and Cl− is increased and the activating effect of external K+ on the Na+ and Cl− effluxes in hyposaline media is inhibited. The permeability of the gill increases progressively in proportion to the time of Ca++ deprivation; it declines when Ca++ is added again to the external medium. The active mechanisms for ion excretion are not reversible. At external Ca++ concentrations from 0.1 to 10 mM the Na+ permeability is constant but the activation of Na+ efflux by K+ shows a maximum at a Ca++ concentration of about 1 mM. For activation of Cl− efflux external bicarbonate must be present, in addition to Ca++, suggesting the existence of a Cl−/HCO −3 exchange. The mechanism by which Ca++ controls the passive branchial permeability is thus probably different from that involved in K+ activation of ion excretion. The Ca++ effect on the K+ sensitive ionic excretory mechanisms seems to be related to intracellular Ca++ movements. Thus, on the one hand, substances such as Ruthenium Red and La+++ which both inhibit Ca++ exchange, in media containing Ca++ and HCO −3 also inhibit K+ activation of Na+ and Cl− effluxes; on the other hand, the ionophore A 23187, a stimulator of Ca++ exchange, when added to these media, activates the Na+ and Cl− effluxes; its maximal effect on the Na+ flux occurs at 2 mM Ca++.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ASW-Ca :
-
artificial seawater minus calcium
- DW :
-
deionised water
- DWCa :
-
deionised water with 1 mM Ca++ added
- DWCaHCO 3 :
-
DW with calcium plus bicarbonate
- DWHCO 3 :
-
DW with 1 mM sodium bicarbonate added
- FW :
-
freshwater (tap water)
- FWK :
-
freshwater with K+ added
- P. D. :
-
potential difference
- SW :
-
seawater
References
Alnaes, E., Rahaminoff, R.: On the role of mitochondria in transmitter release from motor nerve terminals. J. Physiol. (London)248, 285–306 (1975)
Babcock, D.F., First, N.L., Lardy, H.A.: Action of ionophore A 23187 at the cellular level: separation of effects at the plasma and mitochondrial membranes. J. Biol. Chem.251, 3881–3886 (1976)
Bolton, J.E., Field, M.: Ca ionophore stimulated ion secretion in rabbit ileal mucosa: relation to actions of cyclic 3′–5′ AMP and carbamylcholine. J. Membr. Biol.35, 159–173 (1977)
Borisy, G.G., Marcoum, J.M., Olmsted, J.B., Murphy, D.B., Johnson, K.A.: Purification of tubulin and associated high molecular weight proteins from porcine brain and characterization of microtubule assembly in vitro. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci.253, 107–132 (1975)
Bornancin, M., Cuthbert, A.W., Maetz, J.: The effects of calcium on branchial sodium fluxes in the seawater adapted eel,Anguilla anguilla L. J. Physiol. (London)222, 487–496 (1972)
Bornancin, M., Renzis, G. de, Naon, R.: A Cl−−HCO −3 ATPase in the gills of freshwater teleostSalmo gairdneri. Evidence for its microsomal localization. Am. J. Physiol.238, R251-R259 (1980)
Candia, O.A., Montoreano, R., Podos, S.M.: Effect of ionophore A 23187 on chloride transport across isolated frog cornea. Am. J. Physiol.233, F94-F101 (1977)
Carrier J.C., Evans, D.H.: The role of environmental calcium in freshwater survival of the marine teleost,Lagodon rhomboides. J. Exp. Biol.65, 529–538 (1976)
Cittadini, A., Scarpa, A., Chance, B.: Calcium transport in intact Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta291, 246–259 (1973)
Degnan, K.J., Karnaky, K.J. Jr., Zadunaisky, J.A.: Active chloride transport in the in vitro opercular skin of a teleost (Fundulus heteroclitus), a gill like epithelium rich in chloride cells. J. Physiol. (London)271, 155–191 (1977)
Epstein, F.H., Maetz, J., De Renzis, G.: Active transport of chloride by the teleost gill: inhibition by thiocyanate. Am. J. Physiol.224, 1295–1299 (1973)
Evans, D.H., Cooper, K.: The presence of Na−Na and Na−K exchange in sodium extrusion by three species of fish. Nature259, 241–242 (1976)
Evans, D.H., Mallery, C.H., Kravitz, L.: Sodium extrusion by a fish acclimated to seawater: Physiological and biochemical description of a Na-for-K exchange system. J. Exp. Biol.58, 627–636 (1973)
Evans, D.H., Carrier, J.C., Bogan, M.B.: The effect of external potassium ions on the electrical potential measured across the gills of the teleostDormitator maculatus. J. Exp. Biol.61, 277–283 (1974)
Fahn, S., Koval, G.J., Albers, R.W.: Sodium potassium activated adenosine triphosphatase ofElectrophorus electric organ. J. Biol. Chem.241, 1882–1889 (1966)
Fleming, W.R., Nichols, J., Potts, W.T.W.: The effect of low-calcium seawater and actinomycin D on the sodium metabolism ofFundulus kansae. J. Exp. Biol.60, 267–273 (1974)
Frizzell, R.A.: Active chloride secretion by rabbit colon: calcium dependent stimulation by ionophore A 23187. J. Membr. Biol.35, 175–187 (1977)
Greenwald, L., Kirschner, L.B., Sanders, M.: Sodium efflux and potential difference across the irrigated gill of seawater adapted rainbow troutSalmo gairdneri. J. Gen. Physiol.64, 135–147 (1974)
Hitchcock, S.E.: Regulation of motility in non-muscle cells. J. Cell Biol.74, 1–15 (1977)
House, C.R., Maetz, J.: On the electrical gradient across the gill of the seawater adapted eel. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.47A, 917–924 (1974)
Isaia, J., Masoni, A.: The effects of calcium and magnesium on water and ionic permeabilities in the seawater adapted eel,Anguilla anguilla L. J. Comp. Physiol.109, 221–233 (1976)
Karnaky, K.J., Jr., Kinter, L.B., Kinter, W.B., Stirling, C.E.: Teleost chloride cell. II. Autoradiographic localization of gill Na, K-ATPase in killifishFundulus heteroclitus adapted to low and high salinity environments. J. Cell Biol.70, 157–177 (1976)
Karnaky, K.J., Jr., Degnan, K.J., Zadunaisky, J.A.: Chloride transport across isolated opercular epithelium of killifish: a membrane rich in chloride cells. Science195, 203–205 (1977)
Kerstetter, T.H., Kirschner, L.B.: HCO −3 -dependent ATPase activity in the gills of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) Comp. Biochem. Physiol.48B, 581–589 (1974)
Kirschner, L.B., Greenwald, L., Sanders, M.: On the mechanism of sodium extrusion across the irrigated gill of seawater adapted rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). J. Gen. Physiol.64, 148–165 (1974)
Kormanic, G.A., Evans, D.H.: HCO −3 -stimulated Cl efflux in the Gulf toadfish acclimated to seawater. J. Exp. Zool.208, 13–16 (1979)
Langer, G.A., Evank, J.S.: Lanthanum in heart cell culture. Effect on calcium exchange correlated with its localization. J. Cell Biol.54, 441–455 (1972)
MacFarlane, N.A.A., Maetz, J.: Acute response to a salt load of the NaCl excretion mechanisms of the gill ofPlatichthys flesus in seawater. J. Comp. Physiol.102, 101–113 (1975)
Maetz, J.: Seawater teleosts. Evidence for a sodium potassium exchange in the branchial sodium-excreting pump. Science166, 613–615 (1969)
Maetz, J., Cornancin, M.: Biochemical and biophysical aspects of salt excretion by chloride cells in teleosts. Fortschr. Zool.23, 322–362 (1975)
Maetz, J., Campanini, G.: Potentiels transépithéliaux de la branchie d'anguille in vivo en eau douce et en eau de mer. J. Physiol. (Paris)58, 248 (1975)
Maetz, J., Pic, P.: New evidence for a Na/K and Na/Na exchange carrier linked with the Cl− pump in the gill ofMugil capito in seawater. J. Comp. Physiol.102, 85–100 (1975)
Maetz, J., Pic, P.: Microtubules in the “chloride cells” of the gill and disruptive effects of colchicine on the salt balance of the seawater adaptedMugil capito. J. Exp. Zool.199, 325–338 (1977)
Milet, C., Peignoux-Deville, J., Martelly, E.: Gill calcium fluxes in the eel,Anguilla anguilla (L.). Effects of Stannius corpuscles and ultimobranchial body. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.63A, 63–70 (1979)
Moore, C.L.: Specific inhibition of mitochondrial Ca++ transport by Ruthenium red. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.42, 298–305 (1971)
Motais, R.: Les mécanismes d'échanges ioniques branchiaux chez les téléostéens. Ann. Inst. Océanogr. Monaco45, 1–48 (1967)
Motais, R., Isaia, J.: Evidence for an effect of ouabain on the branchial sodium excreting pump of marine teleosts: interaction between the inhibitor and external Na and K. J. Exp. Biol.57, 367–373 (1972)
Pang, P.K.T., Griffith, R.W., Maetz, J., Pic, P.: Calcium uptake in fishes. In: Epithelial transport in the lower vertebrates. Lahlou, B. (ed.), pp. 121–132. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press 1980
Pento, J.T.: Lanthanum inhibition of calcitonin secretions and calcium uptake in porcine thyroid slices. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol.9, 223–226 (1977)
Pic, P.: A comparative study of the mechanism of Na+ and Cl− excretion by the gill ofMugil capito andFundulus heteroclitus: effects of stress. J. Comp. Physiol.123, 155–162 (1978)
Pic, P., Maetz, J.: Differences de potentiel transbranchial et flux ioniques chezMugil capito adapté à l'eau de mer. Importance de l'ion Ca++. C.R. Acad. Sci. (Paris)280, 983–986 (1975)
Pic, P., Mactz, J.: Contrôle des mécanismes d'excrétion branchiale du Na+ par les ions Ca++ et Mg++ du milieu extérieur chez le Flet,Platichthys flesus, en eau de mer. C.R. Acad. Sci. (Paris)287, 817–820 (1978)
Pic, P., Maetz, J.: Etude de la spécificité du contrôle des mécanismes d'excrétion branchiale de Na+ par Ca++ et divers cations multivalents chezMugil capito adapté à l'eau de mer. C.R. Acad. Sci. (Paris)289, 319–322 (1979)
Pic, P., Mayer-Gostan, N., Maetz, J.: Branchial effects of epinephrine in the seawater adapted mullet. II. Na+ and Cl− extrusion. Am. J. Physiol.228, 441–447 (1975)
Pic, P., Ellory, J. C. Lucu, C.: Evidence that K-dependent transport components in addition to Na−K ATPase are involved in Na and Cl excretion in marine teleost gills. J. Exp. Biol.79, 1–6 (1979)
Potts, W.T.W., Eddy, F.B.: Gill potentials and sodium fluxes in the flounderPlatichthys flesus. J. Comp. Physiol.87, 29–48 (1973)
Potts, W.T.W., Fleming, W.R.: The effect of environmental calcium and ovine prolactin on sodium balance inFundulus kansae. J. Exp. Biol.54, 63–75 (1971)
Renzis, G. de, Bornancin, M.: A Cl−/HCO −3 ATPase in the gills ofCarassius auratus. Its inhibition by thiocyanate. Biochim. Biophys. Acta467, 192–207 (1977)
Renzis, G. de, Naon, R., Bornancin, M.: Localisation intracellulaire et caractérisation d'une activité ATPasique sensible aux anions dans les branchies de téléostéens In: Epithelial transport in the lower vertebrates. Lahlou, B. (ed.), pp. 297–315. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press 1980
Reed, P.W., Lardy, H.A.: A 23187: a divalent cation ionophore. J. Biol. Chem.247, 6970–6977 (1972)
Silva, P., Solomon, R., Spokes, K., Epstein, F.H.: Ouabain inhibition of gill Na−K-ATPase: relationship to active chloride transport. J. Exp. Zool.199, 419–426 (1977)
Smith, P.G.: The ionic relations ofArtemia salina (L.). II. Sodium, chloride and water fluxes. J. Exp. Biol.51, 739–757 (1969)
Tobin, A., Akera, T., Baskin, S.I., Brody, T.M.: Calcium ion and sodium-and-potassium-dependent adenosine triphosphatase: its mechanism of inhibition and identification of the E1−P intermediate. Mol. Pharmacol.9, 336–349 (1973)
Vale, M.G.P., Carvalho, A.P.: Effects of Ruthenium red on Ca++ uptake and ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum of rabbit skeletal muscle. Biochim. Biophys. Acta325, 29–37 (1973)
Weiss, G.B.: Cellular pharmacology of lanthanum. Ann. Rev. Pharmacol.14, 343–354 (1974)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The experiments reported in this paper were done with Jean Maetz who tragically died in August 1977. It is the last report about several years of friendly collaboration
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pic, P., Maetz, J. Role of external calcium in sodium and chloride transport in the gills of seawater-adaptedMugil capito . J Comp Physiol B 141, 511–521 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01101474
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01101474