Summary
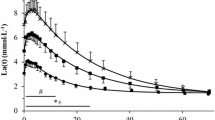
An increased base binding power of the blood induced by alkali administration to subjects performing a supramaximal exercise has no appreciable effect neither on the maximal performance time nor on the total amount of lactic acid or its rate of appearance in blood.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cerretelli, P.: Lactacid O2 debt in acute and chronic hypoxia.In: Exercise at altitude, ed. R. Margaria, pp. 58–64. Amsterdam: Excerpta Medica Foundation 1967.
Dennig, H., Becker-Freyseng, H., Rendenback, H., Schostak, G.: Leistungssteigerung in künstlicher Alkalose bei wiederholter Arbeit. Naunyn-Schmiede- bergs Arch. exp. Path. Pharmak.195, 261–263 (1940).
—, Talbot, J. T., Edwards, H. T., Dill, D. B.: Effect of acidosis and alkalosis upon capacity for work. J. clin. Invest.9, 609–613 (1931).
Dorow, H., Galuba, B., Hellwig, H., Beeker-Freyseng, H.: Der Einfluß künstlicher Alkalose auf die sportliche Leistung von Läufern und Schwimmern. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. exp. Path. Pharmak.195, 264–266 (1940).
Edwards, H. T.: Lactic acid in rest and work at high altitude. Amer. J. Physiol.116, 367–375 (1936).
Gerken, G.: Die quantitative enzymatische Dehydrierung von {spl (+) Lactat für die Mikroanalyse}. Hoppe-Seylers Z. physiol. Chem.320, 180–186 (1960).
Hill, A. V.: Muscular movements in man: the factor governing speed and recovery from fatigue. New York: McGraw-Hill 1927.
Margaria, R.: Aerobic and anaerobic energy sources in muscular exercise.In: Exercise at altitude, ed. R. Margaria, pp. 15–32. Amsterdam: Excerpta Medica Foundation 1967.
—, Aghemo, P., Rovelli, E.: Indirect determination of maximal oxygen consumption in man. J. appl. Physiol.20, 1070–1073 (1965).
— —: Measurements of muscular power (anaerobic) in man. J. appl. Physiol.21, 1662–1665 (1966).
—, Cerretelli, P., di Prampero, P. E., Massari, C., Torelli, G.: Kinetics and mechanism of oxygen debt contraction in man. J. appl. Physiol.18, 371–377 (1963).
— —, Mangili, F.: Balance and kinetics of anaerobic energy release during strenuous exercise in man. J. appl. Physiol.19, 623–628 (1964).
—, Edwards, R. T., Dill, D. B.: The possible mechanism of contracting and paying the oxygen debt and the role of lactic acid in muscular contraction. Amer. J. Physiol.106, 689–715 (1933).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work has been supported by a grant from the Italian National Research Council. Thanks are due also to “Laboratory Glaxo, S.p.A.” for facilities and financial support in the course of the experiments.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Margaria, R., Aghemo, P. & Sassi, G. Effect of alkalosis on performance and lactate formation in supramaximal exercise. Int. Z. Angew. Physiol. Einschl. Arbeitsphysiol. 29, 215–223 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01100533
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01100533