Summary
The effects of hypoxia on different parameters of cell membrane function were studied in 7 and 19 day chick embryonic hearts. The following changes were observed.
-
1.
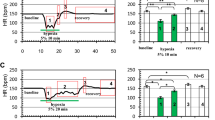
Transmembrane potential: A depolarization of the cell membrane and a decrease in the duration and in the overshoot of the action potential.
-
2.
Intracellular ion concentrations: A decrease in (K)i and an increase in (Na)i. Cellular Ca-content remained constant.
-
3.
K efflux: An increase in the rate coefficient, which was larger in stimulated preparations.
These changes were more pronounced in 19 day than in 7 day hearts. The effects of hypoxia were increased by simultaneous substrate depletion and counteracted by an excess external glucose. We conclude that.
-
1.
The 19 day hearts are more sensitive to oxygen lack than the 7 day hearts. This difference can be correlated with the observation that the younger hearts are able to consume more glycogen during hypoxia.
-
2.
The changes of the resting membrane potential and the overshoot of the action potential correlate with changes in respectively (K)i and (Na)i.
-
3.
An increase in the background K current may be an important factor in explaining the shortening of the action potential during hypoxia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker, P. F.: Transport and metabolism of calcium ions in nerve Progr. Biophys.24, 177–223 (1972)
Bergmeyer, H., Bernt, E.: In: Methoden der enzymatischen Analyse (H. U. Bergmeyer, ed.), S. 1172. Weinheim: Verlag Chemie 1970
Carmeliet, E. E.: Chloride and potassium permeability in cardiac Purkinje fibres. Bruxelles: Editions Arscia S.A. 1961
Carmeliet, E. E., Horres, C. R., Lieberman, M., Vereecke, J. S.: Developmental aspects of potassium flux and permeability of the embryonic chick heart. J. Physiol. (Lond.)254, 673–692 (1976)
Fink, R., Lüttgau, H.: The effect of metabolic poisons upon the membrane resistance of striated muscle fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond.)234, 29–30P (1973)
Guidotti, G., Foà, P. P.: Development of an insulin-sensitive glucose transport system in chick embryo hearts. Amer. J. Physiol.201, 869–872 (1961)
Guidotti, G., Kanameishi, D., Foà, P. P.: Chick embryo heart as a tool for studying cell permeability and insulin action. Amer. J. Physiol.201, 863–868 (1961)
Isenberg, G.: Is potassium conductance of cardiac Purkinje fibres controlled by (Ca2+)i? Nature (Lond.)253, 273–274 (1975)
Isenberg, G., Trautwein, W.: Effect of dihydro-ouabain and lithium ions on the outward current in cardiac Purkinje fibers: Evidence for electrogenicity of active transport. Pflügers Arch.350, 41–54 (1974)
Isenberg, G., Trautwein, W.: Temperature sensitivity of outward current in cardiac Purkinje fibers: Evidence for electrogenicity of active transport. Pflügers Arch.358, 225–234 (1975)
Keppler, D., Decker, K.: In: Methoden der enzymatischen Analyse (H. U. Bergmeyer, ed.), S. 1089. Weinheim: Verlag Chemie 1970
Krnjević, K., Lisiewicz, A.: Injections of calcium ions into spinal motoneurones. J. Physiol. (Lond.)225, 363–390 (1972)
MacLeod, D. P., Daniel, E.E.: Influence of glucose on the transmembrane action potential of anoxic papillary muscle. J. gen. Physiol.48, 887–899 (1965)
Mascher, D., Carmeliet, E.: The effects of hypoxia on the membrane resistance of ventricular muscle fibres of the guinea-pig. Arch. int. Physiol. Biochim.83, 606–607 (1975)
McDonald, T. F., DeHaan, R. L.: Ion levels and membrane potential in chick heart tissue and cultured cells. J. gen. Physiol.61, 89–109 (1973)
McDonald, T. F., MacLeod, D. P.: The effect of 2,4-dinitrophenol on electrical and mechanical activity, metabolism and ion movements in guinea-pig ventricular muscle. Brit. J. Pharmacol.44, 711–722 (1972)
McDonald, T. F., MacLeod, D. P.: Metabolism and the electrical activity of anoxic ventricular muscle. J. Physiol. (Lond.)229, 559–582 (1973)
Noble, D.: A modification of the Hodgkin-Huxley equations applicable to Purkinje fibre action and pacemaker potentials. J. Physiol. (Lond.)160, 317–352 (1962)
Prignitz, R., Müller, U., Hoffmeister, G.: Über die Bestimmung des Extracellulärraumes mit (51Cr) EDTA an der Vorhofsmuskulatur des Meerschweinchens. Experientia (Basel)29, 431–432 (1973)
Roberts, C. M.: The response of the early chick embryo heart to anoxia. J. Cell Physiol.68, 263–268 (1966)
Romero, P. J., Whittam, R.: The control by internal calcium of membrane permeability to sodium and potassium. J. Physiol. (Lond.)214, 481–507 (1971)
Rovetto, M. J., Whitmer, J. T. Neely, J. R.: Comparison of the effects of anoxia and whole heart ischemia on carbohydrate utilization in isolated working rat hearts. Circulat. Res.32, 699–711 (1973)
Shelley, H. J.: Glycogen reserves and their changes at birth and in anoxia. Brit. med. Bull.17, 137–143 (1961)
Sperelakis, N.: (Na+, K+)-ATPase activity of embryonic chick heart and skeletal muscles as a function of age. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.)266, 230–237 (1972)
Sperelakis, N., Lehmkuhl, O.: Effects of temperature and metabolic poisons on membrane potentials of cultured heart cells. Amer. J. Physiol.213, 719–724 (1967)
Su, J. Y., Friedman, W. F.: Comparison of the responses of fetal and adult cardiac muscle to hypoxia. Amer. J. Physiol.224, 1249–1253 (1973)
Trautwein, W., Gottstein, U., Dudel, J.: Der Aktionsstrom der Myokardfaser im Sauerstoffmangel. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.260, 40–60 (1954)
Vleugels, A., Carmeliet, E.: Effect of hypoxia on the duration of the action potential in embryonic chick heart. Arch. int. Physiol. Biochim.81, 775–777 (1973)
Vleugels, A., Carmeliet, E.: Hypoxia increases potassium efflux from mammalian myocardium. Experientia (Basel)32, 483–484 (1976)
Weidmann, S.: Heart: Electrophysiology. Ann. Rev. Physiol.36, 155–169 (1974)
Wojtczak, J.: Hypoxia-induced electrical uncoupling and contractures of cardiac cells. Experientia (Basel) (in press, 1976)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vleugels, A., Carmeliet, E., Bosteels, S. et al. Differential effects of hypoxia with age on the chick embryonic heart. Pflugers Arch. 365, 159–166 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01067013
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01067013