Abstract
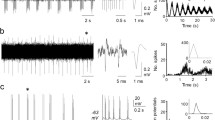
Responses arising in ventral root filaments and antidromic discharges of single sympathetic preganglionic neurons in the lateral horn of gray matter in segment L2 of the cat spinal cord were recorded during stimulation of the white rami communicantes in the same segment. Conduction velocities, thresholds, and refractory periods were determined for individual groups of sympathetic preganglionic fibers. Excitation was conducted more slowly along the intramedullary part of the axons of some sympathetic neurons than along the extramedullary part. In a third group of neurons studied the second antidromic discharge appeared in response to paired stimulation if the interstimulus interval was appreciably longer than their refractory period. It is postulated that axons of sympathetic preganglionic neurons in the lumber spinal cord have a thin intramedullary part and are supplied with recurrent collaterals.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
V. P. Lebedev, "Properties of axons of sympathetic preganglionic neurons in the lower thoracic portion of the spinal cord," Fiziol. Zh. SSSR,57, 1647 (1971).
V. P. Lebedev, "Some special features of responses of sympathetic preganglionic neurons of the lateral horns of the spinal cord to antidromic and orthodromic stimulation," in: Interneuronal Transmission in the Autonomic Nervous System [in Russian], Naukova Dumka, Kiev (1972), pp. 76–90.
V. P. Lebedev and G. P. Mikhailova, "Stereotaxic investigation of the lateral horn of the cat spinal cord," Fiziol. Zh. SSSR,57, 677 (1971).
A. L. Mikeladze, "Endings of afferent nerve fibers in the lumbosacral region of the spinal cord," Arkh. Anat., Gistol., i Émbriol.,48, 3 (1965).
V. A. Skobelev, "Investigation of single sympathetic preganglionic neurons of the lateral horns of the lumbar division of the spinal cord," Abstracts of Proceedings of a Symposium on the Structural and Functional Organization of Autonomic Ganglia [in Russian], Nauka i Tekhnika, Minsk (1973), pp. 89–90.
J. G. Blackman and R. D. Purves, "Intracellular recordings from ganglia of the thoracic sympathetic chain of the guinea pig," J. Physiol. (London),203, 173 (1969).
M. J. Brimble, D. I. Wallis, and B. Woodward, "Facilitation and inhibition of cell groups within the superior cervical ganglion of the rabbit," J. Physiol. (London),226, 629 (1972).
A. H. Davenport and R. T. Bothe, "Cells and fibers in spinal nerves," J. Comp. Neurol.,59, 167 (1934).
A. H. Davenport and S. W. Ranson, "Ratio of cells to fibers and of myelinated to unmyelinated fibers in spinal nerve roots," Am. J. Physiol.,49, 193 (1931).
C. B. B. Downman and N. H. Hazarica, "Somatic pathways through some thoracic rami communicantes," J. Physiol. (London),163, 340 (1962).
J. C. Eccles, R. M. Eccles, A. Iggo, and I. Lundberg, "Electrophysiological studies of gamma motoneurones," Acta Physiol. Scand.,50, 32 (1960).
R. M. Eccles, "Responses of isolated curarized sympathetic ganglia," J. Physiol. (London),117, 196 (1952).
J. Erlanger and H. Gasser, Electrical Signs of Nervous Activity, Philadelphia (1937).
A. Fernandex de Molina, M. Kuno, and E. R. Perl, "Antidromically evoked responses of sympathetic preganglionic neurons," J. Physiol. (London),180, 321 (1965).
C. B. Ferry, "The innervation of the vas deferens of the guinea pig," J. Physiol. (London),192, 463 (1967).
W. C. de Groat and R. W. Ryall, "The identification and characteristics of sacral parasympathetic preganglionic neurons," J. Physiol. (London),196, 563 (1966).
H. Grundfest, "The properties of mammalian B-fibers," Am. J. Physiol.,127, 252 (1939).
M. Kato and J. Hirata, "Sensory neurons in the spinal ventral roots of the cat," Brain Res.,7, 479 (1968).
F. Kirchner, A. Sato, and H. Weidinger, "Central pathways of reflex discharges in cervical sympathetic trunk," Pflüg. Arch. Ges. Physiol.,319, 1 (1970).
J. N. Langley, The Autonomic Nervous System, Cambridge (1921).
V. Perri, O. Sacchi, and C. Cassella, "Electrical properties and synaptic connections of the sympathetic neurons in the rat and guinea pig superior cervical ganglion," Pflüg. Arch. Ges. Physiol.,314, 40 (1970).
S. W. Ranson and P. R. Billingsley, "The thoracic truncus sympathicus, rami communicantes and splanchnic nerve in cat," J. Comp. Neurol.,29, 405 (1918).
M. Réthelyi, "Cell and neuropil architecture of the intermedio-lateral (sympathetic) nucleus of cat spinal cord," Brain Res.,46, 203 (1972).
R. W. Ryall and M. F. Piercey, "Visceral afferent and efferent fibers in sacral ventral roots in cat," Brain Res.,23, 57 (1970).
A. Sato, "The relative involvement of different pathways in somato-sympathetic reflexes analyzed in spontaneously active preganglionic units," Pflüg. Arch. Ges. Physiol.,333, 70 (1971).
A. Sato, "Spinal and medullary reflex components of the somato-sympathetic reflex discharges evoked by stimulation of the group IV somatic afferents," Brain Res.,51, 307 (1973).
A. Sato, N. Sato, T. Ozawa, and B. Fujimori, "Further observations of reflex potentials in the lumbar sympathetic trunk in cats," Jap. J. Physiol.,17, 296 (1967).
A. Sato and R. F. Schmidt, "Spinal and supraspinal components of the reflex discharges into lumbar and thoracic white rami," J. Physiol. (London),212, 839 (1971).
W. D. Willis, R. R. Grace, and R. D. Skinner, "Ventral root afferent fibres and the recurrent inhibitory pathway," Nature,216, 1010 (1967).
Additional information
I. P. Pavlov Institute of Physiology, Academy of Sciences of the USSR, Leningrad. Translated from Neirofiziologiya, Vol. 6, No. 2, pp. 143–151, March–April, 1974.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lebedev, V.P., Skobelev, V.A. & Bushmarina, T.A. Properties of axons of sympathetic preganglionic neurons in the cat lumbar spinal cord. Neurophysiology 6, 111–118 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01062746
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01062746