Abstract
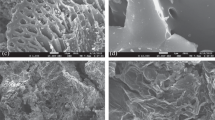
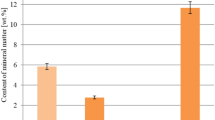
A method is proposed for fabrication of efficient carbon materials based on inexpensive plant wastes from the flax-processing industry. The characteristics of the structure and sorption properties of these carbon materials allow recommending them for bleaching and purifying solutions in different branches of industry. In addition to obtaining and efficient sorbent, the problem of utilization of flax-processing wastes is also solved.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carbon Adsorbents and Their Use in Industry: Proceedings of the V All-Union Conference [in Russian], Perm' (1991). p. 17.
L. I. Fridman and V. A. Perlin, Fabrication, Properties, and Use of Carbon Fibre Adsorbents [in Russian], NIITÉKhim, Moscow (1981).
E. Yu. Katorgina and A. T. Kynin, Method of Evaluating the Pore Structure of Fibre-forming Polymers, Films, and Textile Materials [in Russian], SPGUTD, St. Petersburg (1995), p. 14.
I. A. Semenkova (ed.), Catalog of Active Carbons [in Russian]. Cherkassy (1990).
Additional information
Deceased.
St. Petersburg State University of Technology and Design. Translated from Khimicheskie Volokna, No. 6, pp. 20–22. November–December, 1996.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Emets, L.V., Levit, R.M., Strukova, I.M. et al. Sorption-active carbon materials based on linoleic acid. Fibre Chem 28, 378–380 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01060999
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01060999